This is an automatically translated article.
Hereditary thromboembolic disease is often found in people with deep vein thrombosis, cardiovascular problems, and recurrent miscarriages. Testing for hereditary thromboembolic disease is indicated for adults at risk for blood clotting disorders or for women with unexplained repeated miscarriages.
1. What is hereditary thromboembolic disease?
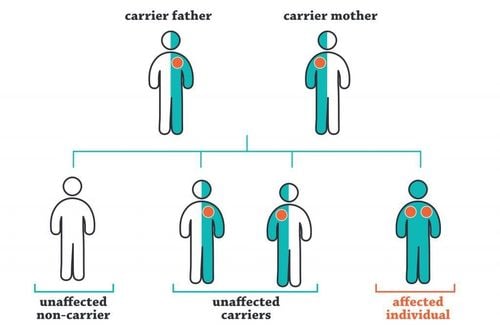
Hereditary thromboembolic disease is an inherited disorder in the blood clotting pathway that causes abnormal blood clots to form. Women with this condition often have vascular complications, leading to miscarriage, stillbirth, preeclampsia, and HELLP syndrome.
Research shows that women who carry the hereditary thromboembolic disease gene are 2-14 times more likely to have a miscarriage than normal women.
2. Liver test to screen for inherited thromboembolic disease gene mutations
The main gene mutations that cause thromboembolic disease are:
Point mutation G1691A on the gene encoding factor V Leiden (FV) Normal in the human body there is an activated protein C with anticoagulant function. The leading cause of vascular embolism is the body's resistance to this protein. This phenomenon occurs due to a type of mutation in the factor V Leiden gene. Accordingly, 60% of women with hereditary thromboembolic disease during pregnancy are caused by factor V mutations. This is also the main cause of drug-related hereditary thromboembolic disease. oral contraceptives.
Mutation in the factor II prothrombin gene G20210 (FII) Factor II (or prothrombin) is one of the important factors in the clotting pathway. Factor II gene mutations occur in 7.8% of women whose miscarriage is related to a clotting disorder. This type of mutation increases the expression level of the factor II gene, which leads to easier blood clotting than usual.
Methylene-tetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) mutations increase blood homocysteine. Homocysteine is normally only present in the blood when the body consumes methionine from food. Hereditary disease caused by mutations in the gene that produces the enzyme methylene-tetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) causes stasis and elevation of homocysteine in the blood, leading to blood clots and hardening of the vessel walls, even in small children. Usually, people with a diet lacking in vitamins B6, B12 and folic acid will make the blockage of blood vessels worse. Research shows that women who are homozygous for the MTHFR mutation have a more than two-fold increased risk of miscarriage compared with non-carriers of the mutation.
Cases of thrombosis and women with multiple miscarriages should be tested for FV, FII and MTHFR mutations by PCR technique.

Bệnh lý di truyền có thể được phát hiện qua xét nghiện gen
3. Who should be tested for hereditary thromboembolic disease?
Note: Genetic testing for thromboembolic disease is not indicated in asymptomatic patients with VTE. Consideration for testing is based on 2 groups of subjects as follows:
3.1. Patients with symptoms of a blood clot It is recommended that genetic testing to screen for thrombophilia is performed in the following patients:
Have symptoms of VTE of unknown cause before age 40 People with exacerbations Abnormal thromboembolism Blood clots in unusual locations Venous thromboembolism of unknown cause in a patient with an immediate relative in 1 of 3 above Women with unknown late miscarriage cause or spontaneous abortion of 3 or more times Unusual signs of skin necrosis, especially with vitamin K antagonists (eg, warfarin) Occurrence of purpura in children and infants born. 3.2. Asymptomatic immediate relatives Gene testing for hereditary thromboembolic disease should also be considered for adult relatives (siblings, parents, children 16 years of age and older) of patients with a history of hypercoagulability, even if they are asymptomatic.
Early identification of a family member's risk for inherited coagulopathy can increase the chances of successful short-term treatment during periods of increased thromboembolic risk (eg. surgery, trauma).
Vinmec International General Hospital is a prestigious medical unit with a team of doctors with many years of experience in diagnosing and treating problems related to Obstetrics and Gynecology, genetic testing. Currently, Vinmec Time City International Hospital is implementing a pre-pregnancy health care and counseling program with the following services:
Genetic counseling before pregnancy Screening to detect healthy people carrying disease genes. equipment for assisted reproductive services Pharmaceutical use and pregnancy Vaccinations Oral Vitamins and Folic Acid (vitamin B9) Food use and pregnancy Prevention of exposure to toxic chemicals, hazardous physical agents Other health problems for you and your husband (wife). Health check-up for couples who are planning a pregnancy, for parents who have been pregnant or given birth to a child with birth defects or problems related to chronic diseases, reproductive diseases. gynecology ... is very important and necessary to minimize the risk that may occur in the next pregnancy.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.