This is an automatically translated article.
In vitro fertilization is an infertility treatment - infertility for women with blocked, damaged fallopian tubes or no fallopian tubes. This method is also applied to elderly patients, endometriosis, irregular ovulation, unexplained infertility, abnormal sperm and immune factors...
1. What is IVF?
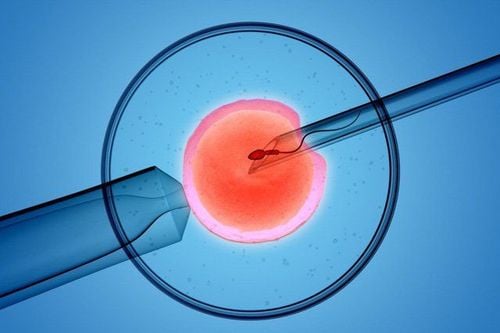
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a treatment for infertility, infertility or other genetic sex-related problems in which the husband's sperm and the wife's egg are fertilized within laboratory to create embryos. After a period of external culture (2-5 days), the embryo will be returned to the woman's uterus to implant and start the pregnancy process.
Worldwide, the chance of successful IVF is about 40-45%. In Vietnam, this rate reaches 35-40%, this number will decrease from 2-10% for older women (after the age of 40).
Thụ tinh trong ống nghiệm IVF
2. In vitro fertilization process
In vitro fertilization is done through the following steps:
Step 1: Preparation
Start with oral contraceptives Some patients will be given oral contraceptive pills one month before the injection cycle ovarian stimulant. This is to ensure that the GnRH agonist is administered at the right time if the patient has an irregular menstrual cycle. There is also evidence that oral contraceptives can prevent ovarian cysts that can sometimes develop during GnRH agonist therapy. Progesterone can be used in patients with irregular or normal menstrual cycles.
Preventing LH Peaks There are two basic ways to prevent premature ovulation before egg retrieval. The first way is to use a GnRH agonist (Diphereline) before entering the cycle of ovarian stimulation. The second is a GnRH antagonist (Cetrotide, Orgalutran) starting 6-7 days after ovarian stimulation.
GnRH GnRH agonist (Diphereline): This drug is given by injection under the skin and comes in two formulations: A short-acting type that requires daily injections, and a long-acting type that lasts 1-3 months. The main principle of this drug is to prevent premature LH peak, if LH rise early will cause ovulation before egg retrieval. Because initial injections of GnRH agonists can increase the release of FSH and LH from the pituitary, it is also used to initiate ovarian stimulation or during the late stages of follicular maturation stimulation.
GnRH agonists can be started after using oral contraceptives. Dosage may be reduced when ovarian stimulation is initiated. GnRH agonists were discontinued on the day of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) administration.
Some regimens can initiate GnRH agonists after ovulation in the pre-ovarian stimulation cycle in the “mid-luteal” regimen, or be used at the onset of menstruation in the “flare” regimen. .
GnrH Antagonist GnRH Antagonist (Orgalutran or Cetrotide): This is another class of drugs used to prevent premature ovulation. Currently, GnRH antagonists are usually given six or seven days after ovarian stimulation and require fewer injections than GnRH agonists.
Ultrasound examination of the pelvis The doctor will do an ultrasound to examine the ovaries. If residual cysts are detected, delay the use of the regimen, use of oral contraceptives, and reschedule the ultrasound for the next cycle. A small number of cases require cyst aspiration. This procedure will be done under ultrasound guidance, the doctor will use a long needle with a syringe to drain the cyst.
Step 2: Ovarian stimulation
With a long regimen, GnRH injection will be started from day 21 of the previous cycle. With a short regimen, ovarian stimulation will begin during menstruation. Some drugs are commonly used to stimulate the ovaries such as: Menogon, Menopur, Foligraf, IVF-M, Gonal-f, Puregon... And with the addition of drugs to prevent premature ovulation, are GnRH antagonists (Cetrotide, Orgalutran). Ovulation induction can be combined with a GnRH agonist (Diphereline), which is used to reduce severe ovarian hyperstimulation. There are many regimens for ovarian stimulation, each regimen is based on a different physiological mechanism despite the use of the same drug mentioned above, but there are groups of patients who respond better to this regimen than to the one above. other. However, do not assume that changing from one regimen to another will result in a change from poor response to good response.
Step 3: Monitor follicular growth
Follicle growth will be assessed by transvaginal ultrasound and hormone blood tests. These investigations will be performed several times during the IVF cycle, and based on these results, the doctor will adjust the dose of the drug to suit the development of the follicle.
Step 4: Complete oocyte maturation and hCG injection.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) (Pregnyl, IVF-C, Ovitrell) is a hormone drug that stimulates complete oocyte maturation. Determining the appropriate date of hCG injection is very important. Your doctor will make a plan because the timing of this injection will determine the time of egg retrieval. In a regimen using GnRH antagonists, a GnRH agonist can be injected to stimulate the final maturation of the follicle.
Step 5: Vaginal aspiration
Eggs will be removed from the ovary with a needle under ultrasound guidance. Anesthesia helps the patient to feel less pain and more comfortable. Tissue damage and infection are rare. Egg retrieval will be performed approximately 34-36 hours after the hCG injection. The anesthesiologist will inject drugs intravenously (analgesia and anesthetic) to reduce discomfort that occurs during this procedure. Most patients sleep during the procedure. A transvaginal ultrasound probe is used to view the ovaries and the follicles in the ovaries. A long needle visible on ultrasound will aspirate each cyst. The aspirated fluid includes follicular fluid, follicular cells and eggs. The doctor will aspirate eggs and follicular fluid into a test tube and the embryologist will look for eggs in the follicular fluid under a microscope.
After aspiration, there are a few cases where there will be little vaginal bleeding and abdominal distension a few days later. Usually, the patient will recover normally in 1-2 days. If the patient appears to have abdominal distension, abdominal distension, vomiting and nausea, little urination.... it is necessary to inform the doctor.
The number of eggs aspirated is related to the number of ovaries, the location of the ovaries that can be aspirated and the number of follicles that develop with ovarian stimulation. On average, each patient aspirated from 8 to 15 eggs.
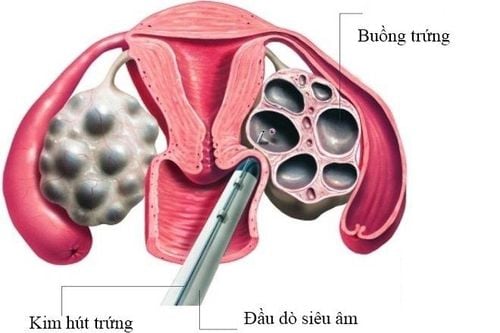
Giai đoạn chọc hút trứng
Sperm and eggs will be put together in special room conditions (culture environment, temperature, humidity and light conditions) for fertilization. The culture medium is created to help the fertilization process take place normally and the embryo develops at an early stage. Thanks to laboratory culture, it is possible to identify which embryos develop well, which are poorly developed or do not develop. Sperm will be collected by masturbation the morning of the day of the aspiration, and the sperm will be separated from the semen. If the patient has difficulty obtaining sperm, a pre-coagulation may be selected as a backup sample and sometimes as the primary source of sperm.
After eggs are aspirated, they will be transferred to the laboratory to be kept in conditions that can sustain growth. The embryo will be supported to grow in a dish or small test tube with the same culture as the fallopian tube and uterus. These test tubes containing these embryos will be put into the incubator to ensure the temperature and concentration of gases such as O2, CO2,...
A few hours after the eggs are aspirated, the sperm will be put into the environment. eggs (IVF), or inserting a sperm into a mature egg is called intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). And the eggs are kept in the incubator. These culture tubes will be periodically examined to assess embryo development.
In the following days, the embryos will be checked for characteristics during development. On day one, the normally developing embryo is characterized by a single cell with two nuclei; This stage is called zygote. Two days after IVF/ICSI, the embryo divides into 4 cells. And on the third day, the embryo contains 8 cells. If cultured to the fifth day, the embryo will develop to the blastocyst stage (embryo sac) with 80 cells or more, with a fluid cavity and a cell mass inside.
Although all steps work well, there are certain situations in the laboratory that lead to a non-pregnancy:
The egg is not fertilized. Having one or more abnormally fertilized eggs, which changes the embryo's chromosome set. The fertilized egg may degenerate before dividing into an embryo, or the embryo may develop incompletely. Infection or failure in the laboratory can result in embryo loss or damage to some or all of the eggs or embryos. Laboratory equipment may be damaged, and or prolonged power failure may occur, which can destroy eggs, sperm, and embryos. Other unexpected situations can affect any stage or interfere with the formation of a fetus. Step 7: Embryo transfer
2-3 days after egg retrieval, the beautiful embryos will be selected for transfer. The number of embryos transferred affects the pregnancy rate and the rate of multiple pregnancies. Maternal age and embryo morphology most influence pregnancy outcome. • The remaining untransferred embryos, if of sufficient quality, will be frozen and can be transferred to subsequent cycles. Embryos are usually transferred on day 3 or day 5 after egg retrieval. The doctor will insert a flexible tube through the cervix into the uterus and place the embryo inside the uterus. There is usually no need for anesthesia during this procedure, and the patient is discharged from the hospital after lying down for a few hours.
Step 8: Supplementing with hormones
Successful implantation of an embryo in the uterus depends on adequate hormonal support. Progesterone is routinely used for this reason. Progesterone can be supplemented by oral, injectable or vaginal suppositories and in some cases a combination of ways. Start adding medication on the day of egg retrieval. Normally, cells in the follicle will produce progesterone after aspiration. During aspiration, these cells may be removed along with the egg. Progesterone supplementation will help the endothelium prepare well to receive the embryo and implant.
The medicine will be taken every day until the day of the βhCG test. If you have a pregnancy test, you will need to continue taking progesterone for a few more weeks.
Step 9: Pregnancy test
It is necessary to take a pregnancy test whether the patient has heavy or light vaginal bleeding. This test helps confirm pregnancy and is performed 10-14 days after embryo transfer. The test can be repeated in two days if the result is positive. If the test is negative, your doctor will instruct you to stop the progesterone medication.
Step 10 – Early pregnancy monitoring
Close pregnancy monitoring is necessary to identify miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy or multiple pregnancy for appropriate treatment. Progesterone is used to support the corpus luteum of pregnancy.

Nội tiết Progesterone
3. Follow-up of follicles during IVF
Follow up the follicles to decide the time of egg retrieval in IVF, during the time of ovarian stimulation injection (average 10-12 days), the patient will have ultrasound and blood test. This is to monitor the growth of the follicles.
During the follow-up of the follicles, the patient will have about 3-4 ultrasounds with transvaginal transvaginal ultrasound. Blood tests to check levels of the hormones estradiol and LH.
The dose of the drug can be adjusted by the doctor according to the response of the ovaries and hormone levels E2, LH during monitoring.
Once the ultrasound and blood tests show that the follicle is large and mature enough for egg retrieval, the doctor will decide when to trigger ovulation with an injection of hCG. Egg retrieval will be done about 35-36 hours after the hCG injection.
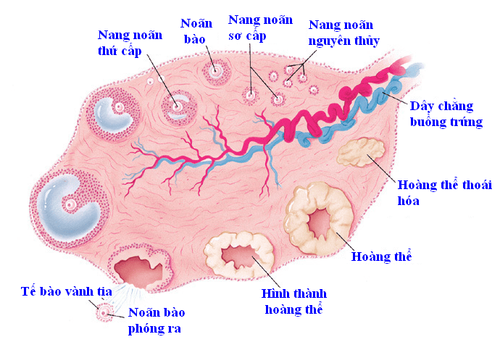
Theo dõi nang noãn trong thời gian chích thuốc kích thích buồng trứng
4. Differences in IVF in vitro fertilization at Vinmec International General Hospital
Vinmec IVF Reproductive Center is the address of infertility - infertility treatment chosen by many couples. So far, the Center has performed fertility support for over 1000 infertile couples with a success rate of 45%-50%. This rate is equivalent to developed countries such as the UK, USA, Australia,...
The center gathers a team of leading experts in the field of obstetrics and gynecology nationally and internationally, trained in centers leading in the world such as in the US, Singapore, Japan, Australia and famous fertility centers in the world. Vinmec Fertility Center can perform most of the advanced assisted reproductive techniques in the world such as: classical IVF, ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection), embryo freezing, culture - embryo transfer, support embryo rupture, reduce multiple pregnancies...help realize the dream of parenthood of hundreds of families across Vietnam.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.