This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Van Huy - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital. The doctor has more than 10 years of experience in the field of Critical Care - Anti-Poison - Emergency.Recorded in medical facilities the number of patients bitten by snakes has increased. Especially due to improper first aid, or according to folk experience, leading to late arrival to the hospital for examination and treatment, many patients may experience gangrene of limbs, coma, sepsis, and even death. Therefore, recognizing venomous snake bites and giving first aid to being bitten by a venomous snake properly is extremely necessary.
1. Identify poisonous and non-venomous snakes
It is difficult to distinguish poisonous snakes from non-venomous snakes. However, it is possible to recognize some common types of venomous snakes based on the external characteristics of snakes: Cobra (cobra emits a characteristic sound), krait snake (body has: yellow piece). black segment), krait snake (body has: white segment, black segment), viper family (large diamond-shaped head or larger triangle). Venomous snakes often have two large teeth in the position of the upper incisors, so when biting often leaves a characteristic bite that can help distinguish venomous snakes. Venomous snake bites often leave 2 round dots that are traces of 2 venomous fangs. And normal snakes (not poisonous snakes) after biting often leave a whole round teeth including many teeth because snakes usually do not have 2 poisonous fangs but have a whole set of teeth. 2 Poisonous teeth are like a needle injected under the skin or injected into a muscle. In some cases, the type of cobra, although at a distance from the victim, still sprays venom towards the victim, causing eye damage leading to systemic poisoning. The cobra family like the cobra, the king cobra, venomous teeth are often sharp, sharp, and leave obvious marks on the skin at the bitten area.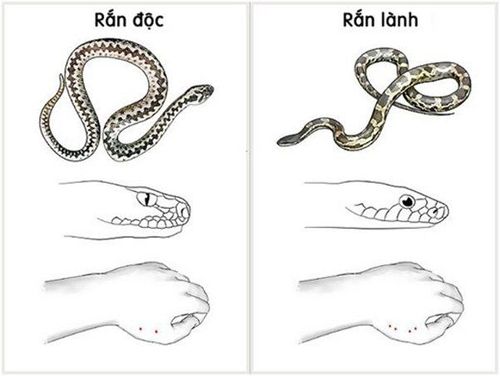
2. First aid for snake bites
First aid for snakebites should be performed immediately after a snake bite, before transporting the patient to the hospital.The goal of first aid:
Remove the venom and slow its movement from the bite wound into the body. By rinsing the wound with clean water, applying pressure at the bite site (non-aromatic), immobilizing the bitten limb to reduce and slow down the movement of the venom Protect the patient's life, prevent and early treatment of complications before the patient reaches the medical facility. Transport the patient in the fastest and safest way to the medical facility No further harm is done to the patient. First aid steps should be taken:
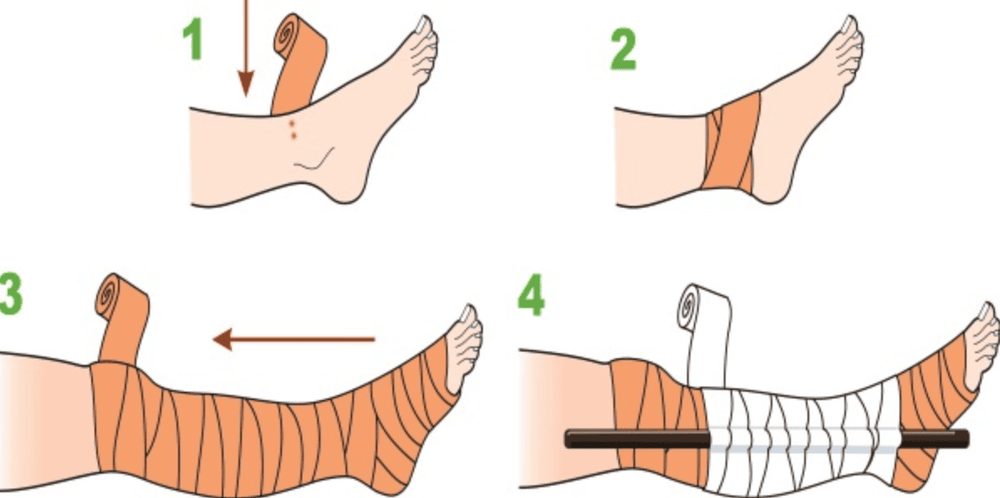
Try to identify the snake bite, color, size, head shape, attack method. If you have caught a snake, take a picture of the snake or bring the dead snake with you to a medical facility. Reassure the patient. Never let the victim walk on his own. Immobilize the bitten leg or arm with a brace Immobilizes with certain types of cobras (snake snakes, kraits, king cobras, sea snakes and some common cobra varieties), immobilization bandages for the purpose of immobilization. delay the onset of symptoms of paralysis. The goal of compression is to reuse the usual elastic used to bandage the knee when playing sports, the elastic bandage will wrap around the bitten limb from above the site of the snake bite. The elastic bandage has the effect of compressing the venous system and the lymphatic system to slow down the movement of snake venom, because snake venom enters the circulatory system mainly due to absorption at the bite site into the lymphatic system, a part of which is very Small particles can enter the intravenous route, but not absorbed into the arteries and capillaries. Therefore, Garo chi should not be bitten because it is not effective but clogs the artery, causing danger to the patient. It can be simply understood that we only use an elastic bandage to compress the superficial venous and lymphatic system in the bitten limb, and never use the Garo rope to let the Garo limb be bitten because Garo will block the artery of the bitten limb. limb and cause limb necrosis. Use elastic bands, cloth bandages or towels, clothes. The bandage is relatively tight but not overly tight (to avoid loss of pulse). Start dressing from the tip of the limb to the base of the limb to the end of the bitten leg and arm. Use a stiff brace to immobilize the bitten leg or arm. The brace works to make the patient unable to move the limb on their own and helps to limit the movement of snake venom. If the bite of a viper causes the bleeding to be unstoppable, it is imperative to apply pressure more tightly than the bite site to stop the bleeding. Because viper venom interferes with the patient's hemostasis, causing the bleeding to continue without stopping, the patient dies from blood loss and hemostasis disorder and bleeding from other internal organs in the patient's body. There is no need to bleed at the site of the snake bite. If the patient has difficulty breathing, give artificial respiration (breathing or by medical means available in place such as balloon squeeze, portable ventilator, ..). If the victim shows signs of circulatory arrest, perform general resuscitation on the spot and wait for medical staff to arrive. Shortness of breath is common in cases of scorpion bites, king cobra bites, or scorpions. Note when transporting the patient so that the bitten area is lower than the heart position, if it is in the legs, arms, you can let the arms or legs hang....to limit the snake venom from moving to the heart and central circulation. the victim to a medical facility as soon as possible. If the patient is awake, he can be taken to a large hospital where specific antivenom is available. Antivenom should be administered early (within the first 4 hours). In case the victim is lethargic, comatose or weak, take them to the nearest medical facility. Any case of snakebite, even if it is determined to be a healthy snake, should be treated and monitored at the hospital like a venomous snake bite, at least for the first 12 hours. If after 24 hours, the treatment is very poor or not effective.
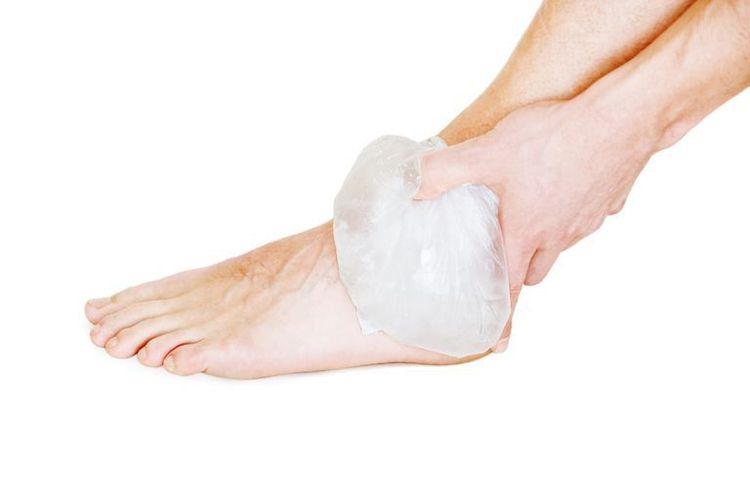
Do not bandage after being bitten by a snake because tight binding can prevent blood from reaching the tied position, making this part easy to necrosis. When the doctor removes the bandage, the poison will simultaneously rush to the heart, causing the patient to go into shock, the patient may die immediately. Extraction, incision, stapling, poking at the bite area: these measures have no benefit, obviously cause additional harm to the patient (damage to more blood vessels, nerves,... worsening infection) and make the infection worse. It allows venom to enter the circulation faster because it causes further tearing and damage during the incision process. Venom Suction: There is no benefit as snake venom is very sticky and does not suck up venom. Applying ice: Has been shown to be harmful. Use folk and traditional medicines, cure with tips: No benefit, when applied can cause infection, when taken, can harm the victim. Delays hospital admission for antivenom serum, also known as antivenom. Attempts to catch or kill snakes: If the snake is dead or caught, it must be brought with the patient to the hospital for identification. At large hospitals, even if the patient cannot bring the venomous snake that has bitten him to the hospital, there are still many ways to determine which snake family the patient has bitten by using tests to identify snakes such as the Rapid VDK Test. , or based on clinical features.
3. Prevention of snake bites
Know about the type of snakes in the area, know the areas where snakes like to live or hide. Wear boots, boots, and long pants, especially at night, and a wide-brimmed hat if you're in the woods or in a wooded area. The farther away from snakes, the better, dead snakes can still bite people. Do not catch, chase or corner snakes in enclosed areas. Do not live near places where snakes like to reside or like to visit such as rubble, rubble, garbage piles, and family animals. To avoid being bitten by sea snakes, people should not catch snakes in nets or fishing lines. Use lights if in the dark or at night. Do not actively catch snakes, tease snakes, use labor protection means with people who raise poisonous snakes.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.