This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Dang Xuan Cuong - Department of Emergency Resuscitation - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Emphysema is a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, common in frequent smokers. If not treated promptly, emphysema can lead to many dangerous complications such as respiratory failure, pneumothorax, pulmonary artery blockage...
1. What is emphysema?
Emphysema is a lung disease that makes breathing difficult. The disease occurs in people whose lungs are damaged, most often due to smoking. Without proper and timely treatment, the lung sacs will gradually weaken and break down, forming large spaces, causing a decrease in the lung surface area, and the amount of oxygen entering the blood will decrease.When the bronchi are damaged, the exhalation will also be affected, the blocked air cannot escape to the outside, and the oxygen-rich outside air cannot go inside, making the patient unable to breathe. provide adequate oxygen, serving the body's activities. Most patients with emphysema have chronic bronchitis. It is caused by inflammation of the air ducts leading to the lungs, leading to a persistent cough that does not go away.
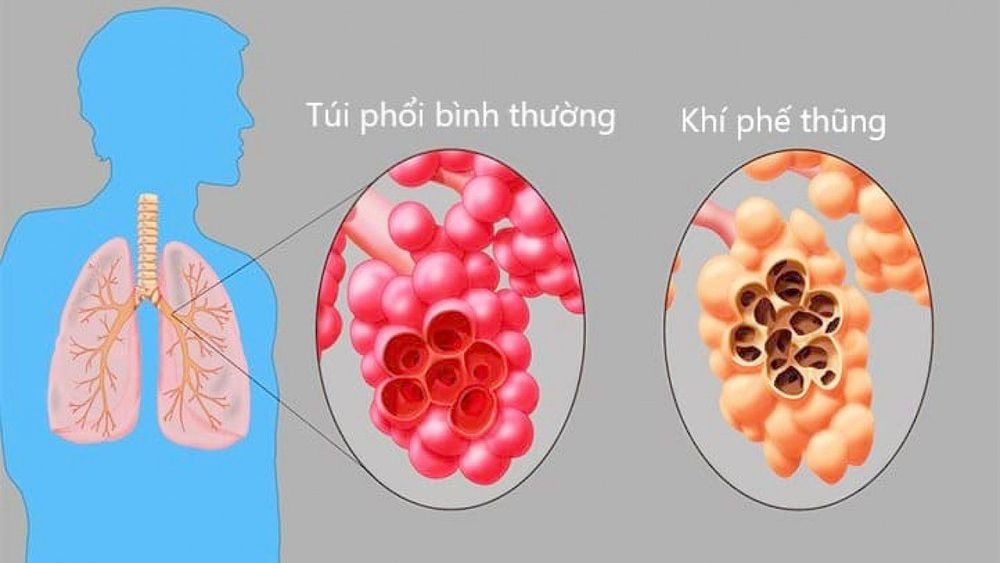
Khí phế thũng là một bệnh lý liên quan đến phổi, khiến bệnh nhân bị khó thở
2. Classification of emphysema
Emphysema is divided into 2 types, including: primary emphysema and secondary emphysema.2.1. Primary emphysema Primary emphysema includes 3 main types and is divided according to the location of the lesion, including:
Central lobular/central follicular emphysema: This is a secondary complication after a stroke. chronic bronchitis. Patients with chronic bronchitis will spread to the bronchioles in the center of the lobules, because the bronchi do not have cartilage, they are very quickly stretched and destroyed into emphysema in the center of the lobules. The alveoli in the periphery of the lobules are still functioning normally, the pulmonary capillaries are not damaged. If the body is deprived of oxygen, it will create anatomical shunts, causing high blood pressure in the circulation, blood stasis in the right heart and leading to congestive heart failure. Pan-lobular/polycystic emphysema: caused by deficiency of A1 antitr and A1 resistance to protease. Distal alveolar emphysema: This condition causes damage to the alveolar sacs and alveolar ducts, forming air bubbles about 1 cm long and occupying the entire chest cavity. 2.2. Secondary emphysema Secondary emphysema can occur in some cases such as:
Emphysema near fibrous tissue Point emphysema/peribronchioles (common in sick people) lung dust).
3. Causes of emphysema
There are many causes of emphysema, the most common being chronic bronchitis, prolonged inflammation from microorganisms, the impact of harmful chemicals, smoke, kitchen smoke, dust... Therefore, people who smoke cigarettes and pipe tobacco have a very high risk of developing emphysema. Tobacco smoke, pipe smoke can temporarily paralyze the bronchioles, bronchioles, and alveoli. These cilia work to push irritants and pathogens out of the respiratory tract. When the cilia are paralyzed, this function will not work. Toxic and irritating substances will be deposited in the bronchi, leading to alveolar infiltrate causing inflammation, fibrosis of elastic fibers, and gastritis. emphysema .The body's lack of AAT protein can also lead to emphysema. AAT protein (Anpha1-Antitripsin) has a protective effect on the elastic structures of the lungs, helping to reduce the impact of some enzymes. A lack of AAT protein can lead to progressive lung damage, leading to emphysema.
Chronic asthma or long-term tuberculosis can also cause frequent stretching of the bronchial walls, alveoli, capillary system of the lung tissue, leading to emphysema
4. Symptoms to recognize emphysema

Người bệnh khí phế thũng thường có triệu chứng ho liên tục, kéo dài
5. How to treat emphysema
The goal of treatment for emphysema is to relieve symptoms and prevent progression and complications. To treat emphysema, patients will be prescribed bronchodilators, anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve shortness of breath, and support to push out sputum. The drug can be used through inhalation (aerosol) or taken directly. Inhaled corticosteroids are commonly used in acute exacerbation or prophylactically. In case of infection, antibiotics must be used. Specific treatment for emphysema will be prescribed by the doctor in accordance with each patient's condition and severity of the disease.6. Prevention of emphysema
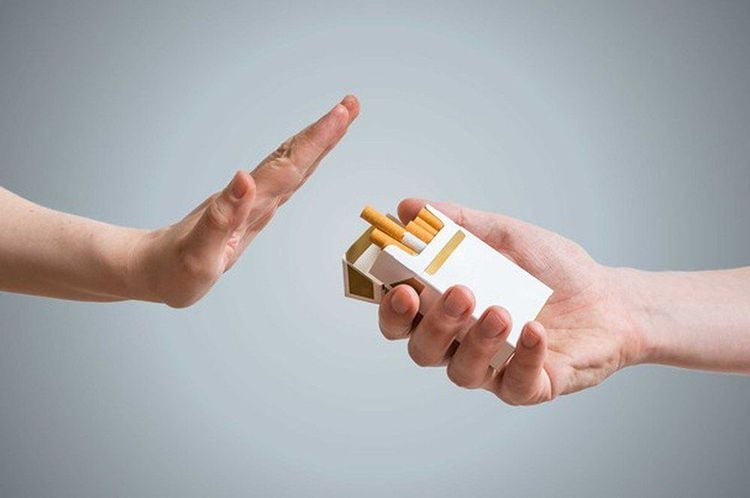

Không hút thuốc lá để phòng ngừa bệnh khí phế thũng
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.