This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Hong Lien - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. Doctor Lien has over 10 years of experience as a radiologist in the Department of Ultrasound at the leading hospital in the field of obstetrics and gynecology in the South - Tu Du Hospital.
Fetal failure is a dangerous condition during pregnancy that greatly affects the fetus. Pregnant women need to recognize early signs of fetal distress during pregnancy and labor to help prevent dangerous complications later on.
1. Intrauterine pregnancy failure
Fetal failure is a condition in which the fetus is deprived of oxygen during pregnancy or during labor. The uterine - placenta - fetal circulation is the place to carry out the task of providing oxygen to the fetus. However, if for some reason a disorder affects the utero-placental-fetal circulation, leading to a decrease in blood flow to the blood lake, or from the placenta to the fetus, making the oxygen exchange between the mother and the baby is interrupted. As a result, the amount of oxygen reaching the fetus is severely reduced, electrolytes in the blood are disturbed and causing fetal distress.
Fetal failure is divided into two categories, corresponding to two time periods: during pregnancy and especially during labor.
Fetal failure in pregnancy : Usually a chronic, long-term form of fetal distress, occurring slowly and without obvious signs, can turn into acute fetal distress during labor. Fetal failure in labor: Acute, sudden, very dangerous, if not treated promptly, the fetus will face brain problems, even death. In addition, the degree of hypoxia more or less, chronic or acute, will affect the degree of fetal distress and the possibility of death. For the hypoxic fetus, the fetus also initially has a compensatory response by adjusting the blood distribution to provide adequate oxygen to the brain, heart, and liver, and reducing oxygen transport to the intestines and skin. However, when the fetus is deprived of much oxygen or for a long time, the fetus will no longer be able to respond to compensate, leading to a lack of oxygen in the brain, heart, and other organs in the body. anaerobic, leading to a decrease in pH, causing fetal acidosis and death in utero, or death after birth.
Therefore, pregnant women need to pay attention to the signs of pregnancy failure to help the fetus develop normally, avoiding unfortunate situations.

2. Signs of pregnancy failure
2.1. Fetal failure during pregnancy
Symptoms of fetal distress during pregnancy:
The height of the uterus grows quite slowly (a sign of fetal underdevelopment) Fetal movements become chaotic or too slow: The fetus has these symptoms Abnormalities in movement, sometimes the baby kicks hard and a lot, then the movements slow down and become less and less. After a while, the mother can feel the baby in the womb almost no movement, indicating a very high risk of stillbirth. To recognize this sign, pregnant women should pay attention to counting fetal movements (from 23 hours onwards, the fetus moves less than 12 times in 2 hours). When counting the number of fetal movements and detecting abnormal signs, pregnant women should be taken to a medical facility immediately to check the status of the fetus.
Fetal heart rate changes: The lack of oxygen during fetal distress will affect the fetal heart rate, leading to the phenomenon that the fetal heart sometimes beats faster (over 160 times/minute), sometimes slows down (down). less than 100 times/minute). This sign is usually checked most accurately when a pregnant woman has a routine antenatal checkup, so tests during a routine antenatal checkup are the best way to detect early signs of fetal distress. Tests:
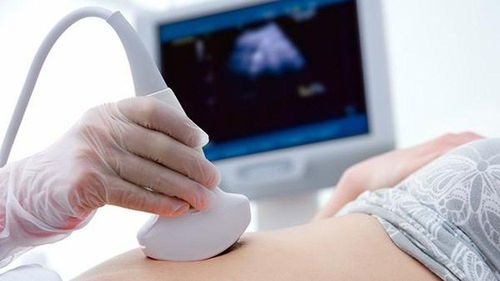
Amniotic fluid: Abnormal blue color (requires amniocentesis) Obstetric monitor, ocytocin infusion or nipple discharge shows early bradycardia (Dip I), late bradycardia (Dip II), fetal heart rate does not respond to the test do not lash out. Ultrasonography determines the amniotic fluid index (valid in old-term pregnancy), Doppler vascular MR, PE and bilateral aorta.
2.2. Fetal failure in labor
Signs of blue amniotic fluid (when water breaks or amniotic fluid is pressed) Auscultation of fetal heart rate (with wooden tube): Over 160 beats/min or less than 100 beats/min. Continuous monitoring of fetal heart rate with an obstetric monitor: The presence of delayed fetal heart rate (Dip II), or a variable or less variable rhythm of less than 5 beats. Ultrasound: Determine the amount of amniotic fluid decreased (amniotic fluid index decreased), decreased coronary artery impedance Measure the pH of fetal head blood and umbilical blood right after birth.

3. Treatment when detecting fetal distress
Pregnant women first need to prepare enough knowledge about pregnancy failure, prepare the best health and psychology to have a really safe and healthy pregnancy. During pregnancy, women need to perform antenatal care on schedule and be closely monitored, especially for those at high risk of fetal distress.
During the examination, the doctor will perform the necessary tests to detect fetal distress, such as fetal heart rate monitoring (stethoscope), vomiting, ocytocin test or nipple monitoring with a monitor. obstetric. When detecting signs of fetal distress during pregnancy, depending on the prognosis, the doctor will consider appointing the pregnant woman to terminate the pregnancy, induce labor, and if that fails, a cesarean section is required.
During labor, pregnant women need to be closely monitored to promptly detect signs of fetal distress. Monitor the mother's health and medical condition, measure fetal heart rate every 10-15 minutes, monitor uterine contractions in accordance with the stage of labor. In addition, continuous monitoring of fetal heart rate with an obstetric monitor to detect Dip II, variable Dip, or fetal heart rate fluctuations less than 5 beats. If there are signs of fetal distress during labor, the doctor will consider appointing a delivery for pregnant women with Forceps forceps, if not qualified to do Forceps, then a cesarean section. In case of pregnancy beyond the due date, the amount of amniotic fluid is reduced and meconium is thick, the cesarean section should be performed, should not be challenged to deliver the lower tract.
In addition to regular check-ups, when seeing any abnormal signs, especially related to fetal movements, pregnant women should be immediately taken to a medical facility for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Department of Medical Examination and Treatment (Ministry of Health)