This is an automatically translated article.
Sterilization is a method of blocking the fallopian tubes to prevent sperm and egg from meeting, this is a safe, permanent birth control method, suitable for those who do not want to have children anymore.
1. What is female sterilization?
Female sterilization is a method of preventing pregnancy by blocking or removing the fallopian tubes so that sperm cannot meet an egg and fertilize it.
Tubal ligation (female sterilization) is considered an almost permanent and safe method of contraception for women..
Tubal ligation can be performed at any time, including after giving birth. child or in combination with another type of abdominal surgery. It is not possible to return to the original state after a tubal ligation if a woman wants to get pregnant. Tubal microsurgery may need to be performed in some special cases, but it does not always achieve the desired effect.
About 600,000 people in the United States have a tubal ligation each year.
2. How is tubal ligation performed?
Tubal ligation procedure will depend on when you have the procedure. Some women get a tubal ligation soon after giving birth, but others decide to have the procedure done later.
You can have a tubal ligation done during a cesarean section or right after a vaginal delivery (while you're still in the hospital), before the uterus contracts too much.
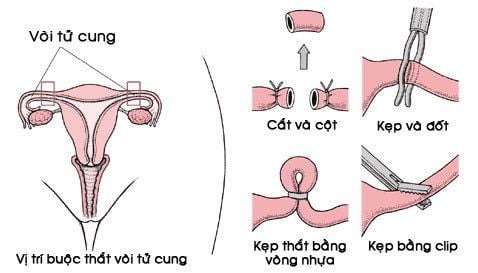
Quy trình thực hiện thắt ống dẫn trứng
If the procedure is done 1 or 2 days after a vaginal birth, you will be given local or specific anesthesia, then the doctor will make a small incision below your navel and remove some or all all of your fallopian tubes go through it. You may have pain at the incision site, but surgery is unlikely to prolong your hospital stay.
You can have an outpatient tubal ligation any time after 6 weeks postpartum, but you will need general anesthesia. The doctor makes a small incision just below your navel and inflates your abdomen with carbon dioxide gas (to make the drains easier to find).
Then the doctor will insert a narrow tube with a light and a small magnifying glass at the end (endoscope) and use it to find your fallopian tubes. The doctor may make another small incision to insert the instrument used to unblock the fallopian tubes.
Your fallopian tubes may be sealed with electrical current or secured with an elastic band or metal splint, or you may have the option of removing parts of the tubes or completely. When the procedure is over, your doctor will sew up small incisions in your abdomen. This procedure usually takes about 30 minutes, after which you will probably be up within 2-4 hours, but you may feel pain for a few days. (See your doctor if the pain gets worse.) You will need time to heal - usually about 1 week - before you start exercising or having sex again.
Also, there is a less invasive method called the Essure method of birth control. This method can be performed after 6 weeks postpartum. In this case, no cutting or incision is needed. The doctor threads a small camera through your cervix and into your uterus, then places a metal implant into each fallopian tube. Once the tissues are transplanted into place, scar tissue eventually forms around each tissue, permanently blocking the fallopian tubes. This procedure usually requires only local anesthesia and takes about 10 minutes. Apart from some minor pain, you should feel back to normal the same day.
However, you will need to have a follow-up X-ray 3 months after the transplant to make sure the tubes are blocked. (Be sure to use a backup method of birth control until then.)
This method carries the risk of perforating the uterus and fallopian tubes, and can travel into the abdomen and pelvic cavity, causing pain and possibly have surgery. If you choose Essure birth control, both you and your doctor must sign a form stating that you have been informed of the risks of taking it.
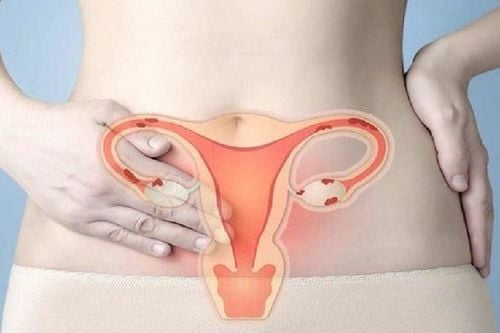
Phương pháp ngừa thai Essure có thể làm thủng tử cung và ống dẫn trứng
3. Will sterilization affect sex drive or menstruation?
Sterilization procedures do not affect your sex drive or hormone production. You still ovulate each month, but the egg will never reach your uterus. (Instead, it will be reabsorbed by your body.) You will also continue to have periods.
4. How effective are these sterilization procedures?
Depending on which surgical technique is used, your chances of getting pregnant in the first 10 years after sterilization range from 1/27 -1/133. Non-surgical sterilization may even be more effective. In the clinical trial, no pregnancies were reported within 5 years of the Essure procedure. However, outside of the trials, some women became pregnant after taking Essure. But some of these are cases that don't come back for a checkup three months after the procedure to make sure the scar tissue has completely blocked the fallopian tubes.
Note that male sterilization (called a vasectomy) is slightly more effective than surgical sterilization for women and is less risky and less expensive.
If you become pregnant, see your doctor immediately, because female sterilization increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy. In this condition, the egg implants itself outside the uterus, usually in one of the fallopian tubes.

Triệt sản nữ có thể gây ra tình trạng mang thai ngoài tử cung
5. Is it possible to get pregnant after tubal ligation?
In some cases, it is still possible to get pregnant after tubal ligation. However, this rarely happens and if you want to get pregnant, the cost will be very expensive. Fertility after tubal ligation is uncertain. Women who have a tubal ligation still have a higher chance of having a successful baby, and the higher the risk of an ectopic pregnancy. This is a voluntary method of birth control, so be sure of your choice before deciding to opt for this procedure.
Fallopian tubes closed by castrol are much harder to repeat properly because heat destroys their delicate lining. Reconnecting blocked tubes with a nonsurgical implant is even less likely to be successful.
In vitro fertilization may be an option if pregnancy is not possible after sterilization, but it is also complicated and expensive.
6. Is sterilization a good option for postpartum contraception?
The advantage of this method is that if you are 100% sure that you don't want to have more children, this is a good option for you because you don't have to remember to take a pill every day and you don't have to take any medications. Anything before having sex, it can be a real big plus for busy and new moms.

Thắt ống dẫn trứng là một lựa chọn tốt để tránh thai sau sinh
Sterilization will not protect you from sexually transmitted diseases such as HIV, herpes and chlamydia. The biggest downside of tricks is their permanence. If you change your mind, the cost to implement is quite high, no guarantee of success. An estimated 20% of women who have sterilization before the age of 30 regret choosing to have the procedure. For women who chose to have sterilization after age 30, only 6% regretted the decision.
To make sure you don't want to have another baby, ask yourself a few questions:
How would you feel if you lost your partner if the other died or due to a divorce or separation ? Do you want to have children with someone else? Have you ever thought about having more children? If you think it's entirely possible, it's best to choose another form of birth control. Currently, there are non-permanent forms of contraception that are as effective as sterilization, including the intrauterine device (IUD) and the contraceptive implant.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: babycenter.com