This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Thien Quang - Internal Oncologist - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Endometrial cancer is on the rise in young women, it grows faster and tends to spread to other parts of the body.
1. What is endometrial cancer?
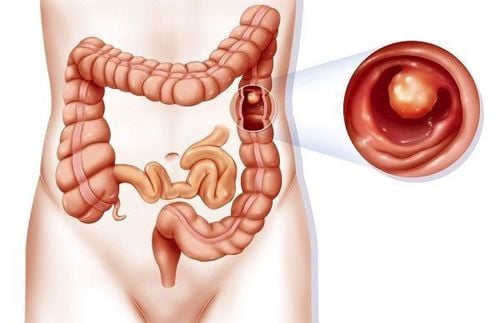
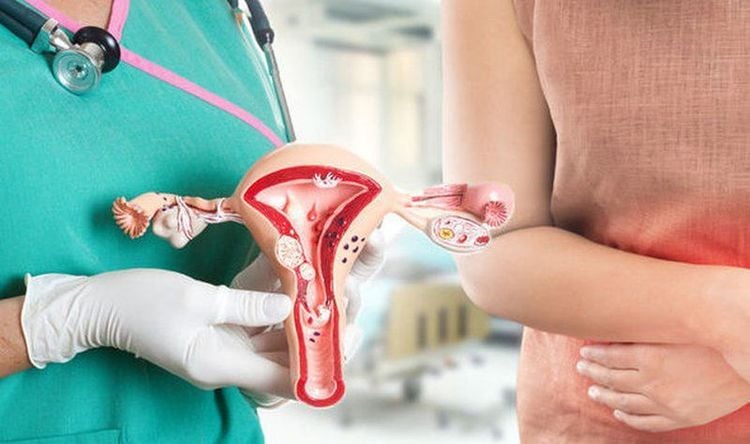
Endometrial cancer is a cancer that develops from the endometrium. This is the most common type of cancer affecting the female reproductive organs. The most common type of endometrial cancer (type 1) is slow growing and is usually found only inside the uterus. Type 2 is less common.
2. How does endometrial cancer appear?
Endometrial cancer starts when endometrial cells start to grow too quickly, thickening the lining of the uterus in some areas, these thickening areas can form a mass of tissue called a tumor. . Cancer cells can also spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body.
3. What factors affect endometrial cancer?
Age - Most endometrial cancers are diagnosed in women who have passed menopause and are over 60 years of age.
Endocrine - The levels of estrogen and progesterone in a woman's body can affect her risk of endometrial cancer. When estrogen is present but there is not enough progesterone, the endometrium can become too thick. This condition can occur in women who have irregular periods, are in perimenopause and menopause, or have certain disorders such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). It can also occur in women who use an estrogen-only method to treat menopausal symptoms.
Overweight - Women with a BMI greater than or equal to 25 have an increased risk of endometrial cancer.

4. Symptoms of endometrial cancer?
The most common symptom is uterine bleeding. For premenopausal women, it includes irregular menstrual bleeding, menorrhagia, or bleeding between periods.5. Diagnosis of endometrial cancer
The diagnostic criteria for endometrial cancer are based on endometrial biopsy results. Your doctor will take a sample of the endothelium and examine it under a microscope.This procedure can be done in the clinic. Another method of mucosal sampling is dilation and curettage (D&C). This procedure is performed with the help of a hysteroscope with a camera, and anesthesia can be applied to reduce discomfort for the patient.
In the case of perimenopause, the gynecologist will consider the signs, symptoms, age and other factors to decide whether to conduct a biopsy or not. Ultrasound has no value in diagnosing endometrial cancer in premenopausal patients.
6. Endometrial cancer treatment?
Surgical treatment Endometrial cancer is usually treated surgically. The doctor will remove the entire uterus and cervix, as well as the two ovaries and fallopian tubes. Nodes and other tissues may also be removed and examined for malignancy. After surgery, the stage of the disease will be determined, to help the doctor decide whether to proceed with further treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation if needed. Cancer is classified into 04 stages, determining the methods and results of treatment, in which stage 4 is the most severe stage.Endometrial cancer treatment endocrine therapy
Cancer is slow growing and has not reached the uterine muscle layer. There were no ectopic malignant cells. In good general health and able to take progestin. Be aware of the limited information available on future treatment outcomes. For some women, the ovaries can be preserved during surgery, which means that the patient can still use the eggs for in vitro fertilization (IVF). However, this option is not for everyone and should be discussed carefully with the treating doctor before making a decision.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article referenced source: Acog.org