This is an automatically translated article.
When your skin is exposed to the sun or UV rays for a long time, it can cause worrying skin problems, such as sunburn, melasma, freckles and even skin cancer. . Protecting and taking care of your skin properly from the very beginning will help you avoid these conditions and prevent premature skin aging.
1. How does sun exposure affect the skin?
The warm rays of the sun can give you a feeling of comfort and ease for a short time. However, prolonged exposure to the sun without protection can damage your skin, leading to premature aging.
UV radiation is part of the spectrum of light from the sun to the earth. It has shorter wavelengths than visible light, which is classified into two main categories, including UVA and UVB rays. Both types of radiation damage your skin in different ways. UVB (short wave) rays are the leading cause of sunburn and redness, while UVA (long wave) rays can penetrate deeper into the skin and cause DNA damage.
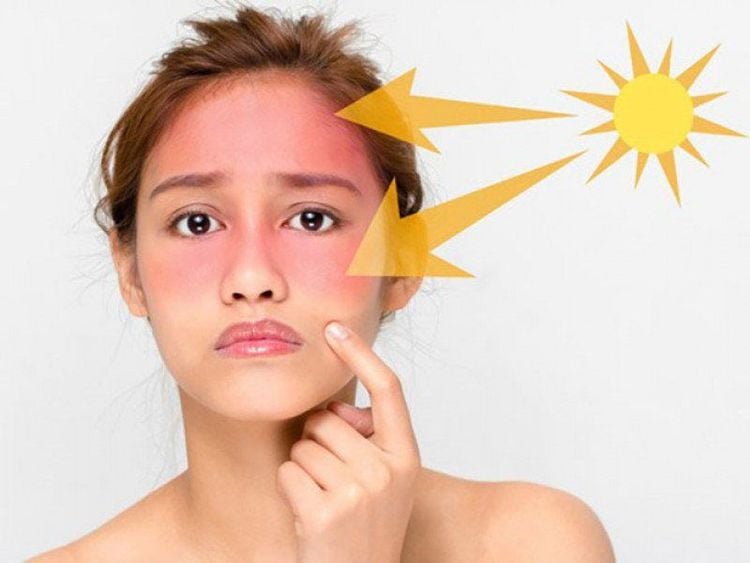
When the skin is exposed to the sun for a long time, the first harmful effect is sunburn. In mild form, the skin will have manifestations such as pigmentation and redness. In more severe cases, your skin may appear with blisters, along with symptoms such as dizziness or nausea.
Unprotected sun exposure can lead to long-term effects on your skin, most notably dryness, tanning and uneven skin tone. Over time, the sun can dry out your skin and deplete essential fatty acids, leaving your skin visibly flaky and wrinkled. In addition, ultraviolet rays from the sun also slow down the rate of skin cell renewal, causing the accumulation of dead skin cells and making the skin dull. And yet, long exposure to the sun can cause stubborn pigmentation or freckles, which are difficult to remove.
So is sun exposure harmful to the skin? When the skin is exposed to the sun for a long time, it can destroy collagen and elastin in the skin. Collagen is a protein that maintains the firmness of the skin, in which elastin is a fiber, helping to support the skin's recovery. Degradation of collagen and elastin in the deeper layers of the skin can lead to signs of premature aging, such as wrinkles.
Although sun damage to the skin is mostly cosmetic, it can become a serious health threat when it comes to skin cancer. Repeated sunburn and unprotected skin from sun exposure can increase the risk of various skin cancers. This is also why sun protection for the skin is so important.

Khi da phơi nắng trong một thời gian dài có thể dẫn đến tác hại là cháy nắng
2. The link between skin cancer and ultraviolet rays
Skin cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer, usually occurring when abnormal skin cells grow uncontrollably. This rapid growth leads to benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous) tumors. Skin cancer includes 3 main types, including: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma. In particular, squamous cell and basal cell carcinoma are the less serious types, accounting for 95% of skin cancers. They are also known as non-melanoma skin cancers, and are highly curable when treated early. As for skin cancer, melanoma, which usually forms from abnormal skin pigment cells, is the most severe form of skin cancer and causes 75% of all deaths. If not treated early, melanoma can spread to other organs in the body and be difficult to control.
In general, ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is considered the leading cause of skin cancer, even UV rays from tanning beds are equally harmful. Exposure to the sun during the winter months carries the same risk of skin cancer as sun exposure during the summer, because UVA rays are usually present in daylight.
Cumulative sunburn mainly causes basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers, while more severe episodes of sunburn (usually before age 18) may increase the risk of developing melanoma. Less common causes include repeated skin exposure to X-rays, or toxic chemicals.
3. Who is at high risk for skin cancer?
Actually, skin cancer can occur in anyone, but the highest risk usually includes people with fair skin, freckles, burns easily, light eyes or blond/red hair. People with darker skin are also more likely to develop other types of skin cancer, but their risk is significantly lower than that of others.
In addition to skin color, other risk factors also contribute to an increased chance of skin cancer, including a family or personal history of skin cancer, outdoor working conditions, and living in an area with high air pollution. after sun. In addition, a history of severe sunburn and having multiple large moles (more than 30) with irregular shapes are major risk factors for the development of melanoma.

Ung thư da có nguy cơ cao thường bao gồm những người có làn da trắng, có tàn nhang
4. What are the common signs of skin cancer?
The most common skin cancer warning signs are abnormal changes in the skin, typically the appearance of new moles, skin lesions or changes in existing moles.
Basal cell carcinoma usually appears as a small, smooth, pearly or waxy bump on the ears, face, and neck. It sometimes resembles a flat pink, red, or brown wound on the arms and legs. Squamous cell carcinoma can appear as a red, hard nodule, or as a flat lesion on scaly skin, which sometimes bleeds and closes. Both squamous and basal cell carcinomas occur mainly in areas of the skin that are frequently exposed to the sun. Melanoma skin cancer usually presents as a pigmented patch or bump. They are sometimes red or white and resemble normal moles, but with a more distinct appearance. In general, melanoma skin cancer often has the following noticeable signs:
Disproportionate appearance of moles or spots. Uneven color of moles or spots, such as brown, black, red, tan, white or blue Moles that have a significant variation in size (larger than 6mm). Have any moles or spots that are growing or changing in color, shape, or size, causing itching or bleeding.
5. Diagnosis and treatment of skin cancer
Skin cancer is usually diagnosed by performing a biopsy. Your doctor will take a sample of skin tissue and then examine it under a microscope.
Treatment for skin cancer is usually determined by each person's condition, including the size, location and type of skin cancer. Treatments for various types of skin cancer include:
Mohs surgery Cryosurgery Topical chemotherapy creams Chemotherapy and biological response modifiers for metastatic skin cancer Radiation therapy
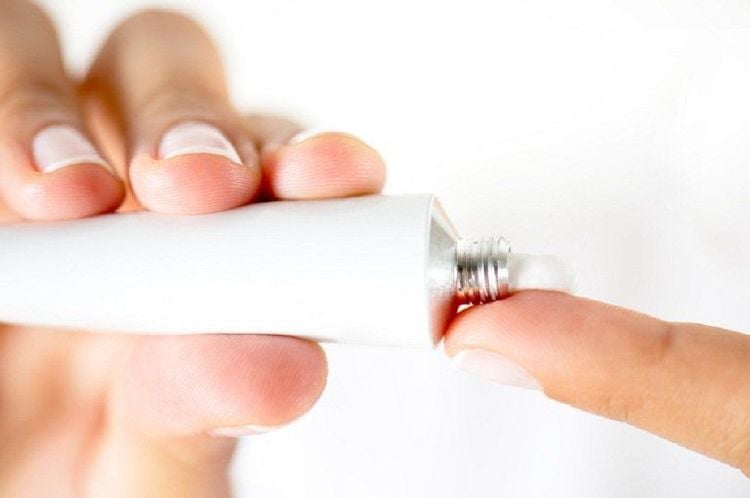
Có thể điều trị ung thư da bằng kem trị liệu hóa học tại chỗ
6. How to protect skin from UV damage?
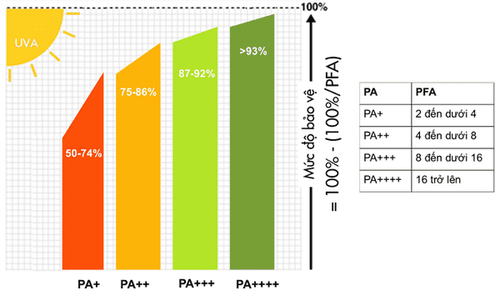
Prevention is better than cure, so protecting your skin from sun damage every day is an extremely important step. In fact, the older you get, the more difficult it becomes for your skin to recover. Ideally, before going out in the sun, you should apply sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher and containing zinc oxide (to block UVA rays). You should reapply sunscreen every 2 hours, or more if you're sweating.
Several other measures to help you protect your skin from the effects of UV rays , including:
Choose clothes, cosmetics and sunglasses with UV protection Wear sunglasses with 100% UV protection and Wear a wide-brimmed hat to protect your face and neck. Avoid prolonged exposure to the sun or limit your exposure to the sun during peak hours, specifically from 10am to 2pm. Check your skin on a monthly basis to detect any changes in your skin early. While it is not possible to completely reverse sun damage to your skin, choosing the right skin care products can help. Combined and combined with daily use of sunscreen can bring about significant improvement. Here are some ways to help reduce sun damage:
AHA exfoliants: You should exfoliate your skin's surface more often to help fade dark spots and reduce skin dryness. This also helps your skin tone become brighter and healthier. Using retinol: Helps stimulate natural cell renewal on the skin and reduces dark spots and wrinkles caused by UV rays Vitamin C: Works to reduce brown spots, making skin whiter and brighter, copper Fight against skin damage caused by environmental pollution Antioxidant Serum: The powerful antioxidants in skin serums will help protect your skin from environmental damage, while increasing effectiveness of sunscreen.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: paulaschoice-eu.com, webmd.com