This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly advised by MSc. Dr. Nguyen Minh Tuan - Pediatrician at the Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Danang International General HospitalHydronephrosis in children is a condition caused by narrowing or blockage of the ureters. One of the most common causes of hydronephrosis in young children is ureteral stricture. The following article will provide information on early diagnosis and treatment of hydronephrosis in children.
1. What is hydronephrosis in children?
Hydronephrosis in children is a condition in which urine is stagnation in the renal pelvis due to obstruction of the ureter due to narrowing of the ureteral ureteral junction.
2. Causes of hydronephrosis in children
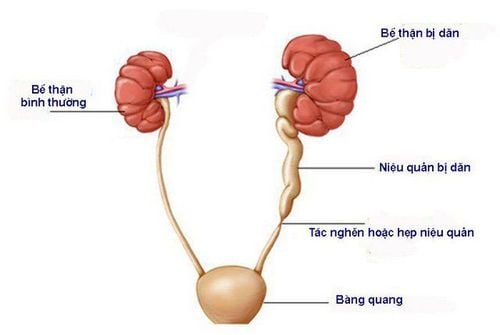
One of the main causes of hydronephrosis in young children is ureteral stricture. This is a congenital disease that develops from the fetal stage with abnormalities in the development of the urinary system such as:
Urethral hypoplasia causes abnormal peristalsis through the junction of the kidney with the ureter; Asymmetry of the muscle wall inhibits peristalsis of the ureter to bring urine out of the kidney, causing hydronephrosis in children; The ureter inserted into the renal pelvis is too high, which changes the shape of the ureter and interferes with the passage of urine from the kidney to the ureter; Abnormalities of the blood vessels in the lower poles of the kidney obstruct the ureters, preventing the passage of urine from the upper renal pelvis; Periosteal vascularization is often associated with junctional stenosis; The relative position of the kidney and the ureter causes the kidney to rotate and move excessively and cause intermittent obstruction; These abnormalities cause the process of bringing urine from the renal pelvis to the bladder to be stagnant, taking place for a long time, causing the kidneys to dilate and causing hydronephrosis in children.
In addition to congenital causes, there are a number of other causes of this disease:
Kidney stones : Too large stones can block the ureters and cause kidney swelling; Tumor or cyst pressing on the ureter and causing obstruction; Blood clots or scarring in the ureters, narrowing the passage of urine. However, the condition is often difficult to detect;
3. Signs of hydronephrosis in children
Some signs of hydronephrosis in young children:
Pain when urinating makes children uncomfortable and cry because of the pain; Back pain, lower abdominal pain; Urinating more than usual, cloudy urine; Fever, nausea and vomiting; Hydronephrosis in young children can affect one or both kidneys. If the disease is not detected and treated in time, the symptoms can become more severe.
4. Diagnosing hydronephrosis in children
Neonatal hydronephrosis detected through prenatal diagnosis by ultrasound during pregnancy. Fetal ultrasound can detect abnormalities in kidney size, amniotic fluid status as well as hydronephrosis.
When there are signs of doubt, the doctor will order additional screening for other factors and monitor the mother's pregnancy health. If children have a fever with cloudy urine, before the fetal ultrasound detected hydronephrosis, little amniotic fluid or oligohydramnios, they should have an ultrasound immediately to see if they have hydronephrosis.
After the baby is born, the following methods will be conducted to accurately diagnose the disease condition as well as the cause of hydronephrosis in the child:
Renal ultrasound (RUS): Re-determine the system kidney and hydronephrosis; Urinary bladder and urethral X-ray (VCUG): The doctor inserts a small tube into your child's bladder and passes fluid through the tube into the bladder. Fluid will show up on the X-ray when the bladder is full and when the baby urinates. This method is used to rule out vesicoureteral reflux. When there is no phenomenon of vesicoureteral reflux, a CT scan - ureteral scan will be indicated to evaluate kidney function and determine the degree of ureteral obstruction as well as the degree of hydronephrosis in the child; Renal nuclear tomography (MAG 3): the doctor injects a small amount of radioisotope into the baby's blood and compares the function of both kidneys and determines the severity of the disease; Other basic blood tests;
5. Treatment of hydronephrosis in children
After the diagnosis of the disease is confirmed, depending on the degree of hydronephrosis, there will be different treatment methods:
With the degree of hydronephrosis in mild children, most will resolve on their own without intervention. surgery card. However, children need to be monitored to promptly detect when a UTI occurs. Your child may be prescribed antibiotics by a doctor to prevent UTIs. If the child has an unexplained fever, the child should have his or her urine checked to rule out a UTI.
With the degree of hydronephrosis in severe children, the doctor may prescribe surgical treatment. If hydronephrosis is caused by a kidney stone, laparoscopic surgery may be required to remove the stone. In addition, one of the most popular surgical methods to treat hydronephrosis today is the retroperitoneal ureteral pyeloplasty technique.
Kidney stasis in young children, if not treated promptly, can cause dangerous complications. Therefore, parents should monitor the child's abnormal signs and take the baby to see a doctor when needed.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.