This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by Master, Doctor Truong Thanh Tam - Pediatrician - Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. Dr. Tam has 15 years of experience working in the field of Pediatrics.About 80% of babies are born with at least one birthmark, which is discolored areas of the baby's body. Some birthmarks will fade or disappear over time, while others cause other health problems for your baby.
1. What is a birthmark?
A birthmark is a term that refers to areas of skin that change color on a baby's body at birth or appear within a few months of birth. More than 80% of babies have some type of birthmark, some of which may last with the baby for the rest of his life, but others that disappear after a while.Most birthmarks fall into one of two categories: vascular or pigmented. Vascular birthmarks are caused by blood vessels below the surface of the skin. They range in color from pink and red to bluish, depending on the depth of the blood vessel. Pigmented birthmarks are usually brown, bluish-gray, or black. They are the result of abnormal growth of pigment cells.
2. Pictures of birthmarks and the most common types
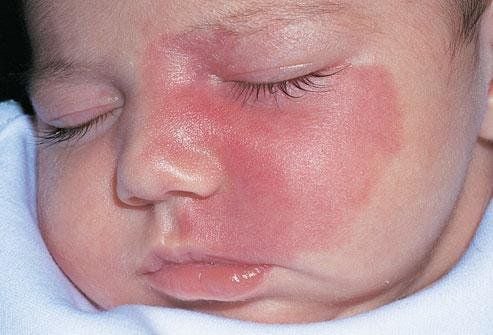
Birthmarks come in many different shapes, sizes, and colors, and they can appear anywhere on the body. Some of the most common birthmarks are:"Stork peck", "angel kiss", orange-pink birthmarks, and vascular stains These are flat pink or purple purple birthmarks formed by cilia caused by varicose veins near the surface of the skin. This is the most common type of birthmark, up to 70% of babies have one or more of these birthmarks. These birthmarks may be more noticeable when the baby is crying or when there is a change in temperature. Birthmarks that appear on the back of the neck, known as stork bites, usually last into adulthood. Birthmarks on the forehead or eyelids are known as angel kisses and they usually disappear by the time a child is 2 years old.
Coffee milk stains These are flat brown or light brown patches, sometimes appearing in clusters. Between 20% and 50% of babies have 1 or 2 of these pigmented birthmarks. They usually fade or shrink as the child grows, although they may darken with sun exposure.
Mole A birthmark made by clusters of pigment-producing skin cells. Moles vary in size and can be flat or raised, black or brown, hairy or not. Many moles do not appear until a child is a few years old. About 1% of babies have moles at birth, which are called congenital moles, or birthmarks. These moles usually start out flat and then become slightly larger and more prominent.
Birthmarks, buttock rash Are birthmarks that appear as large, flat areas of extra pigment on the lower back or buttocks. They most commonly appear in infants with dark skin: 95% to 100% Asian, 90% to 95% East African, 85% to 90% Native American, and 50% to 70% children Hispanics have these birthmarks. Meanwhile, only 1 to 10% of white babies have these birthmarks. Mongolian birthmarks usually fade with age, although they may never go away.
Flat birthmarks aka red birthmarks These are birthmarks that appear at birth, they range in color from light pink to dark purple and can appear anywhere on the body, although they usually appear on face or head. About 1 in 300 babies are born with this wine birthmark. Mild birthmarks may fade, but most are persistent and grow as the child gets older. Sometimes wine birthmarks can thicken and darken. They can also form stones or small lumps on the surface of the skin over decades.
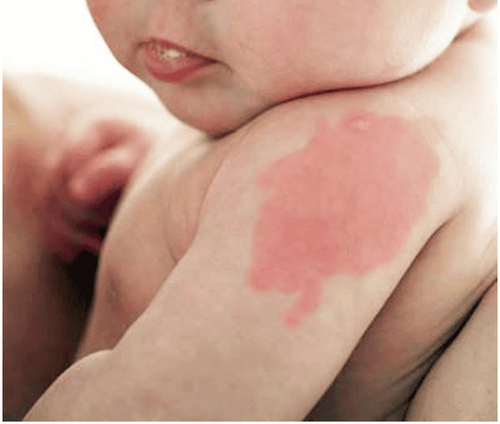

Hemangiomas mainly appear on the head and neck and unlike other birthmarks, they can grow quickly. They usually appear in the first 6 weeks after birth, only 30% of babies are born with them. The growth rate of hemangiomas is usually no larger than 2 or 3 inches in about 1 year. Then, without treatment, they usually stop growing and start to turn white and get smaller. This reversal process can take three to 10 years. While many hemangiomas leave the skin looking normal once they appear, others can cause permanent changes in the skin.
One of the types of hemangiomas is superficial hemangioma, formerly known as strawberry hemangioma, which occurs in 2% to 5% of newborns. This pinkish-red stain tends to develop and then disappear. About 50% of babies with this birthmark will be flat by age 5 and 90% flat by age 9. Another type are hemangiomas, which are deeper (formerly called cavernous hemangiomas) appearing as a bluish-red mass. It develops rapidly during the first 6 months and usually goes away by the time the child reaches adolescence. Such hemangiomas are bluish in color because the abnormal vessels are deeper than superficial hemangiomas.

3. Does the birthmark require medical attention?
Most birthmarks are harmless, and many birthmarks disappear on their own within the first few years of life, says dermatologist Seth Orlow, professor of pediatric dermatology at New York University School of Medicine. There are a few exceptions. In fact, 40,000 US children each year have birthmarks that require medical attention. So it's important to consider all of your baby's birthmarks as they can have potential problems including:Wine birthmarks near the eyes and cheeks are sometimes related to vision problems such as glaucoma or developmental delay. (This is called Sturge-Weber syndrome.) Large hemangiomas, depending on their location, can interfere with a child's eating, vision, or breathing. Hemangiomas can sometimes grow inside, threatening the health of an organ in the body. Some people may be cosmetically disfigured. Birthmarks on the lower spine can extend beneath the skin and affect the nerves and blood flow to the spinal cord. Groups of 6 or more coffee-milk birthmarks could be a sign of an inherited disorder called neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1). Children with NF1 usually have these nodules at birth or by the time they are 2 years old, although the number of nodules can increase in childhood and sometimes later in life. About 50% of people with NF1 also have learning disabilities. Some particularly large moles present at birth increase the risk of becoming cancerous. Some prominent or disfiguring birthmarks can cause psychological harm to a child over time.
4. Can a child's birthmark be removed?
The removal of birthmarks depends on each specific case. Some of the birthmarks mentioned above (such as a hemangioma on the eye) may need to be removed.For many birthmarks, they may fade on their own without causing any physical problems, so your doctor may recommend waiting patiently rather than treating them if the birthmark is not disfiguring or causing other problems. physical problem. However, some experts say early intervention to treat certain birthmarks can be helpful because they don't go away on their own.
If your child is having a worrisome birthmark, talk to the doctor about treatment options.
5. Treatment Options
Depending on the birthmark, treatment options include surgery, laser treatment, and (in the case of certain hemangiomas) topical, oral, or injectable steroids, or topical or oral beta-blockers. Almost all surgical birthmark removal treatments can cause some scarring, according to dermatologist Seth Orlow, professor of pediatric dermatology at New York University School of Medicine.Whereas in the past, wine birthmarks could not be treated, the introduction of the first pulsed dye laser 25 years ago has revolutionized the management of these birthmarks, especially when they appear on the face.
6. How can I help my child deal with the shame of a birthmark?
The best way to deal with people who may be curious or make insensitive comments about your baby's birthmark is to talk to them directly. Most people don't mean insensitivity. If you notice someone pointing or staring at your baby, you can approach that person in a friendly manner and explain that your baby has a birthmark.When you think your child is old enough to understand, explain to him what a birthmark is, why others care about it, and how he can deal with comments.
If your child is attending daycare, preschool or school, talk to staff first to give them information about birthmarks and to communicate how your child feels about his or her appearance. young.
Involve your child's birthmark, especially large or disfiguring birthmarks, as it can make the child lack confidence. Getting information about that type of birthmark will help you feel better when discussing it with your baby's doctor. You may also find it helpful to talk to other parents who have children with similar birthmarks.
Children in the period from 6 months to 3 years old are very susceptible to respiratory problems, respiratory infections, skin diseases and gastrointestinal infections... parents need special attention attention to the care and provision of adequate nutrition for children. The pediatric department at Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for receiving and examining diseases that infants and young children are susceptible to: viral fever, bacterial fever, otitis media, pneumonia in children. With a system of facilities, modern medical equipment, sterile space, minimizing the impact as well as the risk of disease spread, Vinmec will bring satisfaction to customers. and is highly appreciated by industry experts with:
Gathering a team of leading pediatricians: Including leading experts with high professional qualifications (professors, associate professors, doctors, Master's degree), experienced, worked at major hospitals such as Bach Mai, 108.. The doctors are all well-trained, professional, conscientious, knowledgeable about young psychology. In addition to domestic pediatric specialists, the Department of Pediatrics also has the participation of foreign experts (Japan, Singapore, Australia, USA) who are always pioneers in applying the latest and most effective treatment regimens. . Comprehensive services: In the field of Pediatrics, Vinmec provides a series of continuous medical examination and treatment services from Newborn to Pediatric and Vaccine,... according to international standards to help parents take care of their baby's health from birth to childhood. Advanced techniques: Vinmec has successfully deployed many specialized techniques to make the treatment of difficult diseases in pediatrics more effective: neurosurgery - skull, stem cell transplant blood in cancer treatment. Professional care: In addition to understanding children's psychology, Vinmec also pays special attention to the children's play space, helping them to play comfortably and get used to the hospital's environment, cooperate in treatment, improve the efficiency of medical treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: babycenter.com













