This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Pham Thi Tuyet Mai - Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.The combined oral contraceptive pill is a temporary contraceptive that contains two female hormones, estrogen and progestin. This is an effective and widely used contraceptive method.
1. What is the combined oral contraceptive pill?
The combined oral contraceptive pill is a temporary contraceptive containing two hormones, estrogen and progestin. The combination of estrogen and progestin helps prevent ovulation, changes the lining of the uterus to prevent a fetus from growing, and changes the mucus in the cervix to prevent sperm from entering. Using the combined oral contraceptive pill requires the client to take the pill regularly. HIV-infected clients or HIV-infected partners can use the combined oral contraceptive pill, but it should be noted that this method of birth control does not prevent STIs and HIV/AIDS.Besides being known as a very effective method of birth control, the combined estrogen and progestin pill is also used to:
treat acne by inhibiting natural substances that cause acne fish; Limit physical and emotional premenstrual symptoms in women; Treatment of menstrual irregularities, anemia caused by heavy periods or severe menstrual pain; Actively postpone the menstrual period; Sometimes used to treat endometriosis.
2. How to use combined oral contraceptives
2.1. If you are not currently using birth control, start taking it within the first 5 days of your period or within 7 days of the abortion/miscarriage. At any time if you know for sure that you are not pregnant. Additional backup contraception (such as avoiding intercourse or using condoms) is needed for the next 7 days if: begins after the first 5 days of the menstrual cycle, or has no period, or starting from the 4th week postpartum if not breast-feeding and have not had a period. 2.2. If you are using hormonal contraception start taking the pill Immediately if you are using it continuously and correctly or if it is known for sure that you are not pregnant or at the time of repeating the injection.
2.3. If you are using non-hormonal contraceptives, start taking them within the first 5 days of your period. People who are using an intrauterine device can have the device removed at this time. At any time if you know for sure that you are not pregnant. If you start taking the pill more than 5 days after your period, you'll need to use extra contraception for the next 7 days. Women who are using an intrauterine device can have it removed during their next menstrual cycle.
How to use combined oral contraceptives:
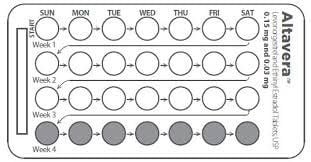
Take 1 pill a day, should be at a certain time to make it easy to remember, in the direction of the arrow on the pill pack (the pill pack should be dated to avoid forgetting). When the pack is finished, take the first pill of the next pack the next day even though you are still menstruating (with a pack of 28 pills) or take a break for 7 days and then continue taking the next pack, even if you are still menstruating (with a pack of 21 pills).
3. Women who should not use combined oral contraceptives
3.1. Absolute contraindications Pregnant or suspected of being pregnant. Breastfeeding within 6 weeks of giving birth. Older women (≥ 35 years old) and regular smokers ≥ 15 cigarettes/day. There are many risks of coronary heart disease (older age, smoking, diabetes, hypertension...) Hypertension: systolic BP ≥ 160 mmHg, diastolic BP ≥ 100 mmHg). Having or currently having cardiovascular and coagulopathy such as vascular disease, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, coagulopathy, ischemic heart disease, complex valvular disease, cerebrovascular accident Hereditary thromboembolism. If you are going to have surgery, you will need to lie down for more than 1 week. Migraine headache. Having breast cancer. Diabetes with complications (kidneys, nerves, retina, blood vessels). Have systemic lupus erythematosus and have antiphospholipid antibodies (or not tested). Existing severe liver disease with severe impairment of liver function such as active acute hepatitis, decompensated cirrhosis, liver tumor (except in cases of benign focal nodular hyperplasia). 3.2 Relative contraindications Are breast-feeding from 6 weeks to 6 months postpartum or not breast-feeding within 4 weeks postpartum. Elderly (≥ 35 years old) and smoke less than 15 cigarettes/day. Have or have high blood pressure: systolic BP 140 to 159 mmHg or diastolic BP 90 to 99 mmHg. Have had or are experiencing hyperlipidemia or high cholesterol from taking oral contraceptives. Have had breast cancer before and have not had a recurrence within the past 5 years. Medical treatment of gallstones or compensated cirrhosis Taking certain medications such as rifampicin/rifabutin, the antiviral drug Ritonavir-booster protease inhibitor, and certain anticonvulsants such as phenytoin , carbamazepine, barbiturates, primidone, topiramate, oxcarbazepine or lamotrigine.

4. Possible unwanted effects when using combined oral contraceptives
Menstrual disorders : Irregular periods: many women using oral contraceptives experience irregular periods, which will decrease and disappear after a few months of using the pill. Missed period: This is also a situation many women encounter when using birth control pills. Bleeding, heavy bleeding (from twice normal) or persistent (8 days or more) Headache: You may be prescribed a pain reliever by your doctor to relieve your headache or be advised to switch to Use another method of birth control or a non-estrogen birth control pill if you have a migraine or your headache gets worse. Nausea, dizziness: If you encounter this situation, you should take the medicine before going to bed or take it while eating. Chest tightness: You can try applying cold or warm compresses to your breasts. Some pain relievers such as aspirin, ibuprofen or paracetamol can be used but should be directed by a doctor. Pimples: You should take another type of birth control pill for at least 3 months if the client has been taking birth control pills for many months and the acne still does not decrease or increase. To be most effective at preventing pregnancy, you need to use another method of birth control if you vomit or have diarrhea while taking the pill. You should consult your doctor to prepare another method of contraception in case it is necessary. Continue your daily oral contraceptive pill even if you have an upset stomach, or do not think you are likely to become pregnant. Note: Do not stop taking the drug on your own.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.