This is an automatically translated article.
Traumatic brain injury is damage to the brain with many different causes. Besides diagnosis and treatment, rehabilitation of traumatic brain injury is extremely important.1. Sequelae of traumatic brain injury
Traumatic brain injury is a condition of brain damage due to traumatic causes, leading to disturbances in perception, cognition, movement, sensory perception and language.
Traumatic brain injury is divided into 2 main groups based on pathophysiology: primary injury and secondary injury:
Common types of primary injury: epidural hematoma, subdural hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage, intraventricular hemorrhage, intracerebral hemorrhage.
Common types of secondary injury: brain herniation, cerebral edema, cerebral infarction or cerebral ischemia after trauma.
2. What are the signs of a traumatic brain injury?
Symptoms of brain injury depend on the type of injury as well as the severity of the injury. Symptoms may appear immediately or develop slowly. People with a mild traumatic brain injury may have or lose consciousness for a short time.
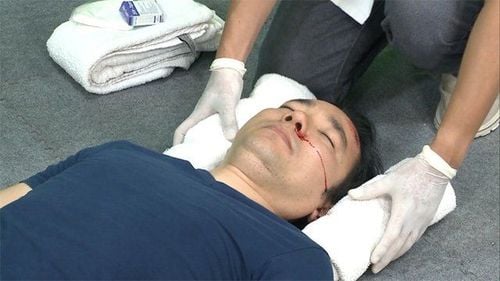
Other related symptoms may include headaches, behavioral disturbances, feeling lightheaded, dizziness, lightheadedness, ringing in the ears, and fatigue. Patients may also experience sleep and emotional disturbances, and trouble with memory, concentration, attention, or thinking.
Moderate or severe traumatic brain injury can cause severe headaches, vomiting, nausea, seizures, inability to wake up, dilated pupils, and slurred speech. In addition, severe weakness or paralysis, loss of coordination, increased confusion, or feelings of restlessness or agitation may also occur.

Đau đầu là triệu chứng liên quan đến chấn thương sọ não
3. Diagnosis of traumatic brain injury
To diagnose a traumatic brain injury, a doctor will perform a physical exam (especially through eye and pupil movements) combined with a basic examination to make an accurate diagnosis.
In addition, the doctor will use the Glasgow scale (range is from 3-15) used to decide the severity of a traumatic brain injury. Computed tomography (CT) of the brain is used to provide the initial assessment of moderate to severe traumatic brain injury.
4. How is traumatic brain injury treated?
For minor injuries, observation and treatment may relieve symptoms (eg, pain relievers for headaches).
During the first 24 hours of trauma, the patient should be awakened every 2 hours to check for signs of secondary injury. Elevating the head and using sedatives can help control symptoms.
When intracranial pressure increases and brain swelling, the patient will be functional monitoring and intravenous mannitol infusion. Severe or heavy bleeding may require interventional traumatic brain surgery (eg, craniotomy to remove blood clots).
The process of cleaning open wounds and washing internal lesions is necessary to help reduce the possibility of infection.
Phẫu thuật chấn thương sọ não can thiệp loại bỏ cục máu đông
5. Recovering from traumatic brain injury surgery
When the brain has been damaged, the daily routine is also greatly affected. To recover from a traumatic brain injury, patients and their families need to strictly follow the instructions of the doctors. For patients with severe trauma and slow recovery, care must always be taken to avoid problems such as joint mobility, skin ulcers, infections, and other physiological functions.
Experts in the rehabilitation industry have researched, proven that early mobilization of patients not only helps to limit secondary injuries, but also helps patients improve motor function as well as rapid cognition. than.
Exercise range of motion Guide the patient to turn on their own or help them change position if consciousness is still poor. Get the patient to sit up early, switch to a chair next to the bed, and practice standing and walking as soon as possible if hemodynamic status, consciousness and motor function allow. Instruct patients on breathing exercises and cough exercises to prevent respiratory complications. Increase contact and talk with patients to improve perceptual, cognitive and language status. Guide and support patients to perform functional motor exercises in bed, next to bed and walking function. Muscle tone control, balance and coordination, gait correction.
Rehabilitation for patients with brain injury takes a long time, and requires providing the patient with essential nutrients for the brain to recover optimally and positively. With traumatic brain injury, the general rule of thumb for the diet during traumatic brain injury recovery is: eat plenty of high-protein foods. Food sources rich in protein include: lean chicken, fish, legumes, cowpeas, peas...
Besides, patients also need to eat foods rich in vitamins and minerals, a Some nutrients are important for brain function like choline, which is important for the formation of neurotransmitters.
Once the patient has recovered from the acute condition, a phased rehabilitation program can be guided.
In the final stage, rehabilitation will help the patient achieve the maximum degree of independence when returning home, able to return to work suitable for his or her condition.
In April & May 2021, when there is a need for examination and treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury at Vinmec Phu Quoc International Hospital, customers will enjoy double incentives:
- Free specialist examination and Received the Rehabilitation Package
- Reduce 50% of the cost for customers with a prescription for post-examination treatment. The program is limited to the corresponding technique of each hospital and to customers who perform this treatment technique for the first time at Vinmec.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.