This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Huy Nhat - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.
Acute respiratory failure is a serious, life-threatening condition that requires prompt treatment.
1. What is progressive acute respiratory failure?
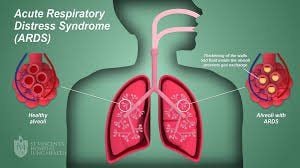
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) occurs when fluid builds up in the alveoli of the lungs. This amount of fluid interferes with gas exchange, causing the amount of oxygen in the blood to decrease, making the organs hypoxic and causing serious consequences.Advanced acute respiratory failure usually occurs in patients who are already severely ill, or have suffered severe trauma. Severe shortness of breath - the main symptom of acute respiratory failure, usually developing within hours to days after sudden trauma or infection.
Many patients with advanced acute respiratory failure did not survive. Mortality rates increase with age and severity of illness. Of the patients who survived acute respiratory failure, some were able to make a full recovery, while the rest faced persistent lung damage.
2. Symptoms of progressive acute respiratory failure

Severe difficulty breathing. Breathing hard or unusually fast. Hypotension. Unexplainably tired, or extremely tired. Advanced acute respiratory failure usually occurs after serious illness or trauma, and most patients have been hospitalized before.
3. Causes of progressive acute respiratory failure
The mechanism by which acute respiratory failure occurs is due to the amount of fluid escaping from the small blood vessels of the lungs, which overflows into the alveoli, where the blood exchanges oxygen. Normally, there is a protective membrane to prevent fluid from escaping from the lumen. Serious injury or illness can damage this membrane and cause fluid to leak out, causing acute respiratory failure.Common underlying causes of acute respiratory failure include:
Infection: The most common cause of acute respiratory failure is infection (a widespread and severe bacterial infection). Inhalation of Toxic Substances: Inhaling high concentrations of smoke or chemical vapors can cause progressive acute respiratory failure. Severe pneumonia: Severe cases of pneumonia usually affect all five lobes of the lungs. Head, chest or other serious trauma: Accidents (such as falling from a height, crashing a car, etc.) can directly damage the lungs or damage the area of the brain that controls breathing. Other causes: Acute pancreatitis, massive blood transfusion, burns,...
4. Risk factors for advanced acute respiratory failure
Patients with advanced respiratory failure are often hospitalized for serious illness, and the risk of developing acute respiratory failure is very high if sepsis occurs.Patients with a history of chronic alcohol abuse face a higher risk of developing acute respiratory failure, and are also more likely to die.
5. Complications of acute respiratory failure

Coagulation of blood vessels: Being on a ventilator during treatment increases the risk of intravascular coagulation. The clot can travel through the circulation to one or both lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. Pneumothorax: In most cases of acute respiratory failure, the treatment requires mechanical ventilation, but one of the complications of mechanical ventilation is causing pneumothorax. Infections: Ventilator patients face a higher risk of developing lung infections. Pulmonary fibrosis: Pulmonary fibrosis due to thickening of tissues and from scar tissue in the alveoli can occur several weeks after the onset of acute respiratory failure. Pulmonary fibrosis makes gas exchange ineffective. Thanks to modern treatments, patients with advanced acute respiratory failure can survive, but many patients suffer lasting damage and sequelae:
Respiratory problems: Many patients can make a full recovery, but there are some patients who suffer from breathing problems for the rest of their lives. Depression: The majority of patients who experienced acute respiratory failure reported that they also faced a depressive episode. Problems with memory and cognition: After acute respiratory failure develops, some patients develop memory loss and cognitive disturbances, which may fade over time or persist forever. far. Fatigue, muscle weakness: Long treatment time makes patients feel tired and weak.
6. Diagnosis of progressive acute respiratory failure

7. Treatment of advanced acute respiratory failure
The first goal of treatment for advanced acute respiratory failure is to improve blood oxygen levels.
Oxygen supply: To improve blood oxygen levels, patients can be given oxygen through a mask, with severe cases requiring mechanical ventilation. Control the amount of fluid in - out: The amount of fluid in and out of the body needs to be tightly controlled to achieve a balance. Treatment drugs: The commonly used treatment drugs in acute respiratory failure include: Drugs to prevent and treat infections. Analgesic. Anticoagulants. Medications to prevent gastric reflux. Sedative. Reference source: mayoclinic.org Doctor Nguyen Huy Nhat has many years of experience in the field of respiratory disease treatment at Hue Central Hospital, Hoan My General Hospital, .. before being a Doctor of Internal Medicine. General Hospital Vinmec Da Nang International
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.