This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Ho Viet Le Diem - General Internal Medicine, Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalDengue fever in adults is caused by the dengue virus, in which the Aedes mosquito is the main vector of transmission through bites. Most dengue patients can be treated on an outpatient basis. However, when the patient has serious signs such as: dengue shock, cerebral hemorrhagic fever... they need to be hospitalized for prompt treatment.
1. Dengue fever in adults: When to be hospitalized?
Dengue fever can mostly be treated and monitored on an outpatient basis. The main treatment includes: Antipyretic, anti-shock monitoring, intravenous fluids. Usually, dengue symptoms go away after 7-10 days. However, it is necessary to quickly bring the patient to the hospital when there are warning signs below:
Lethargy, lethargy, struggling for more than 3 days without improvement. Abdominal pain, liver pain. Vomiting more than 3 times/hour or 4 times/6 hours. Mucosal bleeding. The concentration of HCT increased, platelets decreased. Special attention should be paid to the following cases: Pregnant women, Patients with chronic comorbidities (Heart, liver, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hemolytic anemia. The doctor will perform serological tests including:
Dengue NS1 rapid test for NS1 antigen in the first 5 days of illness, IgM antibody from day 5 onwards; ELISA test for IgM, IgG antibodies Slow test such as: PCR test, virus isolation.
Chẩn đoán sốt xuất huyết ở người lớn bằng xét nghiệm ELISA
2. Treatment of dengue fever in adults
2.1. Symptomatic treatment Antipyretic: In case the patient has a high fever above 39 degrees Celsius, they need to take fever-reducing medicine, cool off with warm water and loosen clothes.
Note that the only antipyretic drug used is paracetamol, the dose is from 10 to 15 mg/kg body weight/time, every 4-6 hours. The total dose of paracetamol should not exceed 60mg/kg body weight/24h; Do not use aspirin (acetyl salicylic acid), analgin, ibuprofen to treat dengue because it can cause bleeding and acidosis.
Oral rehydration: Add more water and electrolytes to the patient through oresol or filtered water, fruit juice, diluted porridge with salt, smoothies, soup...
Infusion: Dengue fever Blood transfusions in adults are indicated when there are signs of: Lethargy, fatigue; Vomiting profusely; Stomachache; Hct increased; Can't eat or drink... The infusion time should not exceed 24-48 hours.
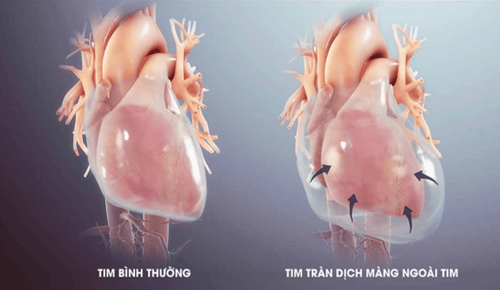
2.2. Dengue shock treatment Dengue shock occurs when the patient has too much extravasation, causing loss of plasma volume in the vessel. Dengue shock patients are often prescribed intravenous therapy. The infusion time stopped after 1 day, the patient was out of shock and showed signs of recovery.
In case the patient has stable clinical manifestations, clear pulse, warm extremities, good urine... or signs of threat of pulmonary edema, overload, the infusion can be stopped.
In case the patient has hemorrhagic fever with accompanying hemorrhagic shock, anti-shock therapy with electrolyte solutions (while waiting for erythrocyte sedimentation)

Sốt xuất huyết nếu không được chữa trị kịp thời sẽ dẫn đến những biến chứng nguy hiểm, dễ tử vong
2.3. Treatment of cerebral hemorrhagic fever Signs of cerebral hemorrhagic fever include: Convulsions, disturbances in consciousness or focal neurological signs. Principles of treatment of dengue in adults with cerebral form are as follows:
Elevate the patient's head to 30 degrees; Give oxygen cylinders; Anticonvulsant for the patient (if any); Treat hypoglycemia (if any); Correction of electrolyte disorders - acid-base; Anti-cerebral edema: indicated when the patient has clinical signs of increased intracranial pressure: Intubation, mechanical ventilation: increase ventilation to keep PaCO2 30-35 mmHg; Paracetamol 10-15mg/kg/time, 4 times a day if there is fever.
3. Notes when treating dengue fever in adults
When treating dengue at home, absolutely do not self-infuse because it can lead to dangerous risks such as edema, allergic shock, respiratory failure... Indication for infusion and drug use Absolutely follow the doctor's instructions.
The 4th day of illness is the most dangerous time because serious complications such as dengue shock, high fever, cold hands and feet, vomiting, blood in the stools may appear... Patients should be closely monitored. and take them to a medical facility promptly when there are serious signs.
Hospital discharge criteria: The patient is fever free for 2 days, awake; Pulse, blood pressure normal; No dyspnea or respiratory failure due to peritoneal or pleural effusion; Platelet count tends to recover > 50,000/m2.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.