This is an automatically translated article.
Hormonal contraceptives work to delay the menstrual cycle. If there is a reason why you need to limit your period, go to the hospital for advice on choosing the right method.
1. What is the difference between continuous and prolonged contraception?
To delay the menstrual cycle, people use the following two methods of hormonal contraception:
Continuous contraception: The use of hormonal contraception without a break for a year or longer. You do not have a period because of continuous use of hormonal contraceptives, Extended Contraception: Is using hormonal contraception for longer than 21 days, as opposed to conventional oral contraceptives. However, throughout the year, you periodically stop using it, when your period occurs.
2. What hormonal contraceptives can be used to delay menstruation?
Depending on your goals, preferences and health conditions, choose different types of hormonal contraceptives:
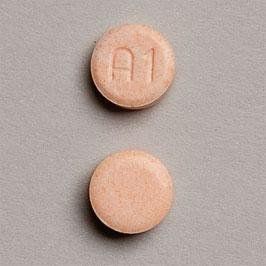
2.1. Birth control pills Estrogen-progestin-containing birth control pills can be used to delay prolonged or continuous menstruation by skipping the placebo and using the pills in the new pack. In addition, there are now several types of birth control pills specifically designed to delay menstruation:
Jolessa: Use Jolessa by taking hormone pills continuously for 84 days or 12 weeks, followed by followed by a week of placebo pills. Thus, menstruation will occur at week 13, about every 3 months. Amethia, Camrese, and Simpesse: Take a hormone pill for 84 days or 12 weeks, followed by a week of a pill that contains very low levels of estrogen. Taking low-dose estrogen pills instead of a placebo helps reduce bleeding, bloating, and other side effects. Rivelsa: Take the hormone pill for 84 days, or 12 weeks. Each tablet contains a constant dose of progestin but an increased dose of estrogen, starting with 20 micrograms (mcg), increasing to 25 mcg and to 30 mcg at three different times during the pill period. Then, take a very low dose of estrogen for the next 1 week. Menstruation will occur at week 13, about every 3 months. The gradual increase in the estrogen content in Rivelsa helps to reduce sudden bleeding during the first cycle of use compared to other drugs. Amethyst: It contains low doses of progesterone and estrogen and is designed to be taken continuously for a year. There is no time off from taking placebo pills or low-dose hormones.

Các thuốc tránh thai chứa estrogen-progestin có thể được sử dụng để trì hoãn kinh nguyệt
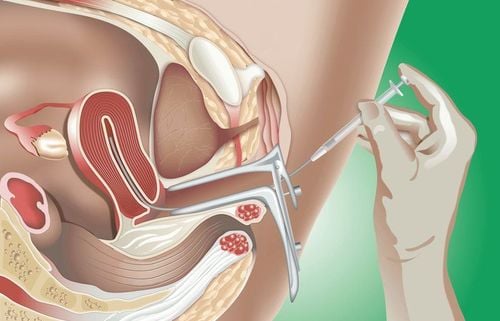
2.2. Vaginal ring (NuvaRing) Like the combined estrogen-progestin pill, you can delay or stop your period with prolonged or continuous use of the IUD:
Hormonal IUDs (Mirena, Liletta) , Kyleena, ...) The hormonal IUD is a long-term form of contraception. Once placed in the uterus, it continuously releases a progestin into the body and stays in place for up to 5 years. The hormonal IUD comes in different dosages. Over time, the frequency and duration of menstrual bleeding will decrease. However, the higher dose IUD (52mg levonorgestrel) was more effective at stopping menstruation altogether. Specifically, after the IUD was inserted with a dose of 52mg levonorgestrel, 20% of women no longer had periods. This number increases to 30 - 50% after 2 years.
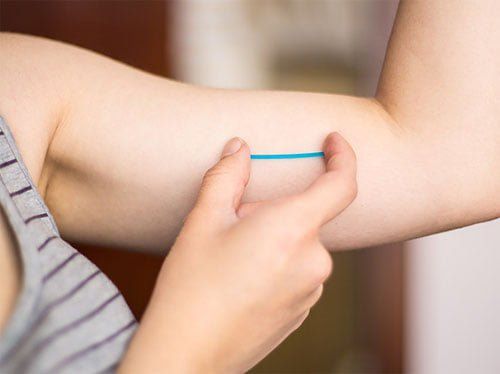
DMPA injection (Depo-Provera) Injection of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) - a 90-day cycle progestin that provides long-term contraception and reduces the frequency or stops menstrual periods altogether. After one year of DMPA injection, 50-75% of women no longer menstruate. The longer you use DMPA, the more likely you are to stop menstruating.
3. What are the benefits of delaying menstruation?
Delaying menstruation works to control unpleasant symptoms caused by menstruation. It is worth considering to use if you:
Have a lot of trouble using tampons (uncomfortable, misaligned causing blood to spill out, ...) Have health problems worsening worsening of periods such as endometriosis or anemia Breast tenderness, bloating, or mood swings 7-10 days before menstruation Headache or other menstrual symptoms during the week of taking the pill placebo Heavy, prolonged and often painful menstruation Or you simply feel uncomfortable when you have your period. Personal reasons like wanting to delay your period come after an important exam, a sporting event, a vacation or a special occasion like a wedding or honeymoon.

Trì hoãn kinh nguyệt có tác dụng kiểm soát các triệu chứng khó chịu gây ra bởi kinh nguyệt.
4. Is delaying menstruation safe for all women?
After medical examination, necessary tests are done and it is concluded that hormonal contraceptives can be used, delaying your period is safe for you. However, delaying menstruation is controversial. Even the doctors who support this option won't mention it unless you're the one suggesting it. If you want, discuss with your doctor to make the right choice.
5. What are the limitations of delaying menstruation?
Sudden menstruation can occur during the first few months of using birth control. However, this will decrease over time, as the body adapts to the contraceptive being used.
Pregnancy can be difficult to notice when regular menstrual periods are delayed. If you experience morning sickness, breast tenderness or unusual tiredness, you should take a home pregnancy test or consult your doctor.
6. What to do when you have a period suddenly?
Menstruation comes on suddenly, often decreasing over time. To minimize this, you need to do a few things:
Stay on schedule: Missing a pill, forgetting to change your vaginal ring, or setting a late DMPA injection schedule increases the chance of sudden bleeding. Monitor sudden bleeding in a calendar or diary: Often, careful monitoring helps you assess sudden bleeding. Go back to regular birth control: You'll probably have less breakthrough bleeding if you don't try to delay your period by skipping weeks of the placebo pill. Quit smoking: Women who smoke are more likely to experience breakthrough bleeding than women who don't smoke. If you use the estrogen-progestin birth control pill or the vaginal ring, taking it occasionally on placebo days can help control unexpected bleeding. As long as you've been using hormonal birth control for at least 21 to 30 days, you can stop taking the pill or remove the ring whenever there's sudden bleeding. After 3 or 4 days of being hormone-free, start taking the pill again or reinsert the ring. Over time, sudden episodes of bleeding should go away and eventually stop.
Bleeding is not a sign that birth control isn't working. Remember to continue using birth control even if you have bleeding to reduce your risk of an unwanted pregnancy. If bleeding is heavy or lasts more than 7 days in a row, contact your doctor.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. examination and treatment at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: mayoclinic.org
SEE MORE
Natural contraception by calculating ovulation What you need to know about contraception while breastfeeding Popular methods of postpartum contraception