This is an automatically translated article.
Postpartum infection is a common obstetric complication due to many reasons, from medical facilities to inadequate infection control procedures, adversely affecting the health of the mother and even the life of the mother.1. What is postpartum infection?
Postpartum sepsis is an infection that occurs in a woman postpartum from the genital tract (vagina, cervix, uterus) during the first 6 weeks postpartum. Some common pathogenic bacteria such as: Staphylococci, streptococci, anaerobes such as Clostridium, Bacteroides...Favorable factors causing postpartum infection in pregnant women such as: Poor nutrition , anemia, pregnancy toxicity, premature rupture of membranes, prolonged labor, fluid closure, procedures such as placenta removal, uterine control...
Common forms of postpartum infection are sepsis perineum, vulva, vagina; endometritis, metritis and peritonitis, pelvic peritonitis, generalized peritonitis, sepsis, thrombophlebitis.
2. Consequences of postpartum infection
The consequences of postpartum infection depend on the type of postpartum infection:2.1. Infections of the perineum, vulva, and vagina Pregnant women who have non-sterile perineal stitches, incorrect technique or no sutures, and gauze left in the vagina are at high risk of infection. perineal. As a result, the site of infection is swollen, red, painful, festering, and the discharge does not smell.
Treat perineal infections with local care: wash with antiseptics; cut thread when festering, close sanitary loincloth, sterile gauze.
2.2. Inflammation of the lining of the uterus
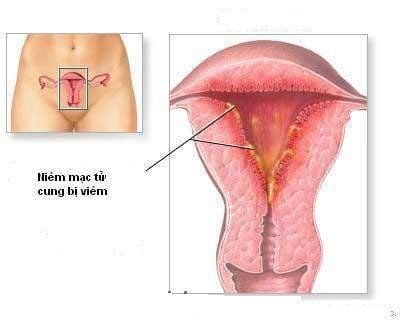
Nguyên nhân gây viêm niêm mạc tử cung :Sót rau, sót màng, nhiễm khuẩn ối, thủ thuật kiểm soát tử cung, bóc rau nhân tạo không vô khuẩn
Consequences of endometritis:
The mother has a fever of 38-38.5oC (a few days after giving birth), fatigue, discomfort. The discharge is profuse, foul, mixed with pus... The cervix is dilated, the uterus is slow to contract, and the uterus is painful. The more severe form of endometritis is total inflammation of the uterus. The inflammatory process spreads to the muscular layer of the uterus, there are small abscesses. Clinical symptoms are more severe than endometritis, easy to cause peritonitis or bacteremia. 2.3. Inflammation of the uterus and around the uterus Inflammation of the uterus, inflammation of the uterus, causing the mother to have a fever 8-10 days after giving birth, other symptoms such as pelvic manipulation see a soft, painful mass, unclear border, limited mobility inhibited, profuse, foul-smelling, slow-closing cervix; slow contraction of uterus.
Pathological progression depends on each case, the disease can be cured with active treatment with a response or become pelvic peritonitis. Treatment measures are for the mother to lie down, apply ice and use appropriate antibiotics; In case the infection has formed a pus pocket, the pus bag must be punctured and drained through the sac with the vagina, if there is no response, the uterus must be removed and antibiotics are used in accordance with high doses intravenously.
2.4. Pelvic peritonitis The inflammatory process is not localized to the uterine lining, but develops into the pelvis and forms pseudomembranous tissues in the pelvic organs and causes adhesions. The reaction of the peritoneum will produce pockets of fluid mixed with blood and pus.
Women with pelvic peritonitis will have more aggressive signs than endometritis. Body temperature gradually increased from 39-40 degrees Celsius, shivering, fatigue, dirty tongue. The disease can be cured with aggressive treatment but can also develop into generalized peritonitis.
2.5. Generalized peritonitis Generalized peritonitis occurs most often due to non-sterile cesarean sections, after endometritis and systemic inflammation of the uterus that are not well treated. After performing obstetric procedures, placental abruption and uterine control; At the same time, it can also be caused by bacteria spreading from pus-filled disease in the fallopian tubes causing peritonitis.
Symptoms of total peritonitis manifest after the mother gives birth about 7-10 days or after a cesarean section about 3-4 days with signs such as:
Dry lips, dirty tongue, sunken eyes Having toxic syndrome , infection The stool may be loose and foul-smelling, with abdominal wall reaction or peritoneal palpation, but often unclear. Abdominal X-ray is unprepared and shows dilated bowel loops, fluid levels, and levels. a little bit; Electrolyte tests record Ca++ components. Cl- decrease . Note the need for differential diagnosis with pelvic peritonitis, functional bowel paralysis. Treatment includes appropriate systemic antibiotics, fluid and electrolyte replacement, partial hysterectomy, and abdominal lavage and drainage.
2.6. Sepsis Sepsis is the most severe form of postpartum infection. Pregnant women with sepsis have systemic symptoms such as:
Continuous high fever, fluctuating temperature, accompanied by high fever with chills, body fatigue. Signs of infection, toxicity: Dry lips, dirty tongue, difficulty breathing, yellow skin, dark urine. Dangerous complications of sepsis:
Functional kidney failure Interstitial nephritis, lung abscess, endocarditis Brain abscess, meningitis,... Prognosis depends on the foci of secondary infection and the Is the treatment correct and timely?
2.7. Thrombophlebitis Thrombophlebitis is common in pregnant women, prolonged labor, obstructed blood vessel (venous system) circulation, fibrin proliferation.
Pregnant women with thrombophlebitis often have symptoms that appear late, 12-15 days after giving birth, common signs are:
Mild fever, chills, rapid pulse. If thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities, the legs are edematous, white, painful, and the heels cannot be lifted off the bed. If not treated promptly, can cause pulmonary embolism, kidney and possibly death.
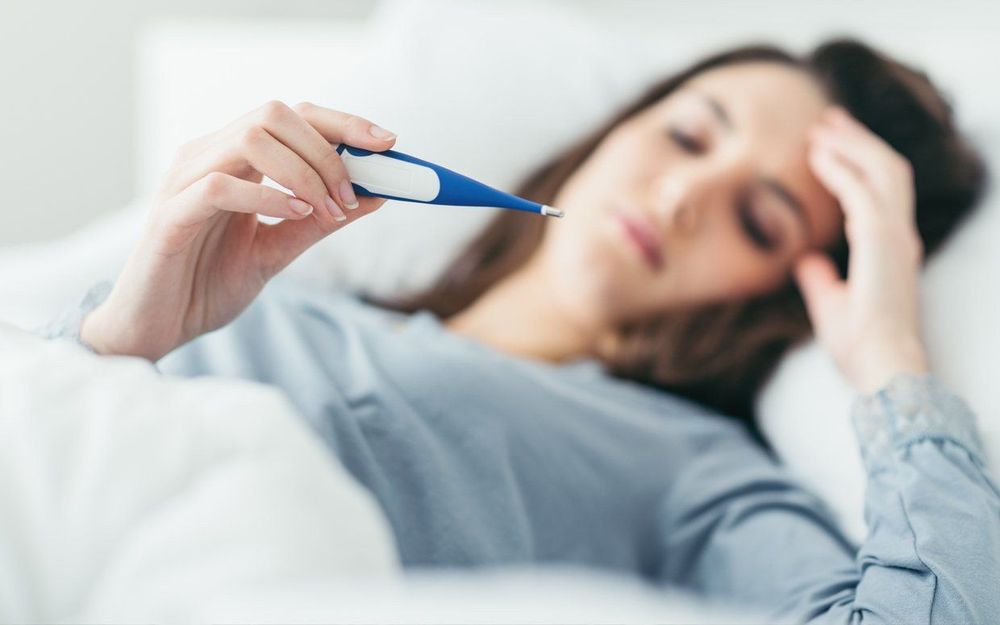

Sản phụ bị viêm tắc tĩnh mạch thường có triệu chứng xuất hiện muộn, sau đẻ 12-15 ngày, sốt nhẹ là dấu hiệu thường gặp
3. Prevention of postpartum infections
Pregnant women should pay attention to the treatment of inflammatory foci during pregnancy: Inflammation of the urinary tract, genitals... Prevention of amniotic infection and prolonged labor. Childbirth: Do not leave vegetables, strictly adhere to the indications for uterine control, aseptic and hygienic regimen. Postpartum: Avoid holding the fluid, clean and take care of the perineum according to the correct procedure.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.