This is an automatically translated article.
Hepatitis is an infectious disease, mainly affecting the liver, caused by hepatitis viruses. Chronic viral hepatitis mostly progresses silently, in the early stages there are often no symptoms, when the disease is discovered, it has turned into cirrhosis.
There are many viruses that cause hepatitis including Hepatitis A Virus (HAV), B (HBV), C (HCV), D (HDV), E (HEV), G(HGV) , in addition to some viruses also damage the liver but are not classified as hepatotropic viruses such as CMV, EBV,... in which Viruses A, B, and C are the most common. Hepatitis can be caused by one virus or by co-infection with two or three different viruses.
1. Hepatitis caused by the hepatitis A virus
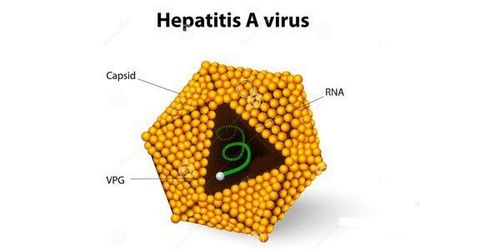
Virus viêm gan A
HAV was discovered in 1973. The virus is transmitted through food or water contaminated by contaminated food or water, found in the feces of patients. Therefore, the disease often occurs in places where sanitation is not guaranteed. Maintaining good hygiene, especially washing hands before eating and after using the toilet is one of the best and most economical ways to limit hepatitis A virus infection. Currently, in our country there is a vaccine to prevent hepatitis A virus. Most HAV infections have no clinical symptoms. Hepatitis A usually has a benign course, does not turn chronic, and goes away completely, but you can still get reinfected with HAV, causing hepatitis A to re-infect.
Trắc nghiệm: Làm thế nào để bảo vệ lá gan khỏe mạnh?
Làm test trắc nghiệm kiểm tra hiểu biết về gan có thể giúp bạn nhận thức rõ vai trò quan trọng của gan, từ đó có các biện pháp bảo vệ gan để phòng ngừa bệnh tật.2. Hepatitis caused by hepatitis B virus (HBV)
Virus viêm gan B (HBV)
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), around 380 million people worldwide have been infected with hepatitis caused by HBV. HBV is a small virus. Unlike other viruses whose nuclear acid is RNA, the only hepatitis virus whose nuclear acid is DNA. Viruses have two different forms: Wild form (WIld form) and mutant form (Mutation form). Hepatitis B virus is transmitted through blood (transmitted through blood transfusion, sexual intercourse, sharing needles, needles, tattoos, piercing,...)
After being infected with the virus, about 10% of people Infection begins with acute hepatitis, the rest are asymptomatic, progressing silently. This is a source of dangerous disease for the community. The younger the age of infection, the greater the rate of chronic infection. Over time, the disease can progress to cirrhosis, liver failure and eventually hepatocellular carcinoma.
3. Hepatitis caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV)
Virus viêm gan C (HCV)
HCV was found in 1989. Like the hepatitis B virus, the hepatitis C virus is also transmitted through blood. HCV has genetic diversity (Researchers have detected at least 6 genotypes and 50 subtypes) so that the virus has the ability to evade the host's immune responses leading to high rates of infection. Chronic HCV infection rate is high > 80% of infected people.
After the treatment is cured, the body cannot create an immune response, so the patient can still be re-infected with HCV. Among patients with acute hepatitis C infection, approximately 50% to 70% develop chronic hepatitis. Chronic HCV infection is one of the risk factors for cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Combined infection with HCV and HBV increases the risk of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma more than infection with one virus. Currently, there is no vaccine against HCV-induced hepatitis, which is due to the lack of suitable cell culture systems and genetic diversity.
4. Hepatitis D Virus (HDV)
HDV was discovered in 1977. This is an incomplete virus, HDV has only an RNA nucleus and an envelope of HBsAg (HBV Surface Antigen). HDV must have HBsAg to become a complete virus to cause disease. Therefore, HDV to cause disease must be co-infected with HBV (HDV and HBV infect the host at the same time) or superinfect with HBV (HBV host body is infected with HDV), never now has an independent HDV infected host. If the patient is coinfected, there is a high risk of developing malignancy, and superinfection is at risk of chronic hepatitis. The HBV vaccine also helps the body to prevent HDV infection.
5. Hepatitis E Virus (HEV)
Virus viêm gan E (HEV)
HEV was found in 1991. The route of transmission of the hepatitis E virus is the same as that of the hepatitis A virus, the E virus is found in the feces and bile of an infected person and is excreted in the feces.
The disease usually has a benign course and is completely cured. Unlike normal people, in pregnant women, if infected with HEV, there is a high risk of becoming malignant hepatitis virus, high mortality rate. The virus has 1 serotype, so after getting sick, the body creates an immune response and is not re-infected.
New virus discovered in recent years. In the composition similar to HCV up to 25%, however, we still do not fully understand the agent and role of HGV, so there is no vaccine to prevent the disease.
Hepatitis virus replicates in the body mainly in liver cells, affecting the function of liver cells. The disease gradually causes cirrhosis of the liver and can turn into hepatocellular cancer, so the disease should be detected and treated as early as possible for those at high risk of exposure such as wastewater treatment workers, injecting drugs,... Viral hepatitis can be prevented by limiting exposure, by vaccination.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has Hepatobiliary Screening packages, which help detect Hepatitis Virus at an early stage even when there are no symptoms. In addition, the comprehensive hepatobiliary screening package helps customers:
Assess the liver's ability to work through liver enzyme tests; Evaluation of bile function; vascular nutrition; Early screening for liver cancer; Perform tests such as Total blood cell analysis, blood clotting ability, screening for hepatitis B, C Assessment of hepatobiliary status through ultrasound images and diseases that have the potential to affect liver disease/cause liver disease. more severe liver disease In-depth analysis of parameters to evaluate hepatobiliary function through laboratory, subclinical; the risk of affecting the liver and early screening for hepatobiliary cancer
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.