This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Vo Thien Ngon - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Danang International HospitalCurrently, the incidence of urinary tract stones accounts for about 2-12% of the population, Vietnam is located in the region of countries with high rates of stones. There are many different types of urinary tract stones, each with different treatment and coping strategies.
1. Classification of urinary tract stones
There are many ways to classify stones. Below are two ways to classify stones that are commonly used in clinical practice.1.1 Classification based on the characteristics and properties of stones
This classification of stones is important to be applied in treatment, giving appropriate treatment methods.
Classification by location of stones:
Kidney stones: Including pyelonephritis, pyelonephritis, calyces, coral stones and semi-coral stones. Ureteral stone : Subdivided into 1⁄3 upper, 13 middle, and 1⁄3 lower. Bladder stones Urethral stones 1.2 Classification based on the chemistry of stones
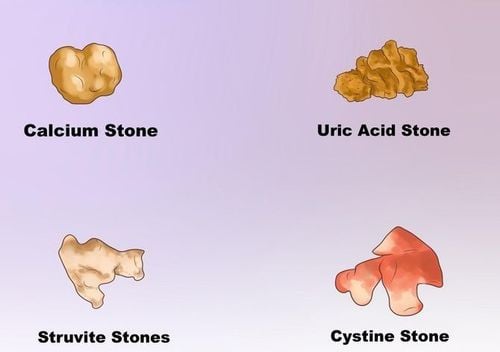
Includes 2 types of stones: inorganic stones and organic stones
Inorganic stones
Calcium oxalate stones: are the main stones, common in Vietnam accounts for > 80% Calcium phosphate stones: Light yellow or dirty white and fragile Calcium carbonate stones: Milky white, fragile. Organic stones
Urate stones: Common in people with hyperuricemia, gout patients. Systin stones: Smooth pale yellow, often recurrent Struvite stones: White yellow, usually due to urinary tract infection
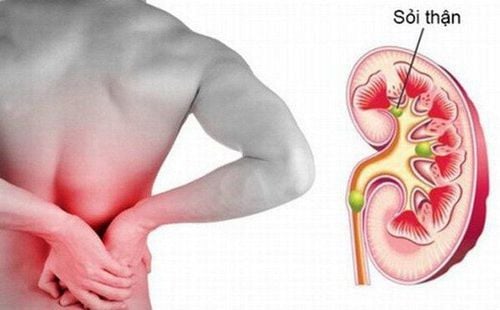
2. Symptoms of urinary tract stones
Chronic lumbar pain: Pain feels heavy, uncomfortable pain in the lower back on one or both sides, pain increases when moving. Acute pain: Typically renal colic, pain appearing suddenly after work, pain from the waist spreading down to the groin and genitals, severe pain without anti-pain posture. Kidney stones fall into the ureter causing ureteral stones. Hematuria: The patient may urinate with light red water like meat wash. Stone in urine: Uncommon but of diagnostic value. Pyuria: The urine is cloudy, seen in patients with pyelonephritis. When there is a urinary tract infection caused by stones causing fluid retention, the symptoms are: High fever, chills, painful urination, frequent urination, headache, vomiting and nausea. Symptoms of bladder stones : Usually caused by urethral stones falling down.
The prominent symptom is urinary incontinence: The patient is urinating suddenly the urine becomes blocked and painful. Diarrhea Painful and bloody urination at the end of the beach. Symptoms of urethral stones
Difficulty urinating, maybe the patient has acute urinary retention. Urination Bitter pee at the top of the beach
3. Treatment of urinary tract stones
Treatment depends on the location and size of the stone to choose the appropriate treatment method.
3.1. Treatment of kidney stones and ureteral stones
Medical treatment in case:
Stone size is less than 5mm, kidney function is still good, ureteral circulation is good The stone has not caused complications, the whole body is not too weak, there is no chronic disease Treatment: Use relaxants smooth muscle, increase exercise, drink a lot of water Medical treatment when there are complications
In case of large stones, affecting kidney function The patient's condition is weak. Do not use surgical methods. Treatment: antibiotics, anti-inflammatory pain relievers, muscle relaxants. Treatment Open surgery: in the world at present, it is rarely applied, but in Vietnam, because it is often late in serious condition, it is still often applied.
When there are many coral stones Occurrence in the lithotripsy method. Stones with narrowing of the urinary tract. Treatment methods include: Open the renal pelvis, open the ureter to remove stones, drain the kidney when there is pus, remove the kidney when kidneys no longer function. Treatment of less traumatic methods: An effective method widely applied in the world, including:
Extracorporeal lithotripsy: Applied when kidney stones or ureteral stones < 2cm, kidney function in good condition, normal renal pelvis and ureteral circulation, no renal pathology such as renal tumor... Lithotripsy through ureteroscopy with laser lithotripsy source: Apply when stones are < 2 cm, kidney function is still good . Percutaneous stone removal: Coral stone, kidney stone or 1⁄3 stone on the ureter with urinary tract malformation. Retroperitoneal endoscopy to remove stones: With stones larger than 1cm, or failed treatment with the above methods. 3.2 Treatment of bladder stones Medical treatment: Small, new stones falling from the ureter, using antibiotics, anti-inflammatory pain relievers, muscle relaxants. Treatment with minimally invasive methods Endoscopic stone removal: When the stone is small < 3cm, no stones can be urinated
Surgical treatment: Indicated when the stone is > 3cm large, bladder stones with diseases causing urethral stricture, Prostate tumor ... 3.3 Treatment of urethral stones Based on the location of the stones to have the appropriate treatment
Stones in the anterior urethra: Pick up the urethral stones through the mouth of the flute The stones in the posterior urethra push back into the bladder Bladder stones and treatment like bladder stones Surgery is applied when: Stones stuck in the urethra cannot be picked up and cannot be pushed into the bladder, stones in bladder diverticulum or urethral stricture.
4. How to deal with urinary tract stones
Drink enough water every day With calcium oxalate stones: Control calcium consumption < 900mg per day, provide enough vitamin D For uric acid stones: Urate stones will dissolve in an alkaline environment, so people with urate stones need to limit foods that cause urine acidification such as meat, fish, eggs... increase the use of foods that cause urine alkalinization such as carbonated drinks, green vegetables, potatoes, and fruits. Regular exercise and sports avoid the deposition of stones. Urinary tract stones cause many complications that affect kidney function, so proactively prevent stones and have regular health check-ups to detect stones early to take treatment measures to avoid too late causing serious complications. masonry.
Currently, at Vinmec International General Hospital, all of the above-mentioned methods of treating urinary tract stones are performed at Vinmec International General Hospital. Customers who choose to treat urinary tract stones at Vinmec will have the following benefits:
Being screened, diagnosed and selected by a team of leading nephrologists in the industry. The doctors perform the treatment techniques proficiently and experienced. Modern equipment system and continuous investment to update the latest medical advances in the world. After treatment, the patient will be consulted by the doctor with all the measures to minimize the recurrence of stones.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.