This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Dang Tien Dat - Doctor of Odonto-Stomatology - Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.Dental pulp disease is a fairly common condition today, in which the symptoms of toothache and tooth loss in young people are often caused by pulpitis. Understanding dental pulp disease will help to effectively treat and prevent the risk of affecting the pulp.
1. Causes of tooth pulp disease
The pulp is a connective tissue consisting of blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves, and plays a role in nerve transmission and tooth nourishment. The pulp chamber and canal system are located in the pulp cavity, surrounded by the hard dentin tissue of the tooth, while the apical foramen is outside this limit. Because of the unique characteristics of the anatomical structure of the tooth pulp, when the pulp is inflamed, it is easy to appear congested, causing pain and even pulp necrosis.Pulp pathology is a fairly common condition, usually inflammation of the histological components of the pulp stem from complications of caries. If tooth decay is not treated properly and promptly, bacteria that stay in the mouth for a long time will enter the tooth with an open pulp through the deep holes and cause disease.
In addition, some other common causative factors of dental pulp disease are:
Bacteria causing pulpitis, periodontitis; Chemicals such as mercury poisoning, lead poisoning; Physical trauma cuts off the blood vessels that feed the tooth pulp; Broken or chipped teeth, excessive tooth wear; Ambient pressure changes suddenly. Due to some improper dental treatment such as: Grinding teeth into or too close to the pulp chamber, grinding teeth with insufficient water will cause the temperature to rise, causing death of the pulp.
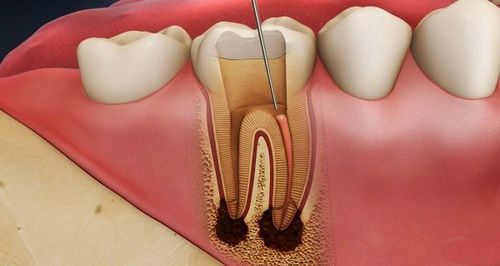
2. Diseases of the tooth pulp
2.1. Reversible pulpitis Reversible pulpitis is a mild inflammation of the pulp tissue resulting from undetected and untreated caries. Patients may not show any symptoms, if they do, it is usually the natural teeth that are sensitive to hot or cold stimuli, sweet or sour foods, causing a transient sensitivity (lasting only a few seconds). to several tens of seconds), then completely disappear when the stimulus is no longer available.In terms of clinical practice, dentists are quite rare cases of patients with reversible pulpitis, because this is the initial mild stage and there is no evidence. Although patients often come to the doctor when the pulpitis has progressed, the sharp pain caused by the pulpitis can still be restored to normal if it is treated promptly and actively, as well as. thoroughly eliminate the factors that cause inflammation.
2.2. Irreversible pulpitis Irreversible pulpitis is divided into two types, painful or painless. The typical myelitis of painful irreversible pulpitis is:
Spontaneous pain; Pain radiating to the head and face on the same side; Pain over one area, patients often do not accurately identify the painful tooth; The pain may last for hours or be as short as a few minutes; Pain that is aggravated by hot/cold stimuli or position changes. For painless irreversible pulpitis, through clinical examination, a tooth with an open pulp can be seen with a deep hole or a dark red, yellow-speckled mass protruding from the pulp chamber.
2.3. Acute pulpitis Typical symptoms of acute pulpitis include:
Prolonged spontaneous pain, often occurring at night and especially when the patient lies down; Pain when stimulated by temperature changes, or food falling into wormholes; Pain may be sharp or dull, localized or diffuse, intermittent or continuous. After the pain is over, the patient will return to normal activities. However, if acute myelitis is accompanied by pus, the patient will experience more intense pain, specifically:
A pulsating pain; There is a feeling of drumming in the ear; The painful tooth is slightly loose and protrudes higher than the remaining teeth. 2.4. Chronic Myelitis Chronic myelitis, common in young adults, is caused by mild but persistent stimuli acting on vascularized pulp tissue.
The pain characteristic of chronic myelitis is usually spontaneous, dull, intermittent, lasting for hours, and the interval between each pain is very short. Sometimes patients only experience a slight pain when chewing, other than that there are no other symptoms.
If the examination will detect a red spot growing between the crown of the tooth, when the dentist uses a probe to poke the tooth with the pulp, it will cause the patient a little pain, but the blood will bleed a lot.
2.5. In fact, patients with pulp necrosis will have no pain symptoms, sometimes after experiencing a history of sharp pain. Through clinical examination, hard tissue damage can be seen, pain appears only when the inflammation has spread to the root of the tooth.
3. Complications of myelitis
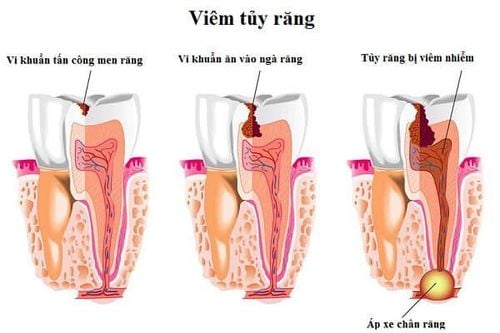
Necrosis, death and pulp rot; Inflammation around the apex and root apex; There is an abscess around the apex of the tooth; Inflammation of lymph nodes, connective tissue and jawbone; Granulomas and root cysts; Loss of teeth, loss of teeth; Distant complications such as maxillary sinusitis and Osler endocarditis. Therefore, patients need to go to the dentist immediately for examination and treatment when detecting teeth with large cavities, physical trauma or abnormal discoloration, accompanied by signs of pain. If the pulp disease is not treated in time, it will progress gradually through the stages of acute pulpitis, chronic pulpitis and then necrosis. The pulp necrotic tooth can escape through the apical foramen or gather at the root, causing more serious complications.
When having problems with the tooth pulp mentioned above, patients can go to Vinmec International General Hospital for examination and treatment. Here, there is a team of well-trained and experienced Dental - Jaw - Facial specialists, complete and modern medical equipment system, professional service quality, helping to improve the diagnostic efficiency. diagnosis and treatment, bringing satisfaction to the patient.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.