This is an automatically translated article.
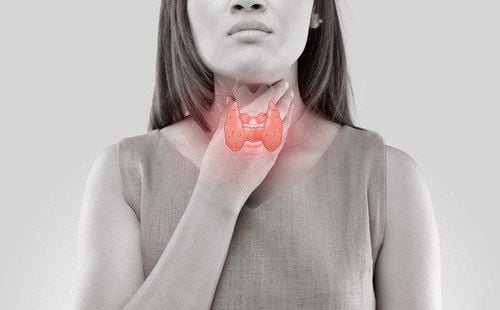
The thyroid gland is an extremely important endocrine gland of the body, playing an essential role in metabolism and growth. Any abnormality of the thyroid gland has a significant effect on the patient.1. What is thyroid disease?
The thyroid gland is located in the front of the neck (located in front of the windpipe) and has the function of secreting, storing and releasing two hormones: T4 (Thyroxine) and T3 (Tri-iodo-thyronine). Thyroid disorders can be the cause of producing too much or too little hormone. Women at risk for thyroid disease include those who have or have had an autoimmune disease (such as diabetes).2. What is the function of the thyroid gland?
The thyroid gland controls the body's metabolism. When the thyroid gland is working properly, the metabolic rate in the body is always stable, not too fast or too slow.The main control of the thyroid gland is the pituitary gland (a gland located in the brain). The pituitary gland produces thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which tells the thyroid gland to release the hormone when needed.
Trắc nghiệm: Loại bỏ tin đồn và tìm hiểu sự thật về bệnh suy giáp
Suy giáp là một hội chứng chứ không phải căn bệnh riêng biệt. Tuy nhiên, vẫn còn rất nhiều thông tin gây tranh cãi về bệnh suy giáp. Hãy cùng trả lời 8 câu hỏi sau để phá vỡ một số nghi ngờ về bệnh lý này nhé!
Nguồn tham khảo: webmd.com
3. How is thyroid disease diagnosed?
Diagnosis of thyroid disease is based on symptoms, physical examination, and laboratory tests. The symptoms of thyroid disease are easy to confuse with symptoms of other health problems.When swallowed, the thyroid gland moves, making examination easier. Therefore, doctors often ask patients to swallow during clinical examination. In addition to a thyroid exam, your doctor will likely do a skin and eye exam, and check your weight and body temperature.
4. Tests to diagnose thyroid problems
The following tests can help find the exact cause of a thyroid problem:Blood tests Thyroid ultrasound Thyroid scan Thyroid scan In a thyroid scan, the patient is given a small amount of an isotope Radioactive iodine. There will be a special camera that detects these areas of the thyroid absorbing radioactive iodine. Scans show areas of the thyroid gland that are either decreased or overactive. Thyroid scan is not indicated for pregnant women.
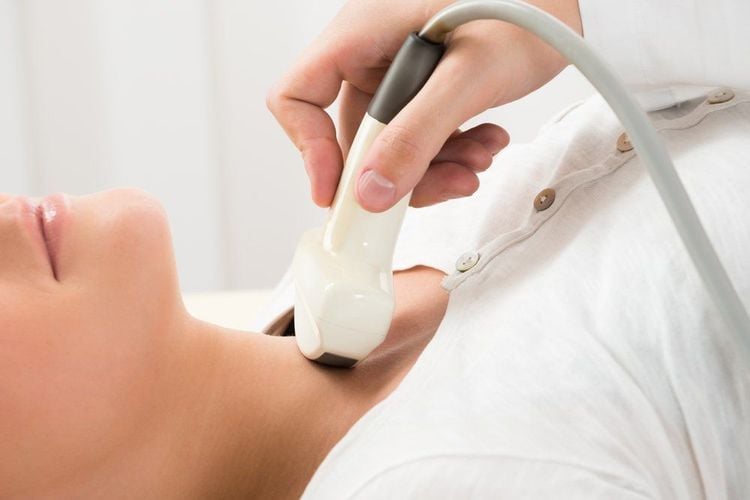
5. What is hypothyroidism?
The thyroid gland does not secrete enough thyroid hormone to maintain normal body metabolism, leading to hypothyroidism.5.1. Causes of hypothyroidism
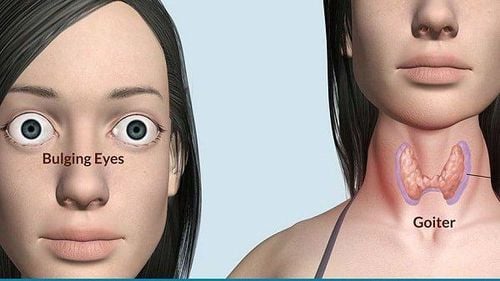
The most common cause of hypothyroidism is thyroiditis, of which the most common type is Hashimoto's thyroiditis. In patients with thyroiditis, the immune system mistakes thyroid cells as "invaders" that cause harm to the body. The body then produces white blood cells that destroy the thyroid gland.At the same time, the pituitary gland releases the hormone TSH, which stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete more thyroid hormone. This need causes the thyroid gland to enlarge, called a goiter. In addition to thyroiditis, a diet lacking in iodine is also a cause of hypothyroidism.
5.2. Symptoms of hypothyroidism
Symptoms of hypothyroidism usually begin and develop slowly. Here are some common symptoms:Fatigue, lethargy. Weight gain. Eat not good. Menstrual changes. Reduced desire. Easy to get cold. Constipation. Muscle fatigue. Swelling around the eyes. Nails are brittle and break easily. Hair loss.
5.3. Treatment of hypothyroidism
Most patients with hypothyroidism are treated with oral thyroid hormone medication, gradually increasing the dose until the thyroid hormone in the blood reaches normal levels.6. What is hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism is the result of the thyroid gland producing too much thyroid hormone, causing the metabolic rate to increase abnormally.6.1. Causes of hyperthyroidism?
The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is Basedow's disease. The disease most commonly affects women between the ages of 20 and 40. Graves' late-stage sign is protrusion of the eyes.In addition, patients after treatment for hypothyroidism, taking too much thyroid hormone may develop hyperthyroidism.
Another cause of hyperthyroidism is hot thyroid nodules, as these nodules produce excess thyroid hormone.
6.2. Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
Common symptoms include:Fatigue. Lost weight. Worried. Heart beats fast. Sweat a lot. Easy to get hot. Menstrual changes Increased bowel movements. Trembling.
6.3. Treatment of hyperthyroidism
Patients may be prescribed antithyroid drugs to reduce the amount of thyroid hormone secreted, beta blockers to control the tachycardia.Where these drugs do not work, the patient may be advised to take a strong dose of radioactive iodine, or in some cases to be treated with surgery.
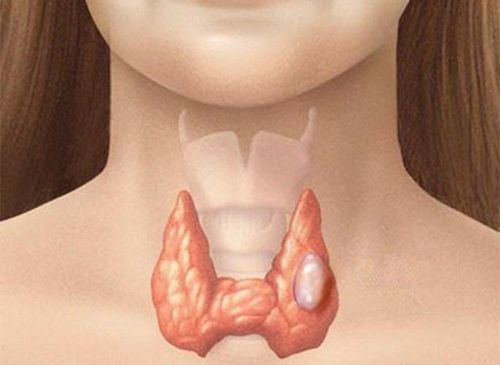
7. What is human armor?
Thyroid nodules are tumors (tumors) that form in the thyroid gland. When a patient has thyroid nodules, the doctor will order an ultrasound, or even a procedure such as a fine needle aspiration thyroid cytology, or a biopsy, to determine whether the nodule is benign (not cancerous) or malignant. count (cancer).If there are no cancer cells, the patient will be prescribed medicine to reduce the size of the thyroid nodule, or surgery to remove the thyroid nodule.
If cancer cells are found, it is necessary to conduct treatment according to the appropriate regimen. Thyroid cancer is often successfully treated.
8. Can thyroid disease in pregnant women be treated?
Currently, there are many drugs to treat thyroid disease that are safe for the fetus and can be used by pregnant women, but patients need to be closely monitored. During pregnancy, radioactive iodine should not be used, because it can damage the baby's thyroid gland and increase the risk of hypothyroidism after birth.9. What is postpartum thyroiditis?
In some women, thyroid problems don't start during pregnancy, but after giving birth. This condition, known as postpartum thyroiditis, usually comes and goes in a short time, and hormone levels quickly return to normal.Thyroid diseases are often left undiagnosed in 20 - 60% of the total population. That is the reason for Vinmec to launch a package of screening and screening for thyroid diseases. Screening & early detection of common thyroid diseases such as simple goiter, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, thyroiditis, thyroid nodules, thyroid cancer, etc. appropriate and timely treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Articles refer to the source Acog.org