This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Vo Thien Ngon - Urologist, Department of General Surgery, Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.Diseases in the penis such as urethritis, foreskin stenosis, penile herpes, ... not only negatively affect health and sex, but can also affect male fertility. gender.
1. Erectile Dysfunction
1.1 Causes of illness Stress, anxiety; Drink a lot of alcohol, smoke a lot; Postoperative symptoms (prostate surgery); Effects of diabetes, high blood pressure, depression, anxiety,... Side effects of some drugs. 1.2 Symptoms of the disease Inability to achieve an erection, unable to maintain an erection long enough to perform sexual activities; The erection lasts a very long time, often more than 4 hours, causing constant pain. However, the condition is not caused by sexual arousal or desire; Other problems: Inability to ejaculate, premature ejaculation, delayed ejaculation, decreased ejaculation, retrograde ejaculation (semen goes into the bladder instead of going out through the penis), pain during ejaculation, etc. 1.3 Preventive measures Limit the use of tobacco, alcohol, and alcoholic beverages; Find out about the medications you are taking to see if they are the cause of your erectile dysfunction. If so, you should consult your doctor to change to another drug; Use drugs that help achieve an erection, for example Viagra. Men pay attention to using drugs in moderation, do not abuse, strictly follow the doctor's advice; Use antidepressant and anxiety medications, see your doctor for advice on this condition;2. Peyronie's disease (curved penis)
Peyronie's disease is a condition in which the penis develops a marked curvature, especially when the penis is erect. This penile curvature is caused by patches of fibrous tissue (scar-like) that develop under the skin of the penis. The disease causes pain in the penis when erect, sometimes unable to have intercourse. Peyronie's disease is common in middle-aged men.Peyronie's disease is a mild disease, the most common sign of the penis being slowly curved or twisted into an angle, painful erections, and thickened patches of fibrous tissue under the skin. The disease develops slowly over months or years, sometimes goes away and goes away in the same way as it appeared and is rarely severe.
3. Orgasm Disorder

3.3 How to avoid Check for and treat potential health problems; Changing medications or treatments for depression; Performing cognitive, behavioral, or sex therapy; Increase stimulation during masturbation and sex by applying new positions or aids.
4. Change in sex drive
4.1 Causes of the disease Decreased sex drive: Due to depression, some relationship problems with the other half or hormonal imbalance; Increased libido: Due to a dramatic and sudden increase in libido (especially in the elderly) or substance use, due to medical conditions that affect the brain. 4.2 Symptoms of the disease The level of a man's sex drive will change markedly. At this point, men can suddenly become addicted to sex or lose all interest in sex.4.3 Prevention Learn and eliminate stressors in your life; Increase consumption of foods that stimulate libido, for example oysters; Exercise more often and regularly; There are innovations in sex life to increase excitement; Consult your doctor for drug treatment or other medically necessary interventions.

5. Sexually Transmitted Diseases
5.1 Causes of disease Men are at high risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases if:Have sex with many different sexual partners; Having sex with someone with multiple sexual partners; Do not use condoms during sex; Sharing needles with others, especially those with a sexually transmitted disease. 5.2 Symptoms There are many sexually transmitted diseases that negatively affect the penis, such as: genital warts, gonorrhea, chlamydia, syphilis and genital herpes. Common symptoms are burning pain when urinating, penile bleeding, sores or swelling in the penis.
Sexually transmitted diseases are:
Gonorrhea
The disease is transmitted mainly through sexual intercourse or by sharing towels and underwear with pus from the urethra or vagina of a person infected with gonorrhea. Men with gonorrhea experience penile pain or pain when urinating. Many cases of urethral stricture, need to urinate many times, easily lead to urethritis upstream, very difficult to treat.
Chlamydia infection
This is the most common of the sexually transmitted diseases. In particular, a dangerous feature of this disease is that up to 40% of cases of Chlamydia infection show no symptoms. In contrast, the disease is often detected only through complications in the late stages. At this time, the treatment is also more complicated and expensive.
Syphilis
Syphilis is caused by a sexually transmitted bacteria. The initial symptom of the disease is painless sores on the penis. This is a dangerous disease that, if not treated properly, can affect many other organs in the body. To treat syphilis, patients are prescribed to take antibiotics in full dose and early according to each stage of the disease.
Penile herpes
The HSV-1 and HSV-2 viruses cause small blisters, papillomas and ulcers on the penis and the lining of the anus. Up to 80% of cases do not show any symptoms, so the risk of transmission is very high. In addition, herpes is often associated with HIV infection.
Penile warts
HPV viruses can cause warts on the penis. Warts are also very contagious through unprotected sex. Its manifestation is skin-colored warts, floating on the penis, scrotum, around the anus, ... There are many methods of treating penis warts and the treatment is not too difficult.
5.3 Prevention To prevent the risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases, patients should:
Avoid sex with people who have abnormal symptoms on the genitals such as sores, developing board; Use condoms every time you have sex; Avoid sharing towels or underwear with others; Thorough hygiene before and after sexual intercourse; Hepatitis B vaccination; HIV test.
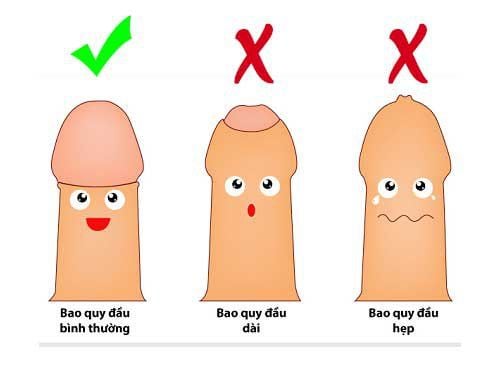
6. Narrow or semi-narrow foreskin

7. Yeast Infection
This is a common disease in the penis, which can cause a number of other serious complications if not detected and treated early.7.1 Causes of the disease Disease is caused by the fungus Candida. A humid environment is a suitable condition for Candida yeast to easily multiply and spread. Besides, having unprotected sex with a partner who has a yeast infection is the most common cause of the disease.
7.2 Symptoms Red, sometimes white, red rash on the penis; The skin of the penis becomes wet; Appearance of a layer of white patches under the foreskin; There is an itching and burning sensation in the genitals. 7.3 Preventions Minimize sexual contact with someone who has a yeast infection; Use condoms during sex; Healthy living, monogamy; Thoroughly clean the genitals, use good sweat-absorbent, breathable underwear so that yeast does not have a chance to grow; People who are not circumcised should keep the area under the foreskin clean. Do not forget to adjust the foreskin to its original position after cleaning and after sexual intercourse.

8. Urethritis
Inflammation or infection of the urethra is usually caused by bacteria. The disease causes painful symptoms for men when urinating.Urethritis includes specific inflammation and non-specific inflammation. With nonspecific urethritis, there are usually several strains of bacteria living in the mouth of the flute. If conditions are favorable, these bacteria will thrive, spreading deep into the urethra and vas deferens, causing inflammation of the testicles - epididymis. Favorable conditions for bacteria in the mouth of the flute to grow and cause inflammation are not keeping the mouth area clean, drinking little water, narrowing the foreskin,...
9. Penile cancer
Penile cancer is a rare form of cancer that can affect the skin and tissues of the penis. Although it develops slowly, the disease can spread to other organs in the body and lead to death.9.1 Causes of the disease Similar to other types of cancer, penile cancer occurs when healthy cells develop into cancerous cells. Malignant cells can spread to several other areas of the body, including glands, lymph nodes, and many other organs. Men have a higher risk of penile cancer if:
Over 60 years old; Frequent smoking; Not paying attention to hygiene of the genital organs; Having many sexual partners; Living in a place with a polluted environment; Have sexually transmitted diseases, HPV infection. 9.2 Symptoms There are lumps or sores on the penis that look like scars, small bumps or an infected wound. In many cases, these lumps and sores will appear on the tip of the penis or foreskin instead of the body; There is a feeling of itching, burning of the genitals; The penis secretes mucus; Change in penis color; Swollen skin of the penis; Penile bleeding; The penis is easily irritated; Floating red spots; Swollen inguinal lymph nodes. 9.3 Prevention To limit the risk of penile cancer, men should:
Limit or completely quit smoking; Clean genitalia, especially the skin under the foreskin; Use condoms and other protection during sex to prevent HPV infection; Get vaccinated against HPV infection.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.