This is an automatically translated article.
Benign tumors are a common condition and can happen to anyone, including men and women. However, unlike melanoma, they usually do not cause cancer or invade other areas of the body. Treatment options for a benign tumor will depend on the extent of the tumor and its location in the body.1. What is a benign tumor?
Benign tumors are tumors that grow inside the body but are not capable of causing cancer. Unlike malignant (cancerous) tumors, they usually do not metastasize to other areas or organs of the body.
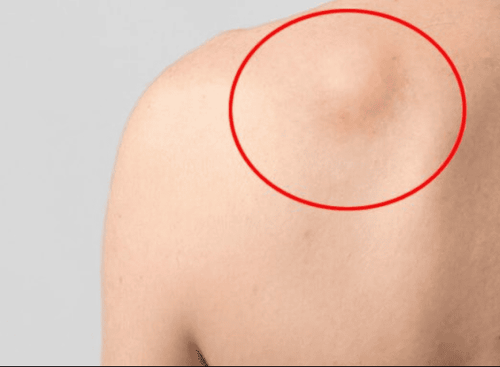
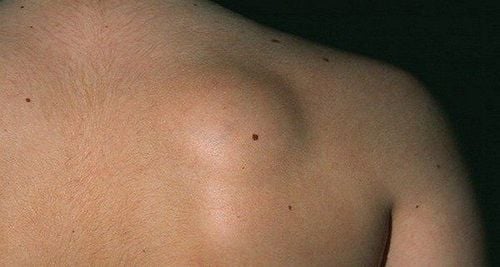
Benign tumors can form and grow in any part. Most of the tumors detected through the patient's perception from the outside are benign. This is also a common condition and occurs in anyone, both men and women.
Trắc nghiệm: Thử hiểu biết của bạn về bệnh ung thư
Ung thư là nguyên nhân gây tử vong hàng thứ 2 trên thế giới. Thử sức cùng bài trắc nghiệm sau đây sẽ giúp bạn có thêm kiến thức về yếu tố nguy cơ cũng như cách phòng ngừa bệnh ung thư.
Bài dịch từ: webmd.com
2. Symptoms of benign tumors
The signs and symptoms of a tumor will depend on where in the body the organ is affected. If there are soft tissue tumors, such as the abdomen, or tumors near the skin, the patient may be able to feel them when touched or touched. Or in the case of a benign tumor in the brain, you will have symptoms such as headaches, memory loss and vision disturbances.
However, not all benign tumors have specific symptoms. The most common signs you may notice include:
Pain; Uncomfortable; Chills; Tired body; Fever; Excessive night sweats; Unappetite to eat; Weight loss. You can easily detect and locate benign tumors, especially those near the skin. Moreover, the size of these tumors is usually not too large to cause pain or discomfort to the sufferer.
3. Causes of benign tumors
Currently, scientists have not found the exact cause of benign tumors. However, it is still possible to explain a number of factors that cause this problem.
Normally, old cells in the body will die and be replaced by new healthy cells. When these cells function abnormally, they divide and grow beyond their limits, forming tumors. The formation and growth of benign tumors is similar to that of cancerous tumors. However, cancer-causing cells tend to attack and spread to other tissues or parts of the body.
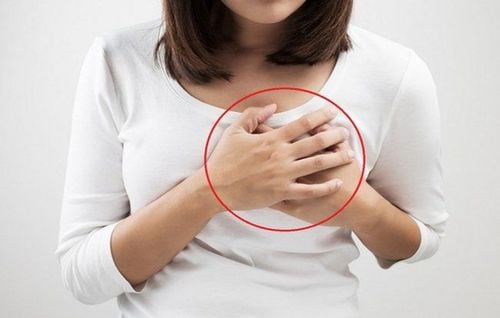
4. Common benign breast tumors
4.1. Benign breast tumor
There are many different causes of benign breast lumps. 2 of the most common causes of this condition are cysts and fibroids. In addition, a number of other factors also contribute to the appearance of lumps, such as scleroderma or fat necrosis. To accurately identify breast lumps, you can perform diagnostic tests at the hospital.SEE ALSO: A 2-step guide to self-examination of breasts at home

4.2. Breast abscess
A breast abscess consists of an inflammatory pocket of pus and a painful lump in the breast. The pus sac is made up of bacteria, debris and white blood cells in the body.
Features of breast abscess, including:
A soft and flabby mass; The skin with the abscess is red, hot, swollen, and painful to the touch; The patient may have a fever and fatigue.
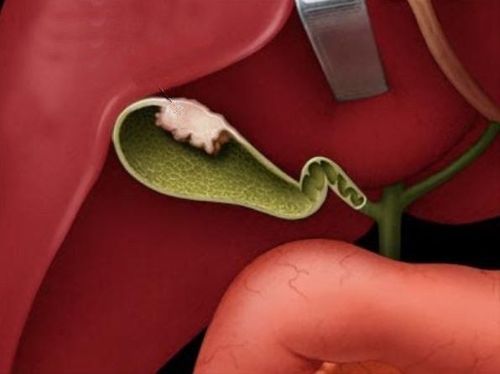
4.3. Benign cysts
A cyst is a fluid-filled sac that is slowly growing inside the breast tissue. This condition most commonly occurs in women between the ages of 35-50 and is most common in those nearing menopause.
Most often, these cysts enlarge and cause pain in the breast just before menstruation. They can even appear overnight. However, cysts are rarely cancerous and they can be caused by blocked mammary glands.
When touching the cyst, you will feel soft or hard, depending on the condition of each person. Closer to the surface of the breast, the cyst will swell, smooth on the outside, but filled with fluid on the inside. Once in the breast tissue, these cysts will feel like hard lumps because they are surrounded by tissue. A doctor may find a cyst during a patient's physical examination. Tests to diagnose cysts, including mammograms, ultrasounds, and needle biopsies.
4.4. Benign fibroids
Fibroids are solid, smooth, and benign tumors that are most common in women between the ages of 20 and 30. Recent studies show that fibroids are increasing in women. menopause are using hormone therapy.
Fibroids are painless, rubber-like growths that move freely. Fibroids usually vary in size and can develop anywhere in the breast tissue.
To diagnose fibrocystic breast cancer, the doctor may use methods such as mammogram, ultrasound, or needle aspiration. For many people, fibroids may not need to be removed. However, as these tumors enlarge during pregnancy and breastfeeding, you will need to have them surgically removed from your body.
4.5. Fat necrosis
Fat necrosis is a condition in which round, lumpy, but painless masses appear due to damaged and broken down fatty tissue inside the breast tissue. Fat necrosis usually occurs in women who have very large breasts, have bruises, or have had breast augmentation. This condition can also be the result of tumor resection and radiation treatment of a previous cancerous tumor.
In certain cases, the doctor will track the tumor through the patient's menstrual cycles. A mammogram may be ordered before a decision is made to remove the necrotic mass. However, these tumors are not usually malignant and they do not increase the risk of cancer.
4.6. Milk cysts
A milk cyst is a fluid-filled mass, usually caused by a blocked milk duct. This condition occurs most often in women who are breastfeeding. This is a benign tumor, which can resolve on its own after lactation ends without intervention from treatments. In certain cases, the cyst will be removed by suction or surgically removed. In addition, antibiotics may also be used to prevent infection.

4.7. Hematoma
A hematoma is a blood-filled mass caused by trauma or surgery to the breast.
4.8. Scleroderma of the mammary gland
Scleroderma is an overgrowth of tissues in the breast lobes. This often leads to breast pain. Although the changes in breast tissue are very small, they can be detected on mammograms as calcifications and tumors.
This condition is often confused with cancer, so the tumor will be removed through surgical biopsy.
Currently, early cancer screening is considered the perfect measure in the timely detection and treatment of all types of cancer. Reduce treatment costs and patient mortality. Vinmec International General Hospital always deploys and introduces to customers the Early Cancer Screening Package at Vinmec - Peace of mind to live well to help with imaging, genetic testing and biomarkers for early tumor detection. .
Choosing the early cancer screening package at Vinmec - Peace of mind to live healthy, customers will get:
Only one gene test can assess the risk of 16 common cancers in both men and women; Early detection of early signs of cancer through imaging, endoscopy and ultrasound; The examination operation is simple, careful and accurate; A team of well-trained specialists, especially in oncology, is capable of handling medical examination and treatment cases. With a system of facilities, advanced and modern medical equipment and a team of doctors with deep expertise and experience, it will help the process of examination and treatment of patients at Vinmec become faster with High efficiency, save cost and time.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: hopkinsmedicine.orgMORE
How are malignant tumors different from benign tumors? Differential diagnosis of malignant tumor - benign tumor by immunohistochemistry Is the diagnosis of benign tumor worrisome?