This is an automatically translated article.
Estrogen and progestin are female hormones. They are secreted by the body to ensure normal sexual development and maintenance of the menstrual cycle in women of reproductive age.1. Why use estrogen and progestin?
Lý do phải sử dụng estrogen và progestin
Some reasons to prescribe estrogen :
To make up for the lack of estrogen due to the body not producing enough, such as in the case of menopause. Estrogen also helps to improve a condition that occurs in the genital skin area, which is vulvar atrophy or vaginal atrophy. Helps prevent osteoporosis when women go through menopause. Estrogen may also be prescribed by a doctor in many other situations.
Currently there is no medical evidence to support the idea that using estrogen helps patients become younger, smooth skin or delay the appearance of wrinkles. There is also no evidence that taking estrogen during menopause reduces emotional and neurological symptoms, unless those symptoms are caused by other menopausal symptoms, such as hot flashes.
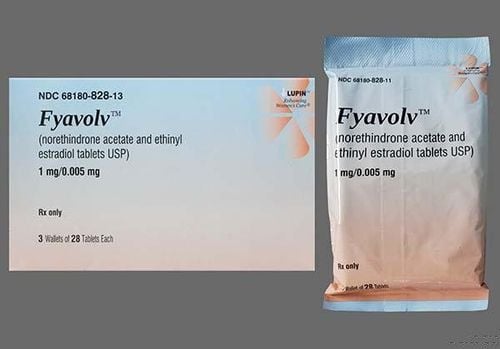
Estrogen and progestin combination pills are usually made as a pill or chewable tablet.
2. Factors to consider before use
Allergies: Tell your doctor if you have a history of allergies, especially drug allergies. Age: There are many drugs that have not been adequately studied in the elderly, so it is not possible to determine exactly whether the drug will work in the same way as it does in the young, and it is impossible to say for sure. In the elderly, does the drug have any other undesirable effects or can cause any abnormality? There is no specific information available on the use of estrogens and progestins in the elderly compared with other age groups. Pregnancy: Estrogen and progestin should not be used during pregnancy or shortly after delivery. Pregnancy does not usually occur in postmenopausal women. Breast-feeding: Estrogen and progestin can pass into breast milk, and can change the composition or decrease the quantity of breast milk, and therefore should not be used while breastfeeding. Drug Interactions: Although some drugs should not be used together, in some cases two different drugs can be used together, although drug interactions can occur. In this case, the doctor may change the dose of the medicine. If you are taking any medications, you should inform your doctor about drug interactions. Using estrogen and progestin with any of the following medicines is not recommended, and your doctor may stop or change the prescription for a different drug:Use estrogen and progestin with any of the following medicines: These are not generally recommended, but can be used in certain circumstances, and your doctor may reduce the dose and change the duration of use:
Amifampridine Anagrelide Apalutamide Aprepitant Armodafinil Boceprevir Bosentan Brigatinib Bupropion Carbamazepine Ceritinib Conivaptan Darunavir Dexamethasone Dabrafenib donepezil Elagolix Encorafenib Efavirenz Etravirine Enzalutamide Erdafitinib Eslicarbazepine Acetate Fosaprepitant Fosnetupitant Fosphenytoin Glecaprevir Griseofulvin isotretinoin Ivosidenib Lesinurad Lixisenatide Lorlatinib Lumacaftor Mitotane Modafinil Nafcillin paclitaxel paclitaxel Protein Netupitant Nevirapine-Bound oxcarbazepine phenobarbital phenytoin primidone Pibrentasvir Piperaquine Pitolisant Pixantrone prednisone Rifabut in Rifampin St John's Wort Sugammadex Theophylline Tizanidine Topiramate Ulipristal Valproic Acid Other Interactions: Certain medications require certain foods to be avoided. Alcohol and tobacco can also cause drug interactions. Please consult your doctor for more information. Other problems: Medical history may affect the use of the drug, fully inform your doctor, especially if any of the following problems are present: Bronchial asthma Hypercalcemia or hypocalcemia Diabetes Epilepsy Cardiovascular disease Kidney disease Benign liver tumors Systemic lupus erythematosus Migraine headache Porphyria - estrogen can make the disease worse Vascular disease (or history of estrogen use) Breast cancer Cancer Bone cancer Uterine cancer Uterine fibroids Genital changes or vaginal bleeding of unknown reason Endometriosis Gallstones High cholesterol or triglyceride levels Liver disease Acute pancreatitis Hypothyroidism Changes vision Protrusion Double vision Partial or complete loss of vision
3. Use of estrogen and progestin

Sử dụng estrogen và progestin cần tuân theo đúng chỉ định của bác sĩ.
When taking estrogen and progestin, the patient may experience nausea and vomiting for the first few weeks, but this will disappear on its own. This can be reduced or prevented by taking the drug during or immediately after a meal.
If you forget to take your medicine, take it as soon as you remember. If it is too close to the time of the next dose, skip the missed dose and do not double the dose.
During treatment, it is necessary to periodically re-examine as prescribed by the doctor. If any unusual problems occur, notify your doctor immediately.
4. Undesirable effects of treatment with estrogen and progestin
Women rarely experience serious adverse events during estrogen replacement therapy. Prolonged estrogen use has been reported to increase the risk of uterine cancer in postmenopausal women. The risk seems to increase with dose and duration of use. When used only in low doses and for less than 1 year, the risk is low. The risk is also reduced when estrogen is used in combination with a progestin. The relationship between estrogen use and breast cancer is controversial.If any undesirable effects appear, immediately inform the doctor. Possible side effects are:
Common: Breast pain or increased sensitivity Dizziness, light sensitivity Headache Rapid weight gain Lower extremity swelling Vaginal bleeding Rare: Abnormal mass in the breast Vaginal abnormal discharge Breast discharge Nausea, vomiting Pain in the chest, groin, legs (especially calves) Abdominal pain Pain or heaviness in the pelvis Sudden or severe headache Sudden unexplained shortness of breath things Suddenly difficult to speak Sudden vision changes Hands and feet Impotence Jaundice, yellow eyes Some unwanted effects will go away on their own without intervention. If one of the following undesirable effects does not go away or greatly affects the patient's life, consult a doctor:
Back pain Abdominal pain Dizziness Dizziness Fatigue Flu-like symptoms Depression Muscle pain Vomiting Vaginitis In case of any unusual problems, the patient should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article referenced source: Mayoclinic.org