This is an automatically translated article.
The most common treatment for brain cancer today is chemotherapy. This therapy is easy to perform and highly effective for patients. The effect is achieved through the use of drugs or cytotoxic chemicals that can eliminate and stop the growth of brain cancer cells.1. Chemotherapy for brain cancer
Chemotherapy uses anti-cancer drugs that are usually given intravenously (IV) or taken orally. These drugs enter the bloodstream and reach most areas of the body. However, many chemotherapy drugs cannot enter the brain and reach tumor cells.
For some brain tumors, medication may be given directly into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF, brain and spinal cord washing fluid), in the brain, or into the spinal canal below the spinal cord. To solve this problem, a thin tube called a ventricular access catheter can be inserted through a small hole in the skull and into the ventricles during a minor surgery.
2. Blood brain barrier
The brain has a protective system called the blood-brain barrier, which helps protect the brain from substances in the blood, such as germs or chemicals, that can damage the brain. Only certain chemotherapy drugs can overcome this barrier.
Não có một hệ thống bảo vệ được gọi là hàng rào máu não
3. Using chemotherapy to treat brain cancer
Generally, chemotherapy is used for rapidly growing brain tumors. Certain types of brain tumors, such as myeloma and lymphoma, tend to respond to chemotherapy better than others. Chemotherapy is not useful for treating some other types of tumors, such as spinal cord tumors, so it is less commonly used for these tumors.
Chemotherapy for brain cancer is often used along with other treatments such as surgery and/or radiation therapy. Chemotherapy may also be used by itself, especially for advanced tumors or for recurrent tumors that come back after other types of treatment.
4. Chemotherapy drugs used to treat brain and spinal cord tumors
You may get chemotherapy as a capsule or tablet that you swallow (oral), or as a liquid through a dropper that is inserted into your vein (intravenously).
Some chemotherapy drugs used to treat brain and spinal cord tumors include:
Carboplatin
Carmustine (BCNU) Cisplatin Cyclophosphamide Etoposide Irinotecan Lomustine (CCNU) Methotrexate Procarbazine Temozolomide Vincristine Temozolomide is a chemotherapy drug most commonly prescribed for the treatment of gliomas. Temozolomide is taken as a capsule taken by mouth at home. Each course of treatment is usually followed by a rest period of several weeks. You may have chemotherapy for up to 6 months.
These drugs may be used alone or in combination, depending on the type of brain tumor. Chemotherapy for brain cancer is cyclical, with each stage of treatment followed by a period of rest to give the body time to recover. Each cycle usually lasts for several weeks.
Carmustine wafers (Gliadel): These wafers contain the chemotherapy drug carmustine (BCNU). After the surgeon safely removes as much of the brain tumor as possible during a craniotomy, thin sheets can be placed directly on or next to the unresectable parts of the tumor. Unlike IV or oral chemotherapy, which affects all areas of the body, this type of therapy focuses the drug at the tumor site, causing fewer side effects in other parts of the body.
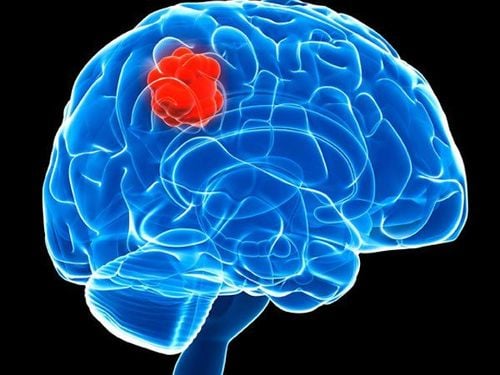
Hóa trị được sử dụng cho sự phát triển nhanh các khối u não
5. Possible side effects of chemotherapy
Chemotherapy drugs can cause side effects. These depend on the type and dose of the drug, and how long the treatment lasts. Some common side effects of chemotherapy can include:
Hair loss Mouth sores Loss of appetite Nausea and vomiting Diarrhea Increased chance of infection (due to too few white blood cells) Ease bruising or bleeding (from having too few platelets in the blood) Fatigue (from having too few red blood cells, changes in metabolism, or other factors) Some of the most effective drugs against mass Brain tumors tend to have fewer side effects than other common chemotherapy drugs. Most side effects usually go away after treatment is finished. There are often ways to reduce these side effects. For example, medication can often help prevent or reduce nausea and vomiting.
Some chemotherapy drugs can also cause other, less common side effects. For example, cisplatin and carboplatin can also cause kidney damage and hearing loss. Your doctor will check your kidney function and hearing if you are taking these medicines. Some of these side effects may persist after stopping treatment.
Be sure to report any side effects to your healthcare provider while you are having chemotherapy. That helps you find the right solution and get treatment in time. Sometimes, it may be necessary to reduce the dose of the drug or it may be necessary to delay or stop treatment to prevent the effects from getting worse.
Thuốc hoá trị có thể gây ra tác dụng phụ như rụng tóc
Early cancer screening is considered a perfect measure in the timely detection and treatment of all types of cancer. Reduce the cost of treatment and especially reduce the mortality rate in patients. Vinmec International General Hospital always deploys and introduces to customers Early cancer screening at Vinmec - Peace of mind to live well to help with gene testing, imaging diagnostics, testing of biological markers to detect tumors Soon. Vinmec International General Hospital has many packages of early cancer screening.
Only one gene test can assess the risk of 16 common cancers in both men and women (lung cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, neck cancer) uterus, stomach cancer, prostate cancer,....) Early detection of early signs of cancer through imaging, endoscopy and ultrasound. The operation is simple, careful and accurate. A team of well-trained specialists, especially in oncology, are capable of handling cancer cases. With facilities, advanced and modern medical equipment and a team of doctors with deep expertise and experience. At Vinmec, the examination process becomes quick with accurate results, saving costs and time for patients.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: cancercouncil.com.au, cancer.org, mayoclinic.org
MORE:
Glioblastoma: What you need to know Brain cancer: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment Brain: What you need to know