This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thi Xuyen - Clinician - Reproductive Support Center - Vinmec Times City International Hospital. The doctor has many years of experience in the field of reproductive health and assisted reproduction.After the baby is born, some women have to deal with the phenomenon of stillbirth. If not handled, the situation of dead birth is very dangerous, affecting life. In case there is a lot of fluid retention and the use of drugs to help the uterus contract to push out the fluid is not effective, the doctor will have to perform cervical dilation
1. Why is the production blocked?
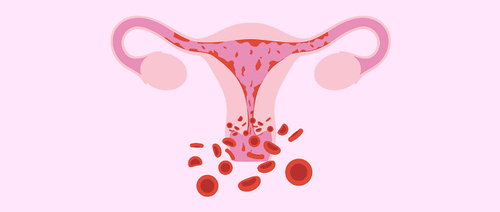
Semen is the discharge from the uterus and genital tract during the first few days of the postpartum (postpartum) period. The discharge consists of blood clots and thin blood that flows from the lining of the uterus. In pregnant and lactating women, the discharge will go away faster because the uterus contracts more quickly. In a caesarean section, the discharge is usually less than in a vaginal delivery. If the discharge is heavy, prolonged, or the dark red blood has stopped, and the bleeding is repeated, it is necessary to monitor the placenta at birth.There are many causes of fluid retention such as: When a woman loses a lot of blood due to poor contraction of the uterus, a long labor time makes the mother exhausted, and the woman carries multiples. In addition, maternity leave often happens to women who lie down a lot, move less, and exercise for fear of uterine prolapse.
2. Some complications after the treatment of fluid retention due to cervical dilatation
The technique of dilation and curettage to clear the remnants of the uterus is usually very safe and complications are rare. However, there are still some risks such as:Uterine perforation. Uterine perforation occurs when the instrument pokes a hole in the wall of the uterus. Most perforations heal on their own. However, if a blood vessel or other organ is damaged, other techniques will be needed to treat it. Cervical injury. If the cervix is torn during dilation and curettage, the doctor may apply forceps to stop the bleeding, administer medication to stop the bleeding, or may close the wound with sutures. Scar tissue on the uterine wall. Rarely, dilation and curettage lead to the formation of adhesions and scarring in the uterus known as Asherman's syndrome. This syndrome will cause irregular menstrual cycles, missed or painful periods, future miscarriages, and infertility. Infection, however, occurs very rarely. Contact your doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms after dilation and curettage:
Bleeding heavy enough that you need to change tampons every hour Fever Pulling cramps longer than 48 hours Increasing pain in the lower abdomen Vaginal discharge with a bad odor .

3. The procedure to perform cervical dilation due to fluid retention
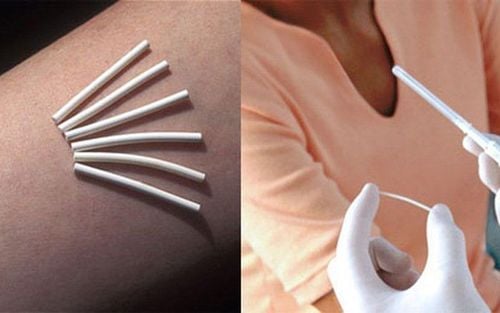
The technique of cervical dilation and curettage is performed at a hospital specializing in obstetrics or gynecology or a licensed medical facility.3.1 Before the procedure Maternity will follow the doctor's instructions about limiting food and drink. The mother should arrange an extra person to accompany her so that she can take her home after the anesthetic wears off. Rearrange your work and life schedule to allow enough time for you to rest and recover from this procedure. In some cases, your doctor may start dilating your cervix a few hours or even a day before the procedure. This helps to gradually open the mother's cervix and is usually done when the cervix has dilated to the standards of this technique. Usually, your doctor will use a medication called misoprostol (Cytotec) taken by mouth or vaginally to soften the cervix, or use dill (laminaria) on the cervix. Algae (laminaria) absorb the fluid in the cervix causing the cervix of the mother to open gradually.
During the procedure:
The woman lies on her back on the table with both feet on the pedal. The doctor will insert the speculum into the vagina and gradually dilate so that the cervix is slowly dilated until it opens wide enough to The doctor will begin to cure the uterine fluid. Because the mother is anesthetized or anesthetized, during the procedure, the mother will not feel pain or discomfort. 3.3 After the procedure The mother spends a few more hours in the recovery room after the procedure, so that the doctor can monitor for bleeding or other complications.
If the mother has general anesthesia, some side effects may be experienced such as nausea, vomiting or sore throat if the intubation is intubated. With general anesthesia or the use of mild sedation, you may also feel drowsy for a few hours after the procedure.
Some other long-lasting side effects may persist for a few days such as:
Mild cramps There is a slight streak of blood on the tampon.
After going home, you can resume normal activities for a day or two afterward.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.