This is an automatically translated article.
Chronic headaches are headaches that recur over and over again, directly affecting the patient's quality of life. Chronic headache has no cure, patients can only minimize the symptoms of the disease.1. Chronic headache
Chronic headaches are headaches that recur over and over again and have a duration of more than 3 months. Chronic headaches are caused by many factors, which can start with an acute attack and last longer than expected.
People with chronic headaches can lead to psychological disorders such as anxiety, depression and personality changes, which not only affect quality of life but also affect social activities.
2. Causes of Chronic Headaches
Non-inflammatory headache Back pain Neck pain due to muscle contraction Pain caused by inflammation Post-operative pain Degenerative pain Arthritis pain Gout pain Traumatic pain Pain in cancer patients,... Pain caused by factors neuralgia Sciatica, postherpetic neuralgia, nerve pain V, pain due to diabetic neuropathy,...
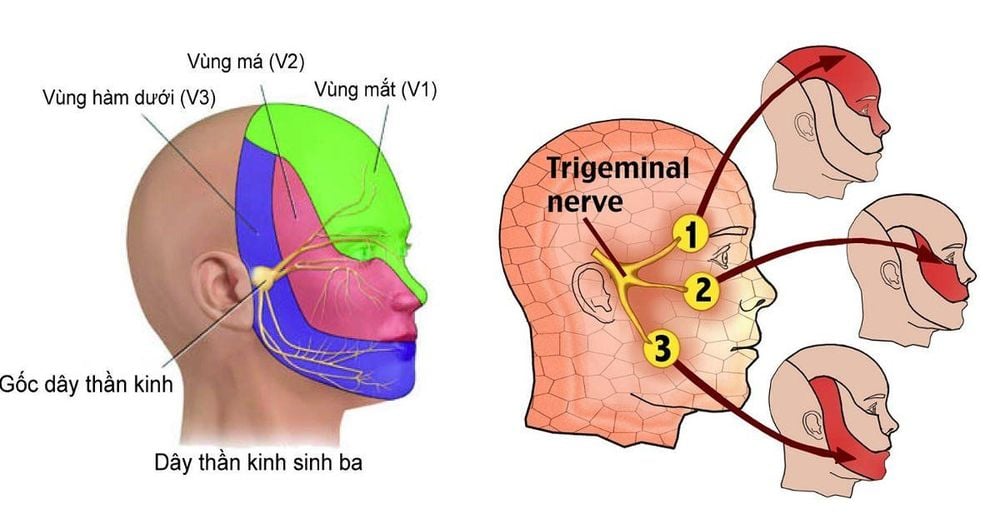
Đau dây thần kinh số V
Post-stroke pain: Post-stroke pain can appear and develop after several weeks or months. This is a sudden brain attack when blood flow to the brain is cut off, leaving brain cells with an acute lack of oxygen. From there, brain cells begin to die, leading to the loss of the ability to control memory and muscles. After a stroke, almost every organ and nervous system suffers severe consequences, leading to symptoms of pain throughout the body. Nervous system damage is the destruction of the protective outer layer of myelin sheath, causing electrical impulses to discharge uncontrollably and cause pain.
Pain after surgery: Usually after surgery, nerve cells are damaged causing persistent and long-lasting pain. Types of surgical neuropathic pain include: CNS pain: Pain that originates from damage to the brain or spinal cord, commonly seen during surgery on nerves in the brain or spine. Peripheral neuropathy: This type of pain originates in nerves that are not part of the brain or spinal cord, such as the nerves in the hands and feet. There are also a number of diseases that also lead to chronic headaches. Headaches caused by brain tumors Headaches appear in the early stages of the disease. Headaches are usually gradual, progressive, and are often accompanied by other symptoms that vary depending on the location and nature of the tumor. Initially, the headache site is usually fixed in the area with the tumor. As the tumor grows, it will compress the surrounding tissues and cause increased pressure in the skull, causing pain that radiates to the entire head.
Headache is rarely severe, usually only dull but persistent and increasing gradually, or pain is more severe in the middle of the night and in the morning and then gradually decreases or disappears when waking up. Pain increases when doing strenuous movements such as coughing, pushing, defecating... or changing positions suddenly like sitting back and lying down.
In the early stages of the disease, common pain relievers such as aspirin, paracetamol have a soothing effect. Later, these drugs are no longer effective.
Another symptom that often accompanies the headache, such as nausea or vomiting, occurs at a later stage, unrelated to eating. The patient easily vomited, vomited, after vomiting, the headache was reduced. Another common symptom is having seizures or mental disturbances (when brain tumors are in the frontal or temporal lobes) such as mood changes, decreased activity, slow consciousness, etc. Depending on the location and nature of the tumor, there will be many other symptoms associated with headache such as weakness, hemiparesis, facial paralysis, strabismus, blurred or double vision, tinnitus, dizziness.
Many other diseases also present with a headache like a brain tumor. Therefore, in order to accurately diagnose or exclude other diseases, it is necessary to examine a neurologist and do some more tests such as EEG, computed tomography, brain angiography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)..
In which, EEG should be done first because it is a harmless, cheap, easy to perform test and more importantly, it helps to detect abnormal areas in the brain early to guide doctors to do it. brain tumor imaging tests.
Treat the root cause of the headache by surgically removing part or all of the tumor. In case the tumor is in an inoperable position, surgery can be performed to drain the cerebrospinal fluid or be treated with chemotherapy or radiation. Symptomatic treatment of pain is mainly the treatment of increased intracranial pressure and cerebral edema with mannitol solution, corticosteroids, furosemide diuretics...
Migraine (Migraine) Common in adulthood, and is more common in women than in men. The disease is familial, usually localized to one side of the head, and has a cyclical course with varied clinical symptoms. People divide migraine into two main types:

Đau nửa đầu (Migraine) thường gặp ở lứa tuổi trưởng thành, và hay gặp ở nữ giới
Migraine without warning signs: At first, the patient has pain on one side of the head in the forehead or forehead - temple, then it may spread to the whole head and end on the opposite side but never the pain spreads to the face. . During the pain, the face is pale, the skin is cold, the goiters are raised, the patient feels like the temples are stretched, the blood vessels in the temples are bouncing and beating with the heartbeat, accompanied by a feeling of nausea and vomiting. , vomit. In some cases, dizziness and loss of balance. Another characteristic is that the pain is increased with exertion, when exposed to light, strong noise, reduced by quiet rest in the dark and by cold compresses or temples. In addition, many patients when Headaches are very sensitive to odors, sometimes they even smell strange odors, however, in pain, there are no objective neurological signs. The progression of this type of headache varies from patient to patient, and can last from a few hours to several days. In some patients, pain is cyclical, occurring only once a month or a year; but there are also cases where the pain is frequent and can change sides, but is always more severe on one side of the head.
Migraine with neurological signs: A temporary brain dysfunction that appears in a few minutes, signaling a headache will come soon after. These signs are usually visual, sensory, and language disturbances. In terms of vision, patients have the feeling of zigzag lines of light running in front of their eyes or seeing everything around them with brilliant colors, in some cases they can't see anything for a few seconds to a few minutes (temporary blindness). ). In terms of sensation, the patient feels like there is an ant crawling or frostbite on one side of the mouth and hand.
Common language disorders are difficulty speaking, not understanding other people's words or not being able to speak at all. In most cases, the sequence of these disturbances is: visual disturbance then sensory and language disturbances, all occurring within minutes, and finally headache with similar characteristics to Migraine has no warning signs.
Regarding the treatment of migraine relief when the attacks are far apart, doctors often give ordinary pain relievers such as aspirin, paracetamol, indomethacin... If the headache does not subside, then use a specific reliever that is a derivative of ergotamine such as gynergen, migwell, or serotonin antagonists such as sumatriptan. Prophylactic treatment when the frequency of headaches is high, at least 3 per month or more.
Psychological headaches Psychological headaches can occur at any age, but usually between the ages of 30-40 years old, women tend to suffer more than men. Although this headache is not dangerous, it affects the patient's work and quality of life. Headaches often appear when the patient has to think intensely or worry about something, lasting from a few minutes to a few days or appearing many times a day.
The feature of this type of headache is a dull ache, feeling like a squeeze, tightening like when we wear a tight hat or tighten a scarf on the head and in some patients it is also accompanied by pain and fatigue in the muscles in the head. head, neck. Often patients have pain on both sides of the head or sometimes pain on one side, sometimes pain on the other.
During the pain, the patient has no fever, no nausea or vomiting, is not afraid of light and sound, or if there is fear, only one of the two phenomena above. Another feature is that the pain does not increase with normal physical activity but increases with emotion. In addition, the pain, although slightly affecting daily activities, is never so painful that it can interfere with the patient's activities. Neurological examination in or out of pain is normal.
Regarding treatment, must combine psychotherapy and drugs, mainly tranquilizers, anti-anxiety benzodiazepines (Seduxen, Valium), antidepressants (Anafranil, Laroxyl), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (paracetamol) , aspirin) and add a muscle relaxant in the case of headaches associated with tension in the muscles around the skull. Patients need to change their lifestyle, give up bad habits in daily life such as work in moderation, alcoholism, smoking, increase exercise, healthy entertainment... Some cures Diseases with traditional medicine also work very well, especially for patients with headaches accompanied by muscle tension around the skull, often combining acupressure massage with physical therapy in the head and neck area.
3. Chronic Headache Prevention
Treating the underlying cause often prevents frequent headaches. If the doctor cannot detect the cause of the disease, the patient will be focused on treatment and prevention of pain.
There are different prevention methods depending on the type of headache. If you are taking pain medication more than three days a week, stop taking it immediately and follow your doctor's instructions.

Thuốc chống trầm cảm
When you are ready for preventive treatment, your doctor may recommend certain medications such as:
Antidepressants : Your doctor may prescribe a tricyclic antidepressant, such as nortriptyline, to treat chronic headaches. These medications can also help treat depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances that often accompany chronic headaches; Other antidepressants: The selective serotonin inhibitor, fluoxetine, may aid in the treatment of depression and anxiety but has not been shown to be more effective than placebo for headaches; Beta-blockers: These drugs, commonly used to treat high blood pressure, are also effective in preventing migraines. Some beta-blockers include atenolol, metoprolol, and propranolol; Antiepileptic drugs: Some antiepileptic drugs can prevent migraines and chronic headaches; Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are very effective in treating chronic headaches, especially if you are reducing the dose of other pain relievers. The doctor will also ask the patient to use it periodically if the headache gets worse; Botulinum toxin: Botox injections may be a viable option for people who cannot fully tolerate daily medications. However, some chronic headaches are resistant to all drugs.
Some measures to prevent headaches Appropriate lifestyle: Have a healthy lifestyle, add enough nutrients in the diet, limit unhealthy foods and drinks, exercise regularly daily exercise,...
Acupuncture : The doctor inserts a hair-thin needle into specific points on the skin. Several studies have shown that acupuncture can help reduce the frequency and intensity of chronic headaches;
Biofeedback : You can manage headaches by better understanding the headache and then changing certain reactions of the body, such as muscle tension, heart rate and skin temperature ;
Massage: This method can relieve stress, relieve pain, and help with relaxation. Massage can be especially helpful if you have muscle stiffness in the back of your head, neck and shoulders;
Herbs, vitamins, and minerals: Some evidence suggests that herbs can prevent migraines or reduce their severity. A high dose of riboflavin (vitamin B2) can relieve migraines;
Taking Coenzyme Q10 pills will help you. Magnesium supplements may help reduce the frequency of headaches in some people. Consult with your doctor to see which treatments are right for you. You must not use riboflavin (vitamin B2), medicinal herbs or herbs if you are pregnant;
Electrical stimulation of the occipital nerves: A small battery-powered electrode is implanted near the occipital nerves at the bottom of the neck. The electrodes will continuously send pulses of energy to the nerves to relieve pain.
Chronic headaches often affect quality of life and have no cure. Therefore, when suffering from chronic headaches, it is necessary to see a doctor for advice and solutions to prevent pain appropriately and effectively.
At Vinmec Times City International Hospital, the department of neuroendocrinology belongs to the clinical medicine division, holding specialized functions in the examination and treatment of diseases related to the central nervous system including: Skull , brain, cerebrospinal vessels, meninges, intracranial nerves, pituitary gland, spine, discs, spinal membranes, and peripheral nervous system (nerves and ganglia outside the brain and spinal cord).
Together with a team of leading specialist doctors in the country, not only good in expertise but also rich in many years of experience and modern equipment and advanced facilities.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.