This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by Master, Doctor Bui Thi Hong Khang - Pathologist - Laboratory Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Carcinogenic agents are classified into 3 main groups: chemicals, radiation and viruses. They can act separately or synergistically. In this article, we'll cover chemicals and radiation that lead to cancer.
1. Chemical carcinogens
Carcinogenic chemicals have a very diverse structure, of natural or artificial origin. The common feature of carcinogens is that they have a very high electron affinity and readily interact with proteins, RNA and DNA molecules. Therefore, most carcinogens are also mutagens, which can cause damage to DNA molecules. Distinguish 2 types of chemicals that cause cancer:
Direct carcinogenic chemicals: Have the ability to directly damage DNA molecules, creating cancer. For example, alkylating substances. It is noteworthy that some alkylating agents such as cyclophosphamide, chlorambucil, which have been successfully used in the treatment of certain types of cancer (ovarian cancer, lymphoma) have the potential to cause a new cancer later (usually). is leukemia).
Indirect carcinogens: Most carcinogens belong to this category, which are not themselves carcinogens, and need to be metabolized in the body to become a true carcinogen. . Example:
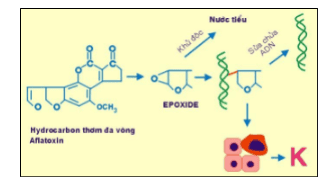
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Found in petroleum (benzanthracene), in tobacco smoke (benzopyrene); When entering the body, it is converted into epoxide, capable of forming a covalent bond with DNA, causing gene mutations, causing skin cancer and lung cancer. Aromatic amines and azo dyes: For example, beta naphthylamine, an aromatic amine widely used in rubber processing plants; Azo dyes are used to color foods to make them look good. These substances when entering the body will be metabolized in the liver, becoming real carcinogens, can cause liver cancer and bladder cancer. Nitrosamin: Nitrates are used as fertilizers, food preservatives; Once in the body, they are metabolized by the resident bacteria in the intestine, combining with amines into nitrosamines. Nitrosamine is a true carcinogen, capable of causing cancers of the gastrointestinal tract. Aflatoxin: A product of Aspergillus flavus, a mold that thrives on poorly preserved grain foods. In the body, aflatoxin is converted to epoxide, which is a strong carcinogen and can cause liver cancer. Arsenic-containing compounds have the potential to cause skin cancer; Pesticides can cause liver cancer.
Trắc nghiệm: Thử hiểu biết của bạn về bệnh ung thư
Ung thư là nguyên nhân gây tử vong hàng thứ 2 trên thế giới. Thử sức cùng bài trắc nghiệm sau đây sẽ giúp bạn có thêm kiến thức về yếu tố nguy cơ cũng như cách phòng ngừa bệnh ung thư.
Bài dịch từ: webmd.com
2. The radiation (radiation)
Radiation energy, in the form of ultraviolet rays of sunlight or in the form of ionizing radiation, can cause transformation of cultured cells, giving rise to cancer in humans and laboratory animals.
2.1. Ultraviolet ray
Ultraviolet rays present in sunlight are divided into 3 types according to wavelength: UVA (320 - 400 nm), UVB (280 - 320 nm) and UVC (200 - 280 nm). UVB is considered the main agent that can cause many different types of skin cancer such as melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma. Caucasians have a higher risk of developing the disease than people of color due to the lack of the protective effect of the pigment melanin in the epidermis (which helps absorb ultraviolet rays). UVC is also carcinogenic, but fortunately it is largely blocked by the ozone layer that surrounds the earth. Thus, the current destruction of the ozone layer by emissions from the ground (such as chlorofluorocarbon refrigerants) is likely to increase the number of skin cancer cases in the future.
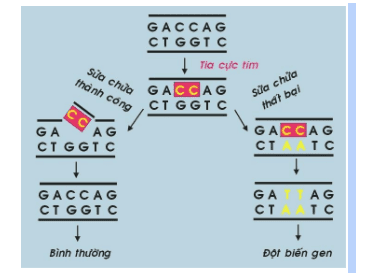
The mechanism of UV carcinogenesis is due to its effect on DNA molecules, creating bridges between pyrimidine bases. If these DNA damage is not repaired in time, gene mutations can occur and lead to cancer.
2.2. Ionizing radiation
There are two types: Electromagnetic waves (X-rays, gamma rays) and charged or high-energy particles (alpha particles, beta particles, protons, neutrons). All are potentially carcinogenic as has been shown by the increased incidence of various cancers in survivors of the two atomic bomb explosions in Japan in 1945 and the explosion of the Tchernobyl nuclear power plant. in the Soviet Union in 1986.
Uranium mining workers also have a 10 times higher incidence of lung cancer than the general population. Even therapeutic doses of radiation can cause cancer if not administered correctly. For example, 9% of children who were irradiated to the chest area as children will later develop thyroid cancer.
There is a difference in the sensitivity of body tissues to the carcinogenic effects of ionizing radiation. Particularly sensitive tissues include hematopoietic tissue, thyroid gland, parotid gland, breast, lung. Otherwise; Skin, bones, and gastrointestinal tract are relatively less sensitive.
The carcinogenic mechanism of ionizing radiation is due to their ability to cause gene mutations and chromosomal disorders.
Please follow the website: Vinmec.com regularly to update many other useful information.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.