This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by BSCK II Pham Thi Van Hanh, Children's Center, Vinmec Times City International Hospital
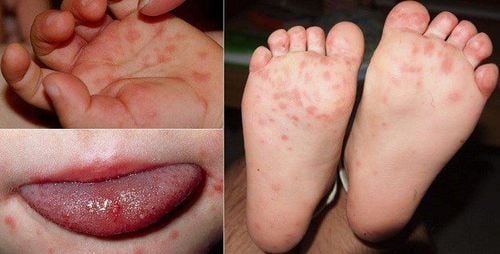
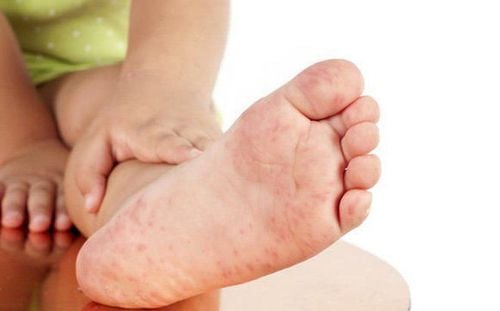
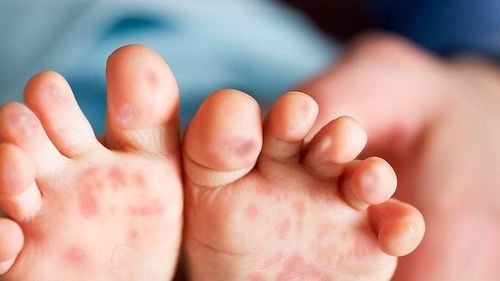
Hand, foot and mouth disease is an acute disease, common in young children, caused by intestinal virus infection. The disease develops in 4 stages, each level will have different symptoms and treatment. If not handled properly and promptly, it will cause many dangerous complications to the brain, respiratory system and cardiovascular system.
1. Signs of serious illness to watch out for - Hospitalization criteria
1.1 Signs of serious illness to watch out for When a child shows the following symptoms, which is a sign of a serious illness, parents need to pay close attention to take them to the hospital early:
Fever over 39 degrees continuously too 48 hours. panic or lethargy, constant startling; Fatigue, profuse vomiting, inability to eat, dehydration or intoxication; Neurological signs: myoclonus, muscle laxity, altered sensation, tremor, unsteady gait; Cardiovascular abnormalities: Heart rate, hypertension, gallop rhythm; Shortness of breath, rapid breathing, irregular breathing, shock, purple veins; Laboratory tests: High white blood cells, high blood sugar. Blood troponin is elevated. Echocardiography: Left ventricular dysfunction. X-ray: Pulmonary edema, enlarged heart. CT, MRI of the brain: Brain stem damage, brain edema; Transition signs to watch out for: Grade 1 sign of change 2: Startle Grade 2 sign of grade 3: High fever that is difficult to lower, tachycardia, high blood pressure, rapid breathing. Severe medical conditions/severe complications: Respiratory failure, pulmonary edema. Meningitis, shock, myocarditis, heart failure, inflammation of the brain (brain stem), spinal cord (lethargy, sensory disturbances, tremor, myoclonus, convulsions, paralysis). Dehydration, electrolytes (due to diarrhea, sore throat, fatigue, poor appetite). 1.2 Hospitalization criteria Hand, foot and mouth disease grade 1, but far from home or have no conditions for care, can be monitored at home
Hand, foot and mouth disease grade 2a to grade 4 requires hospitalization.
Tùy từng cấp độ bệnh mà cha mẹ cho bé điều trị tại viện
2. Treatment
The disease has no specific treatment, only supportive treatment. Need close monitoring, grading, early detection and treatment of complications. Ensure adequate nutrition, improve the health of the baby.
2.1 Specific treatment To be applied depending on the severity of the disease according to the clinical classification.
2.1.1 Grade 1 Hand, foot and mouth disease grade 1 Outpatient treatment and monitoring at the primary health care facility:
Adequate nutrition. Breastfed babies need to continue to be fed breast milk. Oral hygiene, grease to help soothe the skin, mucous membranes, antiseptic. Rest, avoid stimulation, isolate at home. Reduce fever when high fever with Paracetamol dose 10-15 mg/kg/time (oral) every 6 hours. After 1-2 days, the patient needs to be re-examined during the first 8-10 days of illness. Fever children must be examined every day until the fever is gone for at least 48 hours. It is necessary to re-examine immediately when having symptoms of hand, foot and mouth disease of grade 2a or higher such as: + High fever ≥ 390C.
+ Rapid breathing, difficulty breathing.
+ Tremor, startle, lethargy, fussy, vomiting a lot, restlessness, trouble sleeping.
+ Walk unsteadily.
+ Sweating, purple skin, cold hands and feet.
+ Convulsions, coma.
2.1.2 Grade 2 Hand, foot and mouth disease grade 2 inpatient hospital treatment:
Grade 2a
Treat as grade 1. In case the child has a high fever who does not respond well to paracetamol, it can be combined with ibuprofen 5-10 mg/kg/repeat every 6-8 hours if needed (alternating with paracetamol), do not use antipyretic group Aspirin. The maximum total Ibuprofen dose is 40 mg/kg/day. Medicine: Phenobarbital 5-7 mg/kg/day, taken when the child is startled or fussy Monitor closely for signs of movement.

Trẻ mắc tay chân miệng độ 2 thường được điều trị bằng thuốc
Grade 2b
Treatment in emergency room or resuscitation room
Head elevation 30°. Breathe oxygen through the nose 3-6 liters/min. If the child has a fever, it is necessary to actively reduce the fever. Drugs: + Use Phenobarbital 10 - 20 mg/kg intravenously. Repeat after 8-12 hours as needed. (How to use Danotan 100 mg/1ml: mix 1ml with 19ml of distilled water, take the required dose into the solvent, infuse in 30 minutes).
+ Immunoglobulin: Group 2: 1g/kg/day by slow intravenous infusion over 6-8 hours. After 24 hours, if there are signs of grade 2b, the second dose should be used. Group 1: Routine Immunoglobulin is not indicated. If symptoms do not subside after 6 hours of treatment with Phenobarbital, then immunoglobulin should be indicated. After 24 hours re-evaluate to decide on the second dose as group 2.
Monitor pulse, temperature, blood pressure, respiratory rate, breathing pattern, consciousness, rales, urine every 1-3 hours for the first 6 hours , then every 4-5 hours. Measure SpO2 oxygen saturation and monitor pulse continuously. 2.1.3 Grade 3 Inpatient treatment in the intensive care unit, closely monitor the progression of respiratory and circulatory complications (6-8 hours after the appearance of high fever + tachycardia).
Breathing oxygen through the nose bridge 3 -6 liters / min, keeping SpO2 94 - 96%. Early intubation when oxygen fails. Increase ventilation to keep SpO2 from 94 to 96%, PaCO from 30-35 mmHg and maintain PaO2 from 90-100 mmHg.
Bé được đặt nội khí quản sớm khi thất bại với thở oxy
Anti-cerebral edema: head lying 30°, ensure adequate cerebral perfusion pressure, limit fluid (total fluid is 1/2-3/4 of normal need). Phenobarbital 10 - 20 mg/kg IV infusion. Repeat after 8-12 hours as needed. Immunoglobulin (Gammaglobulin): 1g/kg/day by slow intravenous infusion over 6-8 hours, used for 2 consecutive days Dobutamine is indicated when cardiovascular failure > 170 times/minute, starting dose of 5μg/kg/minute IV infusion pulse, gradually increasing 1-2.5 μg/kg/min every 15 minutes until clinical improvement; maximum dose 20μg/kg/min (without Dopamine). Milrinone IV infusion 0.4 μg/kg/min in high blood pressure, for 24-72 hours. Treatment of convulsions if present: Midazolam 0.15 mg/kg/time or Diazepam 0.2-0.3 mg/kg by slow intravenous infusion, repeat after 10 minutes if convulsions persist (maximum 3 times). Active antipyretic. Antibiotics are only used when superinfection or other serious infections have not been ruled out. Monitor pulse, breathing rate, rales, temperature, blood pressure, consciousness, SpO2, every 1-2 hours. If possible, invasive arterial blood pressure monitoring should be performed. 2.1.4 Grade 4 Hand, foot and mouth disease grade 4 is treated as an inpatient in the intensive care unit
Intubation with mechanical ventilation: Increase ventilation to keep PaCO2 from 30-35 mmHg and maintain PaO2 from 90-100 mmHg. Anti-shock: Shock due to damage to the vasomotor center in the brain stem or myocarditis. + If no clinical signs of pulmonary edema or heart failure: Infusion of 0.9% sodium chloride or Ringer lactate: 5 ml/kg/15 minutes, adjust rate according to CVP guidelines and clinical response. In the absence of CVP, it is necessary to closely monitor for signs of overload, acute pulmonary edema.
+ Dobutamine starting dose 5μg/kg/min, gradually increased 2-3μg/kg/min every 15 minutes until effective, maximum dose 20 μg/kg/min.
Acute pulmonary edema : + Immediately stop the infusion if the infusion is in progress
+ Use Dobutamine at a dose of 5-20 μg/kg/min.
+ Furosemide 1-2 mg/kg/time intravenously indicated for fluid overload.
Bé có dấu hiệu bị phù phổi cấp cần ngừng truyền dịch ngay
Adjust acid-base disorders, electrolytes, hypoglycemia and prevent cerebral edema. Continuous dialysis or ECMO (if available). Immunoglobulin: Indicated when the mean blood pressure is ≥ 50 mmHg. Antibiotics are only used when superinfection or other serious infections have not been ruled out. Monitor pulse, temperature, blood pressure, breathing rate, consciousness, rales, SpO2, urine every 30 minutes for the first 6 hours, then adjust according to clinical response; Central venous pressure per hour, if possible, should be invasive arterial blood pressure monitoring.
3. Prevention
3.1 Principle There is currently no specific vaccine. Apply standard precautions and precautions for gastrointestinal infections, with particular attention to direct contact with the source of infection.
3. 2. Disease prevention at medical facilities. Isolation by disease group. Medical staff: wash and disinfect hands before and after providing care. Wear masks. Disinfect surfaces, beds, and chambers with 2% Chloramin B. Note disinfecting the seats of patients and relatives at the examination area. Dispose of patient waste, clothing, bed linen, and reusable care equipment according to procedures to prevent gastrointestinal disease. 3.3 Prevention in the community Personal hygiene, wash hands with soap before eating, after playing with toys, after changing clothes, diapers, after contact with feces, saliva. Do not share personal belongings. Wash toys, utensils, floors, handrails, doorknobs. Wipe the floor with 2% Chloramin B solution or other disinfecting solutions. Isolate sick children at home. Do not let children go to kindergartens, schools, places where children play together in the first 10-14 days of illness.

Rửa sạch đồ chơi giúp phòng tránh bệnh tay chân miệng cho bé
When the baby has the first symptoms of hand, foot and mouth disease, parents should take the child to a reputable medical facility for early examination and treatment, to avoid causing dangerous complications. As a key area of Vinmec Medical system, Pediatrics Department always brings satisfaction to customers and is highly appreciated by industry experts with:
Gathering a team of leading pediatricians: including leading experts with high professional qualifications (professors, associate professors, doctorates, masters), experienced, worked at major hospitals such as Bach Mai, 108.. Doctors All are well-trained, professional, with a mind - range, understanding young psychology. In addition to domestic pediatric specialists, the Department of Pediatrics also has the participation of foreign experts (Japan, Singapore, Australia, USA) who are always pioneers in applying the latest and most effective treatment regimens. . Comprehensive services: In the field of Pediatrics, Vinmec provides a series of continuous medical examination and treatment services from Newborn to Pediatric and Vaccine,... according to international standards to help parents take care of their baby's health from birth to childhood. from birth to adulthood Specialized techniques: Vinmec has successfully deployed many specialized techniques to make the treatment of difficult diseases in Pediatrics more effective: neurosurgery - skull surgery, stem cell transplantation. blood in cancer treatment. Professional care: In addition to understanding children's psychology, Vinmec also pays special attention to the children's play space, helping them to have fun and get used to the hospital's environment, cooperate in treatment, improve the efficiency of medical treatment. SEE ALSO:
3 warning signs of severe stage hand, foot and mouth disease in young children Diagnosis and treatment of hand, foot and mouth disease in infants Hand, foot and mouth disease: 48 hours without fever, rest assured?
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.






![[Vinmec - Q&A with experts] Number 02: Children's health in hot season (Part 1)](/static/uploads/small_20190723_082829_863235_Banner_FB_1200x628_max_1800x1800_png_982bf67b1c.png)