This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by BSCK II Pham Thi Van Hanh, Children's Center, Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Acute diarrhea is a common illness in young children. The disease is caused by many reasons, causing the baby's body to become dehydrated. If not treated promptly, rehydration will cause many dangerous complications. So what is the right way to rehydrate the baby and how to take care of the baby with acute diarrhea?
1. Treatment of acute diarrhea in children
1.1 Treatment goals Prevention and treatment of dehydration, electrolyte disorders; Reduce duration and severity of diarrhea, reduce diarrhea recurrence by zinc supplementation; Malnutrition prevention; Prevention of spread. 1.2 Principles of treatment according to WHO Rehydration and electrolytes: choose an appropriate rehydration regimen based on 3 factors: Degree of dehydration – helps to choose rehydration regimens A and B, Risk of oral failure; Severe comorbidities (hypoglycaemia, metabolic acidosis, electrolyte disturbances) make it possible to choose oral or intravenous fluid replacement. Timely treatment of complications; Specific treatment (antibiotics) if indicated; Supplementing with elemental zinc for 14 days; Nutrition counseling, continuing to feed children according to age; Guidance on signs of serious illness that need monitoring, hygiene, food safety, routine hand washing to avoid community spread. 1.3 Specific treatment regimen Regimen A- Oral
Home treatment for non-dehydrating diarrhea, with no risk of oral failure and no other complications of diarrhea.
Give the child as much extra fluid as possible if he wants to Boost Breastfeeding How to give ORESOL solution (ORS) to reduce osmotic pressure: Children < 2 years old: 50-100 ml after each diarrhea
Children ≥ 2 age: 100 -200 ml after each diarrhea
Other solutions: Clean water, porridge, soup, coconut water, unsweetened fruit juice.
Continue to feed children to prevent malnutrition
Attention:
Solutions to avoid: Sugar-sweetened beverages cause osmotic diarrhea, stimulants cause diuresis. Should be given spoon by spoon, older children take sips by cup. If the child vomits, stop waiting for 5-10 minutes and then continue to give it again. Zinc supplementation: Children < 6 months old, take 10mg of elemental zinc/day x 14 days Children ≥ 6 months of age take 20mg of elemental zinc/day x 14 days Instruct mothers when to bring their children to a follow-up or immediate examination.
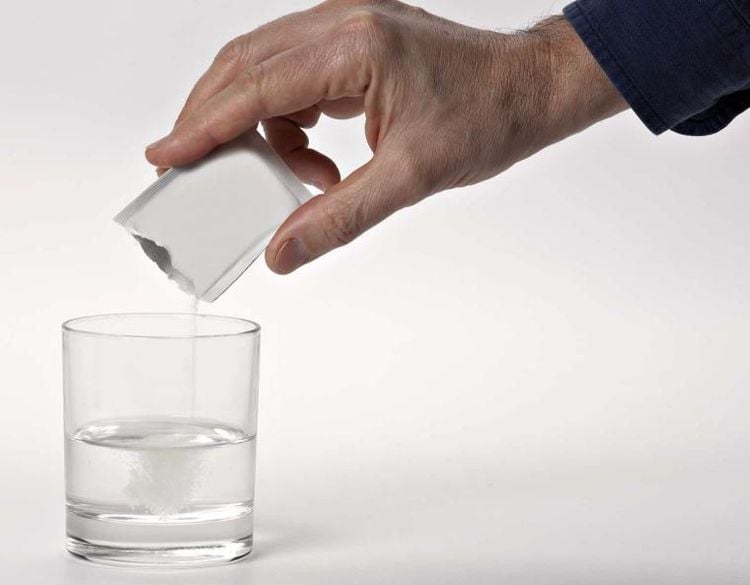

Trẻ bị tiêu chảy cấp có thể được điều trị tại nhà bằng oresol
Regimen B – Oral
Treatment of dehydration with Oresol to reduce osmotic pressure, oral rehydration in medical facilities for children with dehydration but no risk of oral failure and no complications other heavy. Rehydration with Oresol reduces oral osmolality by 75 ml/kg over 4 hours. After 4 hours: reassess and reclassify dehydration: + If severe dehydration occurs: treat according to regimen C
+ If dehydration persists: continue oral rehydration according to regimen B 2nd time. Start giving the child food and drink and continue to evaluate the child more often
+ If there is no longer dehydration: Treat according to protocol A
When oral therapy fails due to: Severe diarrhea, profuse vomiting , poor oral intake: Drink through a nasogastric drip or intravenous infusion of Lactate Ringer solution How to give it:
Children 2 years old, give it by spoon, give 1 teaspoon every 1-2 minutes, for older children, give it to drink. sip by cup.
If the child vomits, stop drinking for 10 minutes, then give it more slowly.
Regimen C
Treatment for children with severe dehydration
Intravenous infusion immediately. While establishing the line for oral administration of Oresol if the child is still able to drink. Infusion solution: choose Ringer Lactate solution (or physiological saline solution) 100 ml/kg. Divide the quantity and time as follows:
*Transmit one more time if the circuit is weak or not picked up.
Reassess every 15 -30 minutes until pulse is strong. If dehydration does not improve give fluids at a faster rate, then reassess every 1 hour until dehydration improves. Note that 100ml/kg is the amount of water lost in severely dehydrated children >10% of body weight, excluding the amount of water that continues to be lost if the child still vomits and has diarrhea to calculate the amount of fluid that needs to be rehydrated.

Trẻ bị tiêu chảy cần được bổ sung đủ nước tránh gây nguy hiểm đến sức khỏe
Reassess when adequate volume of fluid is infused, if: + There are signs of severe dehydration: second infusion with regimen C.
+ There is improvement but still dehydration: stop infusion, give ORS regimen B if not oral failure and no other complications and breastfeeding. If oral failure or other complications persist, continue infusion.
+ If dehydration is gone: Treat with regimen A, breastfeed regularly and monitor for at least 6 hours before discharge.
+ Give Oresol as soon as the child can drink
If not infusion, put a nasogastric tube for Oresol with the amount of 20ml/kg/hour (total 120ml/kg), if possible, transfer to a higher level for infusion Feed back again when the child can eat. Indications for intravenous fluid replacement in acute diarrhea
Children with severe dehydration. The child is dehydrated due to failure of oral rehydration or other serious complications. The child is not dehydrated, but monitoring shows that the child actually fails oral rehydration or has other serious complications. Indications for antibiotic treatment in the treatment of acute diarrhea
Diarrhea with bloody stools. Diarrhea suspected of cholera. There is a systemic or non-intestinal infection. Severe malnourished or immunocompromised. Diarrhea caused by Giardia. Antibiotics used in the treatment of diarrhea causes:
When the cause cannot be determined, use Ciprofloxacin 30 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses for 3-5 days or Ceftriaxon 80-100 mg/kg/day intravenously pulse x 5 days Shigella: Ciprofloxacin 30 mg/kg/day divided into 2 times x 5 days. Cholera: Azithromycin 6 -20 mg/kg/day x 1-5 days. Young samonella - typhoid: only give antibiotics when there is immunosuppression, severe malnutrition, organ transplant. Giardia lamblia: Metronidazole: 30 -40 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses for 7 days. Campylobacter: Azithromycin 5-10 mg/kg/day x 5 days Other drugs in the treatment of acute diarrhea:
Zinc supplementation: Children 1- < 6 months old: 10mg/day x 10-14 days Children ≥ 6 months old : 20mg/day x 10-14 days Probiotics: Correct use of Lactobacillus rhamnosus or Saccharo mycesboulardii, give early at the very beginning of the disease, take for 5-7 days Antiemetic: Ondansetron: can it prevent vomiting in children with acute diarrhea dehydration. Do not use if the child is dehydrated or has a potassium and magnesium disorder

Trẻ bị tiêu chảy cấp nên được bổ sung thêm kẽm
2. Nutrition for children with acute diarrhea
Feed the baby early with a daily diet 4-6 hours after rehydration with increasing amounts If breast-feeding: continue to breastfeed more often and longer. If the baby is not breastfed: Choose the type of milk that the baby has eaten before, do not dilute the milk. Lactose-free milk should not be routinely given to children with acute diarrhea. Avoid foods that are low in energy, protein and electrolytes and high in carbohydrates. When diarrhea is gone, add 1 meal/day in addition to regular meals for 2-4 weeks. Do not use anti-vomiting drugs, take them out.
3. Backup
Breastfeeding: Breastfeed your baby immediately after birth and exclusively breastfeed for the first 6 months. Use vaccines against diarrhea. Fully vaccinated according to the expanded immunization program. Specific prevention of diarrhea with vaccines: Rotavirus, cholera, typhoid. Improve weaning habits. Use clean water for sanitation and drinking. Practice food safety and hygiene when preparing or storing food. Use hygienic toilets.
Tiêm vắc-xin là cách phòng bệnh tiêu chảy hiệu quả nhất cho bé
As soon as the baby has symptoms of diarrhea, the mother should take the baby to the doctor as soon as possible for timely treatment, to avoid causing many dangerous complications.
As a key area of Vinmec Health system, Pediatrics Department always brings satisfaction to customers and is highly appreciated by industry experts with:
Gathering a team of top doctors and nurses in Pediatrics : consists of leading experts with high professional qualifications (professors, associate professors, doctorates, masters), experienced, worked at major hospitals such as Bach Mai, 108.. Doctors All doctors are well-trained, professional, conscientious, knowledgeable about young psychology. In addition to domestic pediatric specialists, the Department of Pediatrics also has the participation of foreign experts (Japan, Singapore, Australia, USA) who are always pioneers in applying the latest and most effective treatment regimens. . Comprehensive services: In the field of Pediatrics, Vinmec provides a series of continuous medical examination and treatment services from Newborn to Pediatric and Vaccine,... according to international standards to help parents take care of their baby's health from birth to childhood. from birth to adulthood Specialized techniques: Vinmec has successfully deployed many specialized techniques to make the treatment of difficult diseases in Pediatrics more effective: neurosurgery - skull surgery, stem cell transplantation. blood in cancer treatment. Professional care: In addition to understanding children's psychology, Vinmec also pays special attention to the children's play space, helping them to have fun and get used to the hospital's environment, cooperate in treatment, improve the efficiency of medical treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.













