This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Specialist Doctor I Tran Thanh Phuoc - Pediatrician - Pediatric Center - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.What is chickenpox?
Chickenpox (also known as varicella) is caused by the Varicella Zoster virus (VZV). The disease can occur at any age, of which children are the most susceptible.The average incubation period is 14 - 16 days (some people can develop the disease earlier - about 10 days, or later - more than 20 days). Chickenpox is transmitted directly through the respiratory tract (talking, coughing, sneezing...) when in contact with sick people. In addition, the disease can be transmitted indirectly through the patient's daily necessities such as clothes, towels, bed sheets...
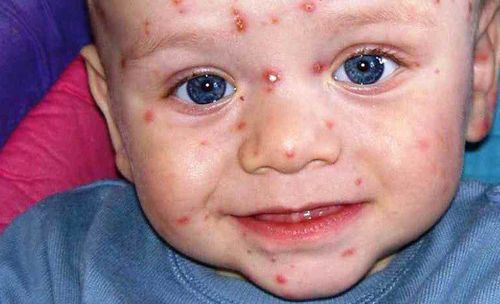
Initially, the patient will have symptoms such as fever, headache or muscle pain, fatigue, or loss of appetite. After that, the patient will develop red round nodules (chicken sores) for about 12-24 hours. The warts will gradually progress to blisters containing clear fluid, which can grow all over the body or scattered throughout the body, averaging from 100 to 500 nodules.
In normal cases, chickenpox will last from 5 to 10 days if there are no complications, the chickenpox will gradually dry, scab, darken the skin where the blisters appear, leaving no scars. However, if the blister is infected with bacteria, it can leave a scar.
Chickenpox can cause dangerous complications such as meningitis,
hemorrhage, sepsis, chickenpox infection, cellulitis, hepatitis, pneumonia... Some cases can cause death if the patient is not treated promptly.
Until now, the best way to prevent chickenpox is by vaccination.
Varieties of vaccines against chickenpox
In the early stages when the virus enters -Varivax vaccine (USA)
Varivax is a live, attenuated vaccine, indicated for the prevention of chickenpox in children over 12 months of age and adults without immunity. .
-Varicella vaccine (Korea)
Varicella is a freeze-dried vaccine of the live attenuated varicella virus (Varicella). After mixing with reconstituted water, it forms a clear, colorless or pale yellow solution indicated for the prevention of chickenpox in children over 12 months of age and non-immune adults.
-Varilrix vaccine (Belgium) Can be given early to children from 9 months of age, the body's incubation period. Depending on each person's condition, this incubation period can last from 7 to 21 days and has symptoms similar to common cold, loss of appetite, fatigue. This is the most contagious period.
Newborns born to mothers with chickenpox are at very high risk of infection. The reason is that the children at this stage are still very immature, so the immune system is not yet able to fight the disease and the mother got sick but was detected late, so she did not isolate the child early. In case the mother is infected 5 days before or 2 days after giving birth, the baby will be highly contagious because the mother's antibodies have not yet formed to pass to the baby. In addition, children will have a high risk of death up to 30%.
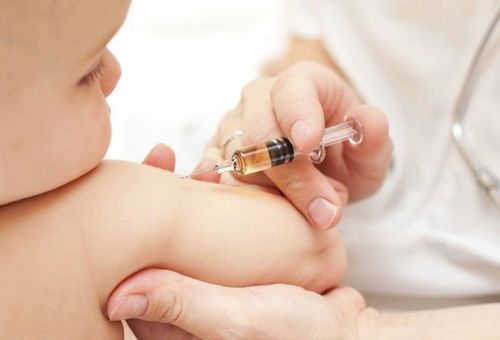
Tiêm vắc-xin phòng bệnh thủy đậu ở trẻ em
When is the chickenpox vaccine given?
If you have never had chickenpox or have not been vaccinated (vaccinated), you can still get it. Children, pregnant or lactating women, the elderly, etc. are subjects with a less active immune system than usual, so the risk of infection increases and is prone to dangerous complications such as: pneumonia, meningitis... can be fatal. Therefore, getting the chickenpox vaccine is the best way to protect yourself against this dangerous disease.For pregnant women, especially during the first 13-20 weeks of pregnancy, having chickenpox can lead to miscarriage or birth defects in the fetus (cranial malformations, multiple malformations in heart disease, microcephaly...). If the mother has chickenpox in the days leading up to the birth, the child is infected with a lot of blisters and is prone to pneumonia complications.
Women should complete the injection schedule at least 3 months before becoming pregnant. Vaccinate (shot) 2 doses at least 1 month apart.
Two doses of the vaccine are up to 98% effective in preventing any form of the disease, and 100% of the cases given the full dose avoid serious illness. All adults who have never had chickenpox, have not been vaccinated (vaccinated), as well as those whose blood tests show no protective immunity to varicella virus should be vaccinated.
Chickenpox vaccine is indicated to create active immunity, prevent chickenpox for the following groups:
Children over 12 months old; Adults, especially women, who want to get vaccinated to protect against chickenpox before trying to get pregnant; Susceptible people, including nursing mothers, if exposed to chickenpox within 3 to 5 days of being exposed to an infected person.
Should I get the chickenpox vaccine while breastfeeding?
Women who are breastfeeding may be considered for measles-mumps-rubella or chickenpox vaccine while in an outbreak-prone area and with a history of incomplete immunization. Breastfeeding women who have chickenpox will pass it on from mother to baby if good isolation measures are not taken. Children who are breast-feeding if they have not been vaccinated against chickenpox, especially before the first 12 months of life if they are infected with chickenpox, are susceptible to serious complications. Therefore, vaccinate against chickenpox before pregnancy and during breastfeeding if the mother has not been vaccinated. Being vaccinated or at high risk is the most effective way to prevent disease for mother and babyNo studies have shown that live and inactivated vaccines when given to nursing mothers are unsafe for both mothers mother and infant. Although the live virus contained in the vaccine can multiply in people who are vaccinated, most of these vaccine viruses are not found in breast milk. Or if the virus contained in the live vaccine can be present in breast milk such as rubella or polio... but the virus usually does not cause illness in the baby because it is already weakened. There is no evidence that passive transmission of antibodies from mother to infant through breast milk can affect the protective efficacy of the live vaccine in the infant. Therefore, breastfed babies must be vaccinated according to the vaccination schedule prescribed for their age.
In case the mother has not been vaccinated against the disease and has never had chickenpox, the chickenpox vaccine can be vaccinated while breastfeeding, without affecting the baby. Rubella, varicella, hepatitis vaccines during lactation.
If you have your own vaccination record, you should check to see if you have been fully vaccinated against chickenpox. If you have had 2 doses of chickenpox vaccine, you do not need to be vaccinated again. Once cured of chickenpox, you have lifelong immunity, so if you have had chickenpox in the past, you do not need to be vaccinated.
Injection schedule and dose Children 12 months - 12 years old: Inject 1 dose of Varivax 0.5ml. dose 2 repeated at least 3 months apart from dose 1 Adults and children over 13 years old, never had chickenpox: 2 injections: 1st dose: The first injection, 0.5ml dose; Nose 2: Inject 0.5ml dose 3 months after the 1st dose. How long does the chickenpox vaccine last? After being introduced into the body, the chickenpox vaccine will take 1-2 weeks to be effective. The immunity of the chickenpox vaccine lasts an average of 15 years. After about 15 years after vaccination, each person can get a booster shot to prevent chickenpox more effectively.
Side effects after vaccination with chickenpox vaccine
Painful swelling, redness, itching, hematoma, hard lump at the injection site Itching, fever and rash, which can manifest within 1-3 weeks after vaccination injection Chickenpox-like rash at the injection site or over the body within 2 to 4 weeks after injection. Reactions such as fever, swelling, pain, and itching will go away on their own after 1-2 days. The rash will also clear up on its own within 4 weeks.
In very rare cases there may be bleeding, nosebleeds or bleeding in the lining of the mouth. If this happens, the mother should take the child or the sick person to medical facilities for care and treatment.
Subjects who are not vaccinated or delayed vaccination against chickenpox The vaccine is not used for subjects such as:
Fever or malnutrition; Cardiovascular disease, liver and kidney dysfunction; There is a history of hypersensitivity to Kanamycin and Erythromycin; Have a history of convulsions within one year prior to vaccination; Cellular immunodeficiency; Pregnant or 2 months before trying to become pregnant; Have had other live vaccines (oral polio vaccine, measles vaccine, rubella vaccine, mumps vaccine and BCG vaccine) within the last 28 days; There is a history of hypersensitivity to any component of the vaccine; Primary or acquired immunodeficiency such as immunodeficiency in AIDS or clinical manifestations of human immunodeficiency virus infection; Patients with acute myeloid leukemia, T-cell leukemia or malignant lymphoma. Patients with severely suppressed immune systems due to radiation therapy or the attacking phase of leukemia treatment Precautions for vaccination with varicella vaccine Need to be fully prepared with adrenaline and other medical means to prevent shock anaphylaxis;
People who get the vaccine can pass chickenpox to people at high risk. Therefore, within 6 weeks after vaccination, vaccinated people should avoid contact with high-risk subjects such as: Pregnant women who have not been vaccinated against chickenpox, immunocompromised people, infants have a mother who has not had chickenpox, a caregiver who is not immune; Women should avoid becoming pregnant for at least 3 months after the injection; Use caution when administering varicella vaccine to nursing women; Delay vaccination for at least 5 months after blood or plasma transfusion and varicella zoster immunoglobulin injection; Within 2 months of receiving chickenpox vaccine, do not use any immunoglobulin unless directed by your doctor; Within 6 weeks of vaccination, do not take medicine containing salicylate; If varicella vaccine is not used concurrently with MMR II (measles-mumps-rubella) vaccine, it should be given at least 1 month apart; Chickenpox vaccine can be used concurrently with oral polio vaccine (OPV) or concurrently with DTAP (diphtheria - tetanus - acellular pertussis) and Hib vaccines. However, it is necessary to inject with a separate pump and inject at different sites. Currently, Vinmec hospital has enough of both chickenpox vaccines: Varivax (USA) and Varilrix (Belgium). Vaccines at Vinmec are preserved by the optimal cold chain (cold storage, refrigerator containing vaccines containing vaccines). over-temperature warning device). Customers and children who come to get vaccinated at Vinmec can view the vaccination schedule and the child's vaccination plan via convenient phone or computer. Vinmec's team of experienced doctors can advise families fully, not only about vaccines, but also provide detailed advice on vaccines and how to care for and nurture children.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.