This is an automatically translated article.
The uterus acts as a nesting cradle for the developing fetus and is also the place where a woman's monthly menstrual cycle occurs. With that important role, the uterus is also the place with the most ups and downs in obstetrics and gynecology.1. Structure of the uterus
The structure of the uterus is anatomically located in the pelvis, pear-shaped, composed of 3 layers, from the outside to the inside, including the outermost serosa layer, followed by the smooth muscle layer and the innermost layer. is the lining of the uterus.The endometrium is composed of stratified squamous epithelium, which is influenced by the body's monthly sex hormones.
2. Benign diseases of the uterine lining

Polyp nội mạc tử cung
About 6 - 10% of patients have no symptoms, diagnosed by chance during physical examination, or hysterosalpingogram to diagnose infertility. Menorrhagia and bleeding are the most common symptoms, especially in the case of large polyps with long stalks hanging down the cervix, with a lot of white blood.
Ultrasound of the uterus and two appendages can detect polyps and determine the location and size of polyps. Hysterosalpingogram with contrast, helps to clearly see the polyp shape, helps to see one or more polyps.
Treatment: polypectomy under laparoscopic guidance; Some authors suggest that it is possible to combine progesterone drugs to improve estrogenic status.
2.2 Endometrial hyperplasia Is a condition of hyperplasia of the endometrium, characterized by an increase in both quantity and density of endometrial components. Endometrial hyperplasia is usually due to hyperestrogenism or to a decrease in corpus luteum progesterone.
In fact, we often see in the following groups of subjects: during puberty, endometrial proliferation due to a non-ovulatory cycle. In the perimenopausal age due to decrease in corpus luteum progesterone and in the postmenopausal age group, it is often due to an increase in exogenous estrogen because of the use of hormone replacement.
Diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia, irregular menstrual cycle, intermenstrual bleeding, menorrhagia, hypermenorrhea. Ultrasound showed an increase in the thickness of the uterine lining. Endoscopic hysteroscopy, showing images such as: thickened uterine lining, irregular endometrial papillae, combined with accurate curettage and biopsy.
Proliferation of the uterine lining in girls does not need treatment, it is necessary to adjust the proper nutrition and get regular rest. For the pre-menopausal age group that needs endometrial biopsy for pathological examination, when the uterine lining proliferates without typical cells, high-dose progesterone can be used for 6 months and then re-examined; In case the pathology results show that there is atypical proliferation of endometrial cells, complete hysterectomy should be treated.
2.3 Endometrial atrophy

Teo nội mạc tử cung xảy ra ở phụ nữ mãn kinh do thiếu hụt nội tiết tố từ buồng trứng
Diagnosis: often without clinical manifestations, sometimes with abnormal bleeding, small amount, recurrence, examination shows atrophy of the external genitalia including vaginal atrophy, cervical atrophy.
Treatment: only ask for treatment when there is an abnormality, often using low-dose estrogen in combination with antibiotics. If treatment is unsuccessful, total hysterectomy should be performed.
2.4 Adhesion of the uterine lumen The feature of uterine adhesions occurs after a trauma, due to adhesions of the superficial uterine wall, secondary to curettage procedures, loss of a uterine cavity. significant amount of the uterine lining. The possibility of uterine adhesions increases when performing curettage procedures on the pregnant uterus, because the uterine lining is often soft and congested during pregnancy, easily damaging the basal cells. In addition, there are causes due to curettage, biopsy, fibroid removal, and plastic surgery that also stick to the uterine lumen.
The location of uterine adhesions can be in the center of the fundus, on both sides or the waist of the uterus, the consequences of uterine adhesions can cause infertility, during pregnancy, it is easy to cause miscarriage, after delivery, the placenta becomes implanted. comb teeth or missing each other.
Diagnosis of uterine adhesions on clinical manifestations of oligomenorrhea, amenorrhea or amenorrhea, severe abdominal pain when menstruating. Hysterosalpingography has contrast, has defects, has atrophy and narrowing of the uterine lumen. Hysteroscopy is valuable in determining the location of adhesions in combination with treatment.
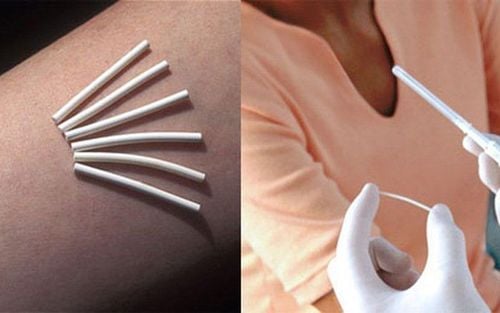
Treatment, combined with hysteroscopy to treat by cutting the adhesion, then placing the silastic plate for 10-15 days, then replacing it with an IUD. In addition, it is possible to combine the use of estrogen once to stimulate the rapid regeneration of the uterine lining after removal of adhesions.
Vinmec International General Hospital provides female customers with a package of gynecological examination and screening. This examination package helps customers to detect inflammatory diseases early, thereby treating the disease easily and inexpensively. At the same time, Vinmec's gynecological examination service package also helps screen and detect cervical cancer early.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.