This is an automatically translated article.
Excessive hair loss becomes a headache for both men and women. This condition is not only unsightly, but it can also be a sign of a medical condition. Therefore, finding out information about hair and hair loss is extremely necessary.
1. What is hair loss? Stages of hair loss
Hair grows everywhere on human skin except in places like palms, soles, eyelids and navel. Many parts have hairs so fine that we can barely see them.
Hair is made up of a protein called keratin that is made in the hair follicles in the outer layer of the skin. As the hair follicles make new hair cells, the old cells are pushed out through the surface of the skin at a rate of about 6 inches a year. The hair you can see is actually a string of dead horny cells. The average adult scalp has about 100,000 to 150,000 hairs and can shed 100 hairs per day.
About 90% of hair follicles are still growing hourly. Each follicle has its own life cycle that can be influenced by age, disease, and many other factors. This life cycle is divided into three phases:
Anagen - hair growth usually lasts from two to eight years. Catagen - transitional hair growth, lasting two to three weeks. Telogen - the resting phase, which lasts about two to three months. At the end of the resting period, the hair falls out, a new hair takes its place, and the growth cycle begins again. As people age, the rate of hair growth slows down.

Rụng tóc kéo dài có thể là dấu hiệu của bệnh lý.
2. Types of hair loss
Certain types of hair loss:
Physiological alopecia is a natural condition, the hair will fall out and thin with age. At some point, many hair follicles will enter the resting phase. As a result, the hair will become shorter and less dense. Hormonal alopecia areata is an inherited condition that can affect both men and women. Male pattern baldness is also known as male pattern baldness. Men can begin to lose their hair as early as their teens or early 20s. Women are also at increased risk of hormonal hair loss after the age of 40. They often experience thinning of the entire scalp with the greatest amount of hair loss at the crown. Alopecia areata often begins suddenly and causes patchy hair loss in children and young adults. This condition can lead to complete baldness (generalized hair loss). But in about 90% of people with the condition, the hair grows back within a few years. Alopecia areata causes the loss of all body hair including eyebrows, eyelashes, and pubic hair. Trichotillomania is a psychological disorder in which the patient pulls his own hair out, leading to hair loss. Children are the most susceptible to this situation. Telogen effluvium is a temporary thinning of hair on the scalp, caused by changes in the hair growth cycle. A large number of hairs enter the resting phase at once, causing the hair to fall out and thin. Scarred alopecia leads to permanent hair loss. Inflammatory skin conditions such as cellulitis, folliculitis, acne, and other skin disorders (such as some forms of lupus and lichen planus) often lead to scarring that destroys the hair's ability to regenerate. Heaters or braids that are too tight can also lead to permanent hair loss.
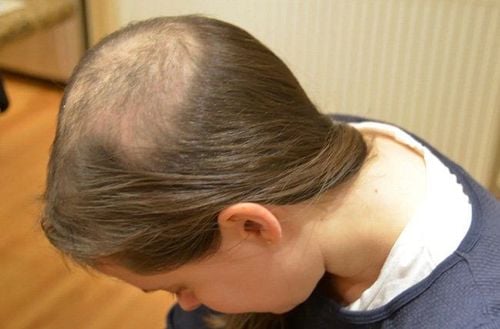
Nguyên nhân rụng tóc có thể do trẻ mắc bệnh lý trichotillomania.
3. What is the cause of hair loss?
Several factors can affect hair loss such as:
Hormones such as abnormal levels of androgens (hormones normally produced in both men and women). Inheritance from parents in both men and women can influence the predisposition to baldness in both sexes. Stress, illness, and pregnancy all carry the risk of temporary hair loss. Ringworm caused by a fungal infection can also cause hair loss. Medications such as: Chemotherapy drugs used in cancer treatment, blood thinners, beta-adrenergic blockers used to control blood pressure, and birth control pills, etc. can all cause temporary hair loss. time. Burns, trauma, and X-rays can cause temporary hair loss. In such cases, normal hair growth usually returns after the wound heals, and unless there is scarring, the hair will never grow back. People with autoimmune diseases can cause patchy hair loss. With alopecia areata, the immune system kicks in for no reason and affects the hair follicles. This happens in most people with alopecia areata. Frequent washing, curling, bleaching, and dyeing processes can all make hair thinner. This is because these techniques make hair weak and brittle. On the other hand, tight braiding, using rollers or hot curlers can also damage and break your hair. However, these conditions are not too serious because the hair can grow back normally. Patients with thyroid disease, lupus, diabetes, iron deficiency anemia, eating disorders, and anemia may experience hair loss. In most cases, when the underlying condition is treated, the hair grows back. Unless there is scarring like some form of lupus, lichen planus or a hair follicle disorder, etc., the hair does not regrow. A low-protein or calorie-restricted diet also increases the risk of temporary hair loss. Above are the basics of hair loss such as: The life cycle of hair, the types of hair loss and the causes that lead to this condition. Hopefully, the above information will help you take measures to prevent hair loss to own healthy hair. Please follow the website: Vinmec.com regularly to update many other useful information.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com