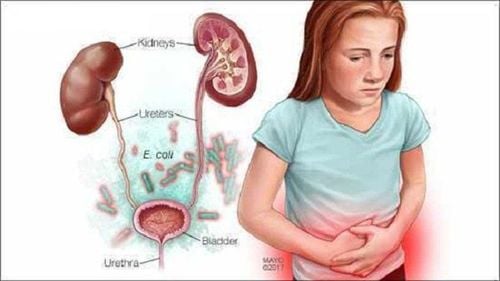
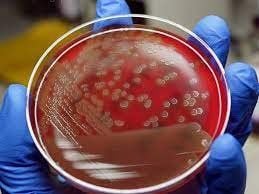
This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with MSc Tran Thi Vuong - Doctor of Microbiology - Laboratory Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.It is important during bacterial culture to avoid introducing additional foreign bacteria into the culture medium. Therefore, in addition to operations that must always be carried out in absolute aseptic conditions, all elements from the environment, containers, culture tools to necessary items must be disinfected before use. .
1. What is the bacterial culture method?
Bacterial culture is the introduction of suspected bacteria into a suitable environment to create conditions for bacteria to grow. Depending on the purpose, culture media have basic nutrients or add special elements (eg salt, bile salts, colorants...) to identify biochemical properties. bacteriology. From there, it helps to initially identify the group of bacteria or bacteria suspected of causing the disease.There are many techniques for culturing bacteria, but they can be classified as follows:
Partition culture:
Identified culture: culture on identified media, in order to detect the biochemical properties of bacteria . Each bacterium has its own set of biochemical properties. Therefore, after 24 h of identification, based on the set of biological and chemical properties to determine the name of bacteria. Proliferative culture: to increase the number of bacteria in the patient sample, especially for the initial patient with few bacteria such as blood, cerebrospinal fluid, pleural fluid... Quantitative culture: to determine the density of bacteria in the primary specimen in a fairly absolute manner. An example of a quantitative culture method is a urine culture. Semi-quantitative culture: to determine the relative density of bacteria in the initial patient sample. Typical of the quantitative culture method is sputum culture. Retained inoculation: Inoculation of named, known bacteria into a medium suitable to preserve the bacterial strain for research or other purposes. Bacterial culture media is also very diverse. Depending on the purpose of culture, depending on the type of patient, depending on the bacterial cause to choose the appropriate culture medium. Solid agar cultures such as blood agar, chocolate agar, MacCon-key agar, UTI agar are common for use with common pathogenic bacteria. Partition culture, quantitative and semi-quantitative culture often use these agar to perform.
Some solid agar selected for each group, each type of bacteria such as: Strepto B agar selective for Group B Streptococcus, SS agar, Hektoen selectively for salmonella, shigella...
Difficult bacteria, or other bacteria. bacteria with special properties need special environments to give priority to pathogenic bacteria to grow such as cholera bacteria need to be cultured on TCBS medium...
The medium for growing proliferation is usually a liquid medium such as BHI, 2% glucose broth, alkaline peptone media
The identification medium can be either solid petri dish or slant agar to find the chemical vatogenic properties of the bacteria, thereby determining the name. bacteria.
After bacteria are introduced into these media, the best ambient temperature and atmospheric conditions should be provided for bacterial growth. Most bacteria need a temperature of 35 oC±1, a normal atmosphere can grow. Some bacteria need more CO2 in the environment such as gonococcal, meningococcal ... some need anaerobic conditions. Equipment commonly used to incubate bacteria is a normal incubator or an incubator that provides 5% CO2.
In the content of this article, I would like to mention the method of partitioning with common bacteria

2. Bacterial culture isolation
Isolation is an important step in bacterial culture.The purpose of the isolation method is to isolate bacteria from the primary population forming pure strains of bacteria (clons) called colonies. When bacteria grow and develop on the surface of solid media will form colonies. Each group of bacteria, each type of bacteria has a characteristic colony morphology. The person doing the test to identify the colony character, will select the suspect colony to identify the pathogenic bacteria.
Bacterial isolation cultures can be performed directly with the primary specimen, or with bacteria that have been previously inoculated on solid agar (in case the initial isolate has not yet isolated separate colonies). turn).
It is important to culture isolates to avoid introducing additional foreign organisms into the culture medium. Therefore, in addition to operations that must always be carried out in absolute aseptic conditions, all elements from the environment, containers, culture tools to necessary items must be disinfected before use. .

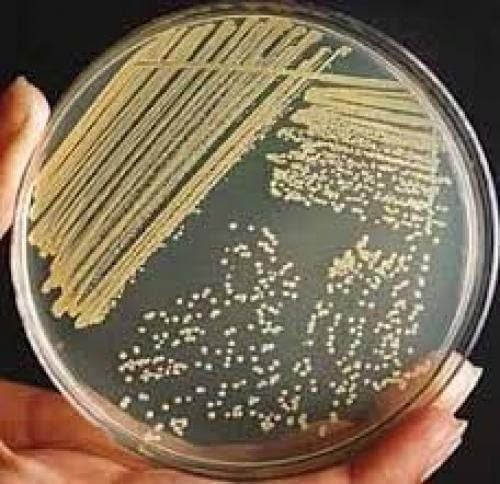
Samples in places where there are resident bacteria such as nose, throat, pharynx, feces, sputum will grow many different types of colonies. The examiner will select the suspect colony for identification.
In summary, partition culture is the first and very important step in the bacterial culture process. The technician's technique and experience also play an important role in providing accurate bacterial culture results.
In addition, to ensure accurate and timely results, taking samples plays a prerequisite role. Getting the right position and the right technique will give the most accurate and timely results!
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.