This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Nguyen Tung Hoanh- Department of Resuscitation - Emergency - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Mercury and most of its compounds are extremely toxic to human health, so when using mercury-containing products such as thermometers, fluorescent light bulbs,... we often are advised to exercise extreme care, even when throwing them away. Mercury leakage incidents are especially serious in the event of mercury being burned (e.g. a fluorescent lamp factory fire, .. ) which will cause mercury to rise in high concentrations, combined with wind emission. spread over a large area, greatly affecting human health.
Learning about the physical and chemical properties of mercury, including its evaporation temperature, will help us be more proactive in responding to mercury leaks.
1. Physical and chemical properties of mercury
1.1 Physical properties Mercury is a heavy, silvery white liquid metal at room temperature. Solid mercury is malleable and can be cut with a knife.Mercury has a density of 13.69 g/cm3, freezing point is −38.83 °C, boiling point is 356.73 °C.
Mercury is a metal with poor thermal conductivity but good electrical conductivity. .
1.2 Chemical properties Mercury has the chemical symbol Hg, which stands for Hydrargyrum, in Greek Hydrargyros - a compound word meaning "water" and "silver", referring to the characteristics of mercury. It is liquid like water and has a metallic luster like silver.
Mercury does not react with most acids, except for oxidizing acids such as concentrated sulfuric acid, nitric acid or aqua regia. Similar to silver, mercury reacts with hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gas present in the atmosphere.
Mercury has the ability to dissolve many metals to form amalgams, except iron, so mercury is often stored in iron containers.
2. How toxic is mercury?
Mercury is a less toxic metal, but its vapors, compounds and salts are extremely toxic, causing damage to the nervous system, digestive system, respiratory system, immune system and kidneys for the human body. People.Mercury poisoning can lead to a number of diseases such as acrodynia (pink skin disease), Minamata disease (nerve disease caused by mercury poisoning, named after the environmental disaster caused by mercury emissions in Japan). , Hunter-Russell syndrome (a genetic disorder that causes disabilities in children, causing children to have average or below average intelligence, more severe causes mental retardation, bone deformities, ..).
Symptoms of mercury poisoning depend on the type, dose, manner and duration of exposure, but in general common symptoms include muscle weakness, poor coordination, numbness of hands and feet, skin rash, weakness Sensory (hearing, visual, language) In people with long-term exposure to mercury vapor (eg factory workers,...) there are also tremors, cognitive impairment and sleep disturbances. sleep.
Many studies have shown that acute exposure from 4-8 hours to mercury doses from 1.1 to 44mg/m3 will lead to chest pain, shortness of breath, hemoptysis, and impaired lung function. present with interstitial lung disease.
Acute exposure to mercury vapor has been shown to cause profound central nervous system effects, including psychotic reactions characterized by delirium, hallucinations, and often euphoria. want to commit suicide in the patient.
Children with mercury poisoning have red cheeks, nose, lips, hair loss, teeth and nails, short-term rash, muscle weakness, sensitivity to light.
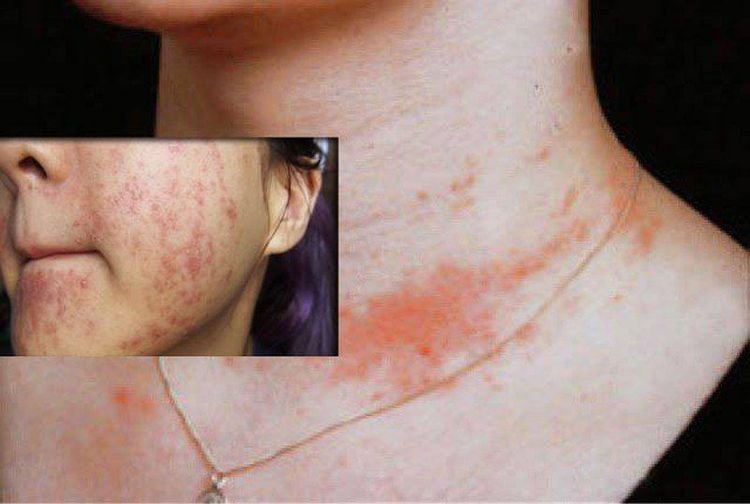
Ngộ độc thủy ngân gây phát ban trong thời gian ngắn
3. At what temperature does mercury evaporate?
Mercury is a highly volatile metal that can evaporate even at room temperature. Its vapor is colorless and odorless, so it is difficult to detect the presence of mercury in the air.When spilled out of the container, the mercury separates into small droplets and is widely dispersed. They will evaporate faster if in ventilated conditions. For every 10°C increase in temperature, the evaporation rate of mercury doubles, which is why mercury fires often have very serious consequences due to the strong evaporation of mercury, combined with wind. mercury will be dispersed long distances, seriously affecting human health.
Mercury after evaporation will circulate in the air, soil and water, forming chemical compounds and transforming into different physical forms of mercury. They can accumulate in the food chain and enter the human body when these foods are ingested.
In Vietnam, the limit of mercury in the air in the working area is regulated by the Ministry of Health as follows:
Organic mercury: 8 hour average (TWA) 0.01mg/m3; Maximum each time (STEL) 0.03mg/m3. Mercury and inorganic mercury compounds: 8-hour mean (TWA) 0.02mg/m3; Maximum each time (STEL) 0.04mg/m3.
4. Mercury is in which items?
Mercury is used in a number of items such as thermometers, fluorescent lamps, barometric instruments, sphygmomanometers, mercury switches, mercury relays, etc. However, due to mercury's toxic properties So many countries have called for replacing mercury with other materials that are safer when making these items. For example, replacing mercury in thermometers and sphygmomanometers with galinstan, or replacing mercury sphygmomanometers with mechanical pressure gauges.Mercury is also used for scientific research and in amalgams (alloys of mercury with other metals) for dental restorations.
5. How to handle small-scale mercury leaks?
Although mercury is very toxic to human health, under current conditions, not all mercury-containing items can be replaced by other safer devices, such as: Thermometers or fluorescent bulbs are items that contain mercury but are still widely used today.Therefore, if we do not have the conditions to find another method to replace them, it is best to learn how to respond when mercury leakage incidents occur in daily life, such as thermometer breakage, manometer or light bulb,...
Although the amount of mercury in the above items is quite small, only a few grams, it is enough to cause harm to health. Mercury can easily evaporate at room temperature and be absorbed through the lungs and into the bloodstream if we breathe it in. Mercury vapor is heavier than air, so it can exist in higher concentrations near floors, making it very dangerous for young children to crawl or play in these areas.

Nhiệt kế bị vỡ nên làm gì?
5.1 Preparations Before Cleanup: Keep children and pets away from the spread of germs. Mercury; If you have touched or come into contact with mercury, you should remove your shoes and clothes and put them in two sealed plastic bags. Prevent mercury from spreading: Mercury is prone to breaking down into small particles and spreading around, so it's a good idea to put something as a barrier around the mercury area, for example sand or a towel or cloth. Use powdered sulfur or mixtures if available: Sulfur will react with mercury to form a nonvolatile precipitate (HgS); and mixtures will form a bond with the mercury, making it easier to clean. Check for vents in the sieve or manhole, and seal them to prevent mercury vapor from entering until cleanup is complete. The spread of airborne mercury must be reduced to prevent unnecessary exposure: Turn off heaters, ventilation and air conditioners, and seal ventilation openings. Close the door of the room where the problem occurs to prevent mercury from escaping, and seal the door slots with duct tape. Open the window outside the room, can turn on more fans. Note:
Do not pour or allow mercury to run down the drain; Do not wash items contaminated with mercury in the washing machine. Prepare cleanup tools: Tools to collect mercury include:
Drip suction tool; Syringe without needle; Hard cover or card; Zinc or sulfur powder (*); Rubber scraping broom; Plastic garbage collection. (*) Zinc and sulfur will react with mercury to reduce the amount of vapor. When exposed to mercury, sulfur turns brown.
Containers include:
Plastic box with lid; Tray or box; Zippered plastic bag; Garbage bag; Bandage. Protective tools include:
Plastic sheet; Rubber gloves; Plastic boots (boots); Eye protection glasses. Note:
Absolutely do not use a broom or vacuum cleaner to clean mercury: This method not only does not remove mercury vapor, but also spreads more mercury into the air.
Wear proper protective clothing: To limit mercury exposure to your skin and clothing, you should wear rubber gloves, plastic boots or cover your shoes with a plastic bag. Also wear safety glasses, if available.
5.2 Cleanup Procedure Picking up visible mercury particles: Use equipment with a good light source to detect all mercury droplets in any location. You use the plastic card to gently push the mercury drops on the floor and toward other drops to combine them into larger droplets, then let the mercury slide onto the plastic card and dump them in the prepared trash.
Note: Do not use a rake to sweep mercury particles because they may break and disperse further.
Put the mercury in a plastic container: If needed, you can use a dropper or syringe to collect the drops of mercury. Small mercury particles will be removed with adhesive tape. Place the mercury in a plastic jar or zippered plastic bag, do not use a glass container because it is very dangerous to let them break.
Tighten the lid of the plastic container to prevent liquid and mercury vapor from escaping to the outside, then place the plastic container inside the plastic bag for safety.
Sprinkle with sulfur or zinc powder: The sulfur or zinc powder will react with the remaining mercury on the floor. Use these 2 powders on hard-to-reach areas such as cracks and crevices to minimize mercury vapor release. Once used to collect mercury, the powder must be disposed of properly.
These powders are included in commercially available mercury cleanup kits.
5.3 After Cleaning Continue to circulate air to the outside: Ventilate as much as possible to get the air in the room where the problem occurred completely to the outside air.
Pack and note any items suspected of mercury contamination: Packaging materials must be safe and be labeled “Contaminated with mercury”. Labeling and handling requirements may vary depending on whether a mercury leak occurs in a household or business.
Note:
Do not let people who step on mercury wear shoes out of the mercury leak area; Do not put mercury in the trash; Do not leave mercury or items containing mercury in a burner or high heat place. Consider getting rid of essentials: Carpets and other soft items where mercury has spilled can still be contaminated even after cleaning. Do not use a vacuum cleaner with these items because vacuuming introduces mercury into the air and inhaling mercury is more dangerous than touching it. If the amount of mercury collected is less than the amount of mercury spilled, you should consider removing the carpet completely, especially if there are pregnant women or young children in the room.
Never burn or expose mercury-contaminated items to a heat source, as this can release mercury into the air.
Reference source: dhs.wisconsin.gov