This is an automatically translated article.
Article by Specialist Doctor II Pham Tien Ngoc - Emergency Doctor - Emergency Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Vomiting is a phenomenon in which food in the stomach is pushed up into the esophagus and then out into the mouth with pressure. Vomiting in children is not usually due to a medical condition, but it is also not subjective. Here are some causes of vomiting and nausea in children.
1. Definition of vomiting in children
Vomiting in children has 2 forms, which are:
Acute vomiting: Usually manifests from a few hours to a few days and is common in the emergency department. In the initial approach, it is necessary to exclude potentially life-threatening conditions such as intestinal obstruction, diabetic ketoacidosis, adrenal gland disease, increased intracranial pressure,... Chronic vomiting: Common in the clinic examination and may not require urgent treatment.
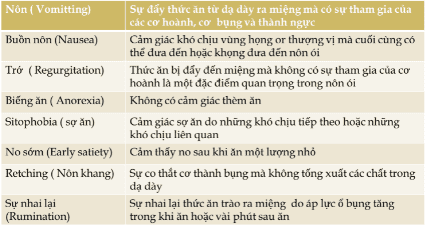
Nôn ở trẻ em
2. Causes of differential diagnosis according to age
Causes of needing to differentiate vomiting and nausea according to age:
Neonates and young children: Gastroesophageal reflux disease, food protein-induced enteropathy, inflammatory bowel syndrome Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome, pyloric stenosis, adrenal insufficiency, intestinal obstruction, Hirschsprung, metabolic disorders,.. Children: Gastroenteritis, infectious diseases (pharyngitis) streptococcal), gastroparesis, virus (occurs many hours after eating), intussusception, anaphylactic reaction, adrenal disease, raised intracranial pressure, migraine, cyclic vomiting, eosinophilic esophagitis, drug overdose...
3. Tests to be performed at initial assessment
When a child has vomiting, tests should be performed to evaluate and provide appropriate treatment:
Test patients with severe, persistent vomiting (over 12 hours in infants, more than 24 hours in patients with vomiting). for children younger than 2 years and over 48 hours if the child is older) or unexplained vomiting. Tests to do: Complete blood count, electrolytes, blood sugar, BUN, creatinine, amylase, lipase, liver enzymes, urinalysis, general abdominal ultrasound,...
4. Principles of treatment of vomiting in children
Attention to treatment of vomiting in children according to the cause:
Electrolyte abnormalities; Metabolic abnormalities; Malnutrition. Antiemetics:
Benefits in persistent vomiting; Do not use: Unexplained vomiting, anatomical abnormalities, conditions that have not been ruled out by surgery, .. Vomiting in children can be a physiological manifestation, however, if this condition persists and affects the When it comes to the health of the baby, parents need help from a doctor to examine and determine the cause of the disease early, to avoid bad consequences.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.