This is an automatically translated article.
Labor is a natural physiological process of a woman during pregnancy, helping to bring the fetus and its appendages out of the uterus through the vagina. This is a fairly important process during pregnancy, so pregnant women need to be closely monitored at specialized medical facilities such as pulse monitoring, vital index monitoring, and uterine contractions. ..1. Monitoring of normal labor
1.1 Monitoring vital indicators Pulse monitoring:Pregnant women need to have their pulse taken every 4 hours during labor. After giving birth, pregnant women need to have their pulse counted immediately and in the first hour, the pulse should be counted every 15 minutes, the second hour, it should be every 30 minutes. For the next 4 hours, count the pulse every 4 hours. Normal pulse in the range of 70-80 beats/min, fast pulse ≥100 beats/min, slow pulse ≤60 beats/min. Blood pressure monitoring:
During labor, pregnant women need to have their blood pressure measured every 4 hours. After birth, blood pressure should be measured immediately, then every 1 hour in the first hour after birth, and blood pressure should be measured regularly if bleeding problems or rapid pulse occur later. If the systolic blood pressure is >140 mmHg or the diastolic blood pressure is >90 mmHg or both, the pregnant woman is prescribed antihypertensive drugs and then transferred to a higher-level hospital. If blood pressure is <90/60 mmHg, resuscitation should be performed and transferred to a higher level for management. Particular attention should be paid to cases of high blood pressure or shock. Monitor body temperature:
Body temperature should be measured every 4 hours. If the body temperature is ≥38°C, at the commune level, the patient should be cooled down by applying a cool compress, wiping his body and then transferred to the upper level for treatment. Make sure pregnant women drink enough water. Observe the general condition of the pregnant woman, if the pregnant woman is tired, has signs of exhaustion, struggles or has difficulty breathing, it should be treated promptly and transferred to a hospital or medical facility at a higher level to find the cause and treat it. treat.

Trong quá trình chuyển dạ, thai phụ cần được đo huyết áp 4h/lần
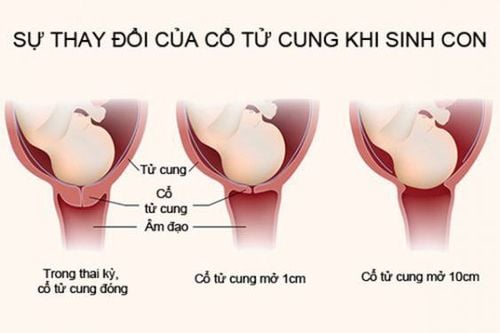
High head High head Good head Low head, low score includes 3 small levels: high pass, medium pass and low pass. Percentage monitoring is required to detect stalled labor.
When there is no progress in the fetal position, consider surgery.
2. Abnormal labor monitoring
Trong những trường hợp cuộc chuyển dạ có dấu hiệu bất thường, nhân viên y tế cần theo dõi sát sao 6 yếu tố kể trên bao gồm theo dõi chỉ số sinh tồn, theo dõi tim thai, cơn co tử cung, tình trạng ối, độ xóa mở cổ tử cung, độ lọt của ngôi thai
3. Monitoring of labor in pregnant women with HIV
Consider the prognostic factors of labor to determine the fertility method for the mother, limit the Forceps procedure, pull the scissors, and take blood from the baby's scalp to prevent the possibility of HIV infection. Hold the amniotic sac to the end and cut the episiotomy when the tip is low. Use antiretroviral drugs for both mother and baby according to the protocol of the Ministry of Health. Labor plays an important role for the delivery as well as the health of both the mother and the newborn, so the mother needs to be monitored for her vital signs, uterine contractions, amniotic fluid status... closely and if there are any signs such as fetal distress, prolonged labor, it should be considered and appropriate indications.Vinmec International General Hospital offers a Package Maternity Care Program for pregnant women right from the first months of pregnancy with a full range of antenatal care visits, periodical 3D and 4D ultrasounds and routine tests to ensure that the mother is healthy and the fetus is developing comprehensively. Pregnant women will no longer be alone when entering labor because having a loved one to help them during childbirth always brings peace of mind and happiness.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.