This is an automatically translated article.
Ceretam is a drug used in myoclonus, dizziness, ischemia... So what should be noted when using Ceretam to be effective and safe? Let's learn about the drug Ceretam in this article.
1. What is Ceretam?
Ceretam drug is a drug prepared in the form of film-coated tablets with the active ingredient Piracetam, content 800mg.
Piracetam acts on a number of neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine, noradrenalin, dopamine... This explains the positive effect of piracetam on learning and improves the results of memory tests.
Piracetam can alter neurotransmitters and contribute to altering the metabolic environment for nerve cells to function properly. It also increases glucose mobilization and utilization independent of oxygen supply, facilitates the pentose pathway, and maintains energy synthesis in the brain. Piracetam reduces blood viscosity and reduces platelet aggregation when used in high doses. In the case of abnormally stiff red blood cells, piracetam can restore the deformability of the red blood cells and the ability to pass through the capillaries. Piracetam is also effective against muscle tremors.
2. What effect does Ceretam have?
Ceretam is indicated in the following cases:
Treatment of symptoms of brain function decline in the elderly such as dizziness, memory impairment, poor concentration, lack of alertness, poor attention to self , mood swings and behavioral disturbances. This can be considered an early manifestation of the onset of pathological aging such as Alzheimer's disease, Alzheimer's disease in the elderly, or mixed cerebral infarction. Treatment of vertigo Treatment of alcoholism Treatment of coma due to poisoning or vascular damage, dizziness and/or loss of consciousness due to head injury Treatment of myoclonic tremor of cortical origin, possibly in combination with other other anticonvulsants. Treatment of acute ischemia, paying attention to age, severity of stroke is an important factor to predict survival after acute ischemic stroke. Treatment of sickle cell anemia Ceretam should not be used in the following cases:
Patients with hypersensitivity to piracetam, pyrrilidone derivatives or to any component of the drug. Patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 20ml/min) Patients with hepatic impairment Children under 16 years of age Intracerebral hemorrhage
3. Dosage and usage of Ceretam
Ceretam is taken orally. The daily dose may range from 30 to 160 mg/kg/day (can be divided into 2-4 doses) depending on the indication for treatment. Treatment of psycho-organic syndromes in the elderly: an initial dose of 4.8 g/day for several weeks, then a maintenance dose of 1.2-2.4 g/day Treatment of alcoholism: for a short period of time. In the beginning of treatment, a high dose of 12 g/day can be used, followed by a maintenance dose of 2.4 g/day. Treatment of myoclonic tremor of cortical origin: Initial dose 7.2g/day, increased by 4.8g/day every 3-4 days to a maximum dose of 24g/day (divided into 2-3 times/day/day) day). The dose should be maintained at the same dose when co-administered with other anticonvulsants. Based on clinical signs, the dose of other drugs may be reduced. Treatment with piracetam should be continued until brain disease persists. However, you can try reducing or stopping the medication every 6 months. Note that the dose should be reduced gradually by 1.2g/day to avoid the risk of sudden relapse.
4. Undesirable effects of the drug Ceretam
When taking Ceretam, patients may experience undesirable effects such as restlessness, emotionality, excitability, sleep disturbance and anxiety. The incidence of these symptoms was less than 5% in clinical trials and was more common in elderly patients receiving doses above 2.4 g/day.
Some patients complain of fatigue or drowsiness while taking the drug. In addition, Ceretam can also cause some gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, diarrhea, or some other symptoms such as headache, dizziness, tremor, sexual arousal.
5. Notes when using Ceretam
Ceretam should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment because piracetam is eliminated primarily by the kidneys. Renal function should be closely monitored while taking the drug.
The increased half-life of piracetam is directly related to impaired renal function. Dosage for patients with renal impairment is adjusted according to creatinine clearance as follows:
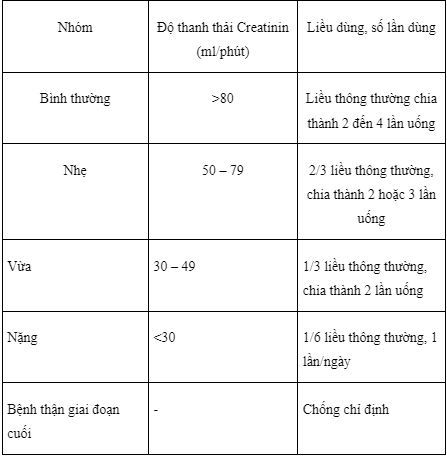
Ceretam should be used with caution in patients with coagulation disorders, major surgery or major bleeding because piracetam affects platelet aggregation.
Piracetam can cross the placenta, so do not use Ceretam during pregnancy. Ceretam should not be used by nursing women.
Ceretam can cause tremors and drowsiness, so do not use this medicine when driving or operating machinery.
7. Drug interactions
Ceretam may interact with the following drugs:
Thyroid extracts (T3 + T4) : there has been 1 case of confusion, excitability and sleep disturbance when these substances were used concomitantly with piracetam. . Antiepileptic drugs such as clonazepam, carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbitone and sodium valproate: no interactions with Ceretam have been observed. Acenocoumarol: In a single-blind study in patients with recurrent venous thrombosis, piracetam at 9.6 g/day did not alter the dose of acenocoumarol required to achieve an INR 2.5 to 3.5, but When compared with the effects of acenocoumarol alone, the addition of piracetam at a dose of 9.6 g/day markedly reduced platelet aggregation, β-thromboglobulin release, fibrinogen levels, and von Willebrand factors. VIII: C; VIII: vW: Ag; VIII: vW: RCo) and whole blood and plasma viscosity.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.