This is an automatically translated article.
Nanotechnology in cosmetics has been applied and is developing more and more strongly. So how is the application of nano in cosmetics, is nano cosmetics safe?1. What is nanotechnology in cosmetics?
Currently, there is no legal definition of nanotechnology in cosmetics. However, when talking about nanotechnology, it means using materials with a size as small as 1-100 nanometers in cosmetics.
Nanotechnology in cosmetics uses two main groups of materials, namely:
Soluble and/or biodegradable nanoparticles, which break down into molecular components (eg some liposomes and emulsions). nano) for use on the skin. Products using this group of materials are generally not subject to safety concerns. Insoluble, stable, biostable nanoparticles (e.g. titanium dioxide (TiO2), fullerenes and quantum dots). Products using this group of materials are often concerned about safety, because they can cross natural biological barrier membranes, have the ability to interact with organs and cause harm.
2. Applications of nano in cosmetics
Although nano-sized materials make up only a very small part of the ingredients of cosmetics, this technology is growing day by day. Applications of nano in cosmetics are used as follows:
Sunscreen uses zinc oxide nanoparticles to block ultraviolet rays while minimizing the white coating on the skin. Sunscreen uses ivy's nanoparticles to block ultraviolet rays. The lotion uses proteins derived from stem cells to stop the aging process of the skin. These proteins are encased in liposomal nanomolecules that fuse with the skin cell membranes to allow delivery of the proteins. A lotion in which nutrients are encased in nanoparticles suspended in liquid form, forming a nano-emulsion. Nanoparticles in cosmetics are smaller in size than those in conventional emulsions, so the nanoparticles will be able to penetrate deeper into the layers of skin cells to provide necessary nutrients. Hair creams use nanoparticles called ethosomes to deliver nutrients that promote hair growth.
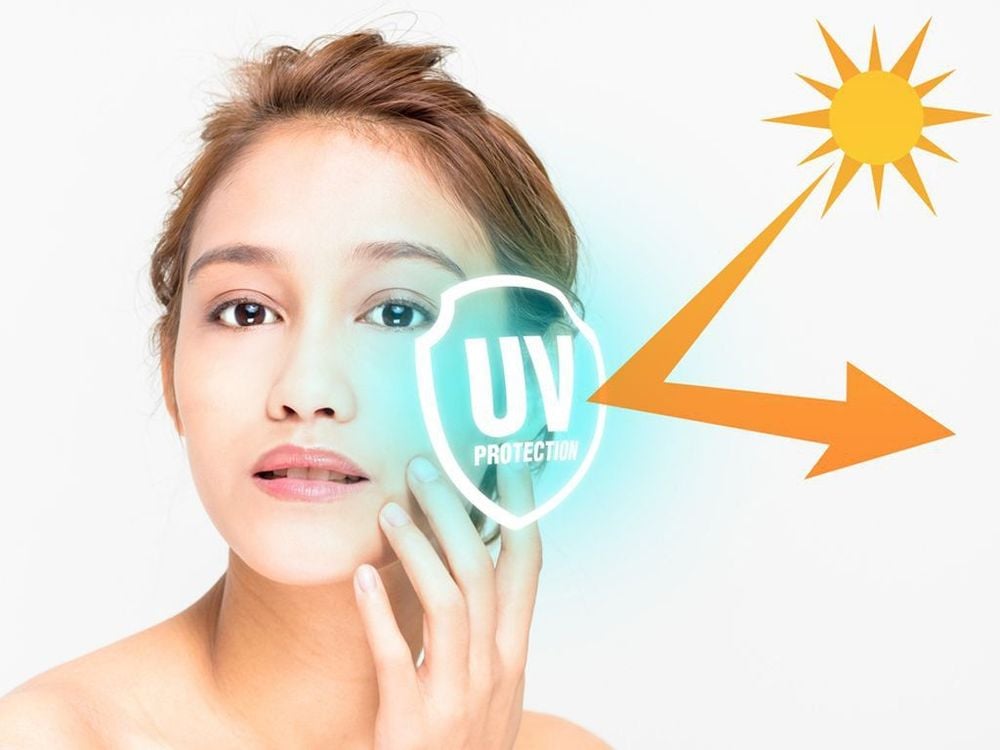

Ứng dụng công nghệ nano trong mỹ phẩm với sản phẩm kem chống nắng
3. Factors determining the safety of nano cosmetics
Currently, the use of nanotechnology and nano-sized materials in cosmetics is closely monitored by the FDA with related research. In order to be placed on the market, companies and individuals marketing cosmetics have a legal responsibility to ensure that nano products and ingredients in cosmetics and their safety under the conditions of use are labeled. Fit.
The safety of nanocosmetic products is determined by the following criteria:
Type of nanomaterial used Stability of the material Absorption of the skin Route of contact How nanomaterials are formulated in cosmetics Compared with larger-scale particles with the same chemical composition, nanomaterials in cosmetics can have distinct chemical, physical and biological properties and the use of nanomaterials in cosmetics may raise questions about the safety of the product for its intended use.
To evaluate the safety of cosmetics using nanomaterials, several important factors need to be addressed, including:
Physical and chemical properties Aggregation and size distribution of nanomaterials under various conditions toxicity testing conditions and as expected in the end product Impurities Potential sugars in contact with nanomaterials Aggregation potential of nanoparticles in final cosmetics Dosimetry for in vitro toxicity studies and in vivo In vitro and in vivo toxicity data on nanomaterial components and their impurities, dermal penetration, potential for inhalation, skin and eye irritation and sensitization studies, Research on mutagenicity and genotoxicity. Nanotechnology in cosmetics uses very small nanomaterials such as sunscreens, lotions, and hair growth creams to penetrate the skin deeper and more effectively.
Understanding nanotechnology in cosmetics will help you know how to use it safely and effectively with your skin.
Reference source: fda.gov